Angiopoietin Receptor
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for Angiopoietin Receptor Research
Creative BioMart is your ultimate destination for all your angiopoietin receptor-related research needs. Our broad range of curated products and customized services are designed to support you in exploring the mysteries of the angiopoietin receptor world.
- Within our product offerings, you will find a premium selection of recombinant proteins, native proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, GMP proteins, assay kits, and others. All are crafted with a focus on quality and precision to meet your research demands.
- Furthermore, we offer an abundant database of resources on angiopoietin receptors, encompassing essential insights into associated pathways, protein functions, protein interactions, relevant literature, and others.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEK-153H | Recombinant Human TEK, Fc-His tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc/His |
| TEK-3177H | Recombinant Human TEK, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| TEK-154H | Active Recombinant Human TEK protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
About Angiopoietin Receptor
The angiopoietin receptor, also known as Tie-2 (tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin-like and EGF-like domains 2) or Tek receptor, is a transmembrane receptor protein that plays a crucial role in angiogenesis, vascular development, and maintenance of vascular integrity. It is the primary receptor for angiopoietin ligands, particularly Angiopoietin-1 (Ang1) and Angiopoietin-2 (Ang2).
The angiopoietin receptor, Tie-2, is a member of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. It consists of an extracellular region, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular region. The extracellular region contains immunoglobulin-like and epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domains, which are involved in ligand binding. The intracellular region possesses a tyrosine kinase domain responsible for initiating intracellular signaling upon ligand binding.
The angiopoietin receptor predominantly binds to two ligands, Ang1 and Ang2. Ang1 is considered the primary agonist of Tie-2, promoting vessel maturation, stability, and quiescence. It enhances endothelial cell survival, suppresses inflammation, and supports vascular remodeling. On the other hand, Ang2 acts as a context-dependent agonist or antagonist. It can either enhance or destabilize vessels, depending on the presence of other signaling molecules and the local microenvironment.
Upon ligand binding, the angiopoietin receptor initiates signaling cascades that regulate angiogenesis and vascular function. Activation of Tie-2 leads to autophosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues within the intracellular domain, providing docking sites for downstream signaling molecules. This triggers various intracellular pathways, including PI3K/Akt, MAPK/ERK, and PLCγ, which mediate cellular responses such as survival, proliferation, migration, and vascular stabilization.
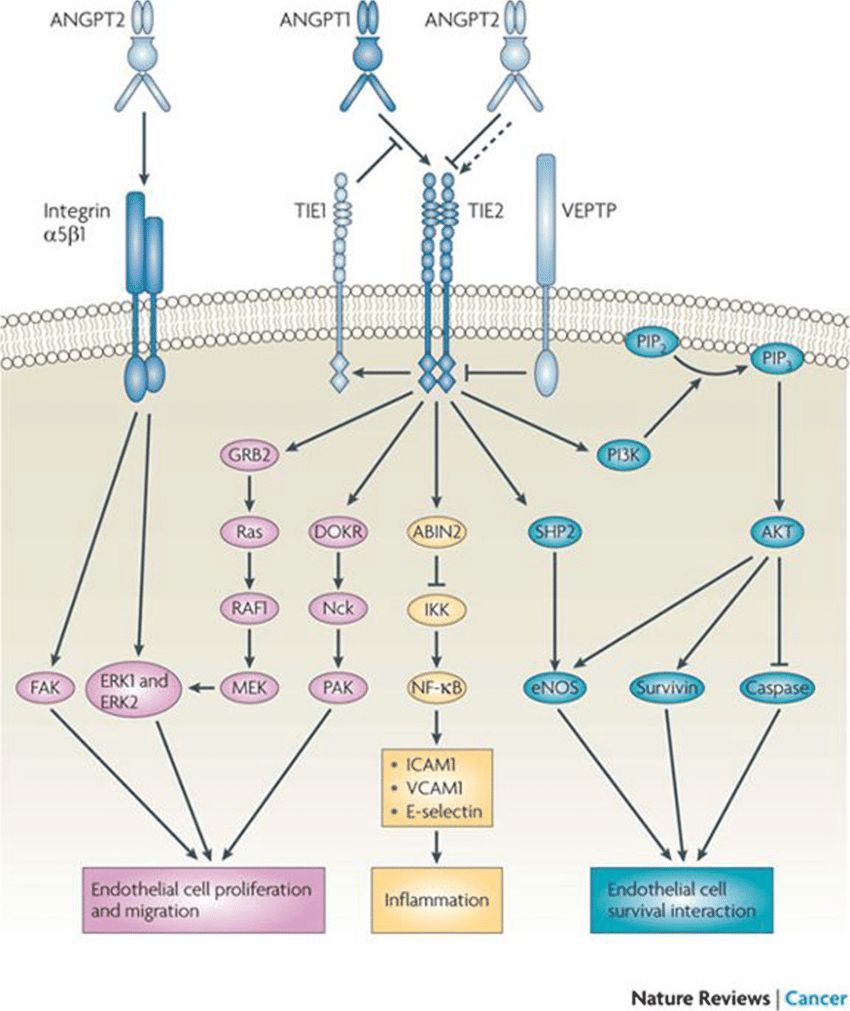 Fig.1 Schema of the angiopoietin1/2 and Tie-2 pathway. (Gillen J, et al., 2019)
