IL-10 Family
Creative BioMart IL-10 Family Product List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for CXC Chemokines & Receptors Research
Creative BioMart offers a wide array of products pertaining to CXC chemokines and receptors, including recombinant proteins, native proteins, GMP proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, assay kits, and others.
We provide researchers with an expansive collection of resources that cover various facets of CXC chemokines and receptors, allowing for a detailed exploration of pathways, protein functions, literature, specialized research areas, and other key topics. These comprehensive resources empower researchers to gain a profound understanding of the critical importance of these essential biomolecules, facilitating thorough insights into their pivotal roles.
Our Featured Products
| Class | Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CXC Chemokines | CXCL8-3703H | Recombinant Human CXCL8 protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CXCL9-11728H | Recombinant Human CXCL9, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His | |
| CXCL10-08H | Recombinant Human CXCL10 protein | Human | E.coli | N/A | |
| CXCL11-65S | Active Recombinant Swine Chemokine (C-X-C motif) Ligand 11 | Pig | Yeast | N/A | |
| Cxcl12-11719M | Recombinant mouse Cxcl12, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST | |
| CXC Chemokine Receptors | CXCR3-261H | Recombinant Human CXCR3 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| CXCR4-504H | Recombinant Human CXCR | Human | Wheat Germ | N/A |
About CXC Chemokines & Receptors
CXC chemokines and their receptors are key components of the immune system and play crucial roles in various physiological and pathological processes. Chemokines are small proteins that regulate the migration and activation of immune cells, while chemokine receptors are expressed on the surface of immune cells and enable them to respond to chemokine signals. CXC chemokines belong to a subgroup characterized by the presence of a pair of cysteine residues separated by another amino acid (represented as 'X') in their amino acid sequence.
CXC chemokines are produced by various cell types, including immune cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, in response to inflammatory stimuli, infection, or tissue damage. They act as chemoattractants, guiding immune cells to specific locations within the body. CXC chemokines can be classified into two major subgroups based on the arrangement of their N-terminal amino acids: ELR+ CXC chemokines and ELR- CXC chemokines.
ELR+ CXC chemokines, such as interleukin-8 (CXCL8), contain a tripeptide motif of glutamic acid-leucine-arginine (ELR) at the N-terminus. They are potent chemoattractants for neutrophils and play a crucial role in the recruitment of neutrophils to sites of inflammation. ELR- CXC chemokines, on the other hand, lack the ELR motif and have a broader range of functions. Examples of ELR- CXC chemokines include interferon-gamma-inducible protein 10 (CXCL10), monokine induced by gamma interferon (CXCL9), and growth-regulated oncogene-alpha (CXCL1).
CXC chemokines exert their effects by binding to specific chemokine receptors expressed on immune cells. The receptors for CXC chemokines are G protein-coupled receptors, a large family of cell surface receptors that transmit signals into the cells upon ligand binding. The major CXC chemokine receptors include CXCR1, CXCR2, CXCR3, and CXCR4, among others. These receptors are expressed on various immune cell types, such as neutrophils, monocytes, T cells, B cells, and dendritic cells.
Upon binding to their respective chemokine receptors, CXC chemokines initiate intracellular signaling pathways that regulate immune cell migration, activation, and other cellular responses. The activation of CXC chemokine receptors triggers signaling cascades involving G proteins, kinases, and other intracellular effectors, leading to changes in cytoskeletal rearrangement, cell adhesion, and chemotaxis.
The functions of CXC chemokines and their receptors extend beyond immune cell migration. They also play roles in inflammation, angiogenesis, tissue repair, cancer progression, and various immune-related disorders. Dysregulation of CXC chemokines and their receptors has been implicated in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, atherosclerosis, and cancer.
Table 1. Receptors, signaling pathways of CXC chemokines, and their role in cardiovascular disease. (Lu X, et al., 2022)
| CXC chemokines | Receptor | Pathways | Main role |
|---|---|---|---|
| CXCL1 | CXCR1,CXCR2 | PI3K/AKT | Proinflammatory effects, Promoting angiogenesis |
| CXCL2 | CXCR2 | ERK1/2, PI3K/AKT | Proinflammatory effects, Promoting angiogenesis |
| CXCL3 | CXCR2 | PI3K/AKT | Proinflammatory effects |
| CXCL4 | CXCR3 | ERK1/2, MAPK | lnduction of macrophage differentiation, Anti-angiogenesis |
| CXCL5 | CXCR2 | PI3K/AKT | Proinflammatory effects, Promoting angiogenesis |
| CXCL6 | CXCR1,CXCR2 | PI3K/AKT | Proinflammatory effects |
| CXCL7 | CXCR2 | PI3K/AKT | Proinflammatory effects |
| CXCL8 | CXCR1,CXCR2 | PI3K/AKT, MAPK, ROS, ERK | Proinflammatory effects, Promoting angiogenesis |
| CXCL9 | CXCR3 | lmmunization | |
| CXCL10 | STAT3, STAT6 | Anti-angiogenesis | |
| CXCL11 | |||
| CXCL12 | CXCR4,CXCR7 | PI3K/AKT, mTOR, NF-κB, JAK/STAT, ERK1/2 | Hematopoiesis, Promoting angiogenesis, Anti-inflammatory action |
| CXCL13 | CXCR5 | PI3K/AKT | Anti-inflammatory action, Anti-apoptosis |
| CXCL14 | CXCR4 | PI3K/AKT | lmmunization,Anti-angiogenesis |
| CXCL15 | - | - | - |
| CXCL16 | CXCR6 | PI3K/AKT | lmmunization,Promoting angiogenesis |
| CXCL17 | CXCR8 | - | - |
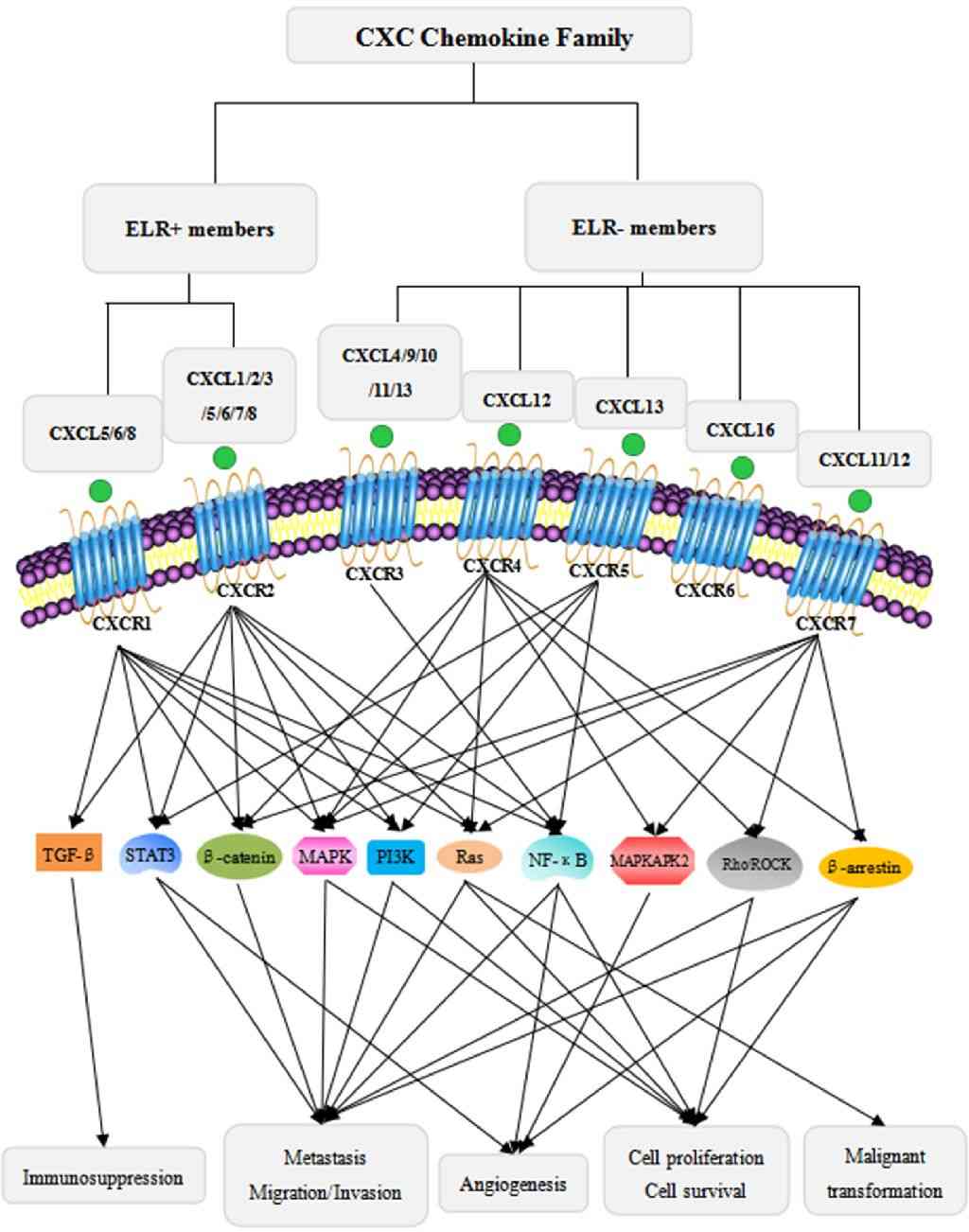 Fig.1 Classification of the CXC chemokine family and the major signaling pathways of CXC chemokines in cancer progression. (Wu T, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Classification of the CXC chemokine family and the major signaling pathways of CXC chemokines in cancer progression. (Wu T, et al., 2022)
Role of CXC Chemokines & Receptors in Diseases
CXC chemokines and their receptors play significant roles in various diseases and pathological conditions. Dysregulation of these chemokines and receptors can contribute to disease development, progression, and immune system dysfunction. Here are some examples of how CXC chemokines and receptors are involved in different diseases:
- Inflammatory Diseases: CXC chemokines are central players in inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, and inflammatory bowel disease. They promote immune cell recruitment to inflamed tissues, contributing to tissue damage and chronic inflammation. For instance, the CXC chemokine receptor CXCR2 and its ligands CXCL1 and CXCL8 are involved in neutrophil recruitment in rheumatoid arthritis, leading to joint inflammation and destruction.
- Infectious Diseases: CXC chemokines and receptors play important roles in host defense against infectious diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, and parasites. They contribute to immune cell recruitment to the sites of infection, aiding in the clearance of pathogens. For example, CXCL10 and CXCR3 are involved in the recruitment and activation of T cells during viral infections, including HIV, hepatitis C, and influenza.
- Cancer: CXC chemokines and their receptors can influence tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. They contribute to the recruitment of immune cells, such as tumor-associated macrophages and T cells, to the tumor microenvironment. Additionally, CXC chemokines can stimulate tumor cell migration and invasion. The CXCR4-CXCL12 axis is particularly implicated in cancer metastasis, as CXCR4 promotes tumor cell migration to organs expressing high levels of CXCL12.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Dysregulated CXC chemokines and receptors have been associated with autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Aberrant chemokine signaling can contribute to immune cell infiltration into the affected tissues, perpetuating inflammation and tissue damage. For instance, CXCL10 is implicated in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis, as it attracts autoreactive T cells to the central nervous system.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: CXC chemokines participate in the development of cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction. They contribute to the recruitment of monocytes and other immune cells to the arterial walls, promoting inflammation and plaque formation. CXCR2 and its ligands have been implicated in atherosclerosis development, while CXCR4 is involved in myocardial infarction by regulating the recruitment of stem cells to the injured heart tissue.
- Allergic Diseases: CXC chemokines and receptors are involved in allergic diseases like asthma and allergic rhinitis. They contribute to immune cell recruitment and activation in the airways, leading to inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness. For instance, CXCR2 and its ligands play a role in eosinophil recruitment in asthma, contributing to airway inflammation and remodeling.
Understanding the roles of CXC chemokines and receptors in diseases provides insights into disease mechanisms, potential therapeutic targets, and the development of novel treatment strategies. Targeting CXC chemokines or their receptors has emerged as a promising approach in the development of therapeutics for various diseases, including the use of chemokine receptor antagonists or neutralizing antibodies to disrupt chemokine signaling and modulate immune responses.
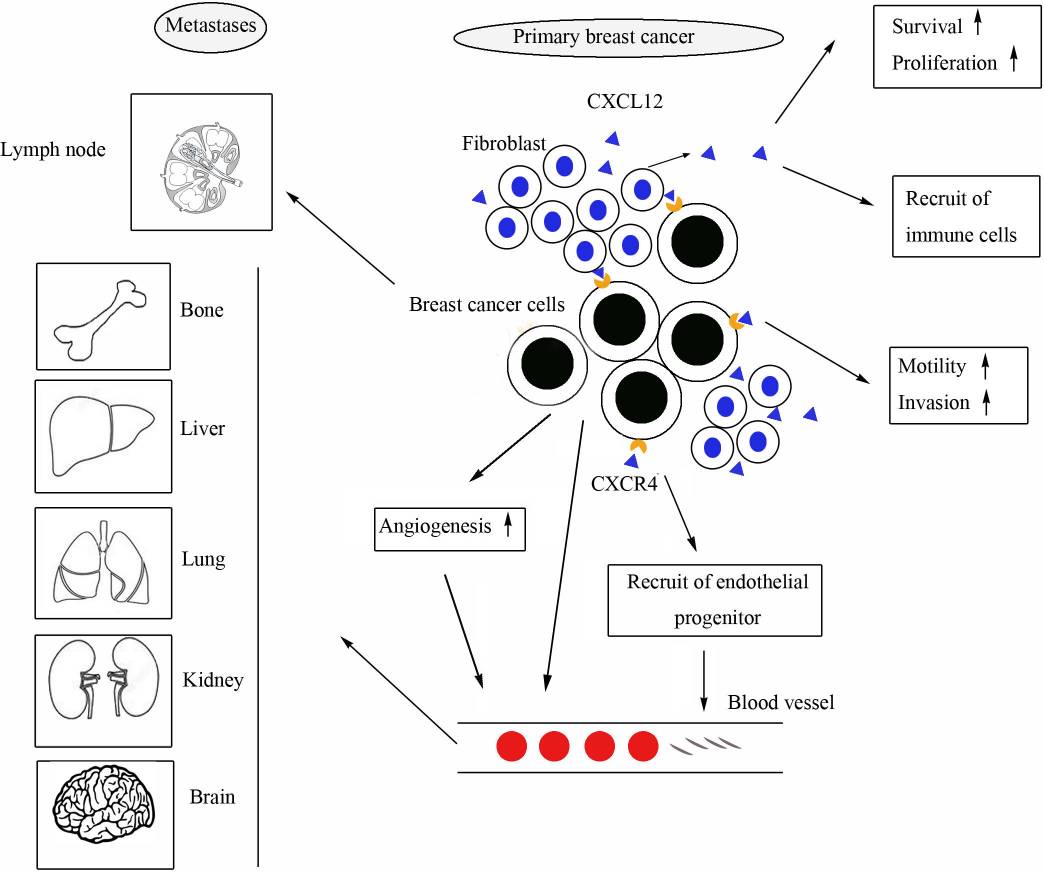 Fig.2 The role of CXCL12/CXCR4 in breast cancer. (Liu H, et al., 20202)
Fig.2 The role of CXCL12/CXCR4 in breast cancer. (Liu H, et al., 20202)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Wu T, Yang W, Sun A, Wei Z, Lin Q. The Role of CXC Chemokines in Cancer Progression. Cancers (Basel). 2022;15(1):167.
- Lu X, Wang Z, Ye D, et al. The Role of CXC Chemokines in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2022;12:765768.
- Liu H, Yang Z, Lu W, et al. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: A new strategy for breast cancer therapy. Cancer Med. 2020;9(11):3786-3799.