Fig.1 Schema of the angiopoietin1/2 and Tie-2 pathway. (Gillen J, et al., 2019)
Research on Angiopoietin Receptor
Research on the angiopoietin receptor (Tie-2 or Tek receptor) has been extensive and continues to uncover new insights into its role in angiogenesis, vascular development, and disease pathogenesis. Here are some notable areas of research on the angiopoietin receptor:
- Angiogenesis and Vascular Development: Researchers have investigated the mechanisms by which Tie-2 signaling regulates angiogenesis and vascular development. Studies have explored the interactions between the angiopoietin ligands (Ang1 and Ang2) and the receptor, the downstream signaling pathways activated by Tie-2, and the cross-talk with other signaling molecules involved in angiogenesis. This research has contributed to our understanding of the molecular events underlying blood vessel formation and stabilization.
- Vascular Stability and Barrier Function: The angiopoietin receptor has been studied for its role in maintaining vascular stability and barrier function. Researchers have examined how Tie-2 signaling regulates endothelial cell-cell junctions, vascular permeability, and endothelial barrier integrity. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing therapeutic strategies targeting vascular leakage and diseases associated with abnormal vascular permeability, such as acute lung injury and diabetic retinopathy.
- Cancer and Tumor Angiogenesis: Given the importance of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis, research has focused on the angiopoietin receptor's role in cancer. Investigations have explored the expression and activation of Tie-2 in various types of cancer, including breast, lung, and colorectal cancer. The dysregulation of Tie-2 signaling has been associated with tumor angiogenesis, tumor progression, and poor prognosis. Targeting the angiopoietin receptor and its signaling pathways has emerged as a potential therapeutic approach for anti-angiogenic cancer treatments.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: The angiopoietin receptor has been implicated in cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and heart failure. Researchers have investigated the alterations in Tie-2 expression and activation in these conditions and their impact on vascular remodeling, plaque stability, and cardiac function. Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying Tie-2 dysregulation in cardiovascular diseases may provide insights into novel therapeutic targets for these conditions.
- Therapeutic Targeting of Tie-2 Signaling: Researchers have explored the therapeutic potential of targeting Tie-2 signaling in various diseases. Strategies such as the use of recombinant angiopoietin ligands, agonistic antibodies, or small molecule inhibitors have been investigated to modulate Tie-2 activity and downstream signaling pathways. These approaches hold promise for the development of targeted therapies for angiogenesis-related disorders, including cancer, ocular diseases, and cardiovascular diseases.
The research on the angiopoietin receptor has provided valuable insights into the complex mechanisms of angiogenesis, vascular development, and disease pathogenesis. Further investigations are needed to uncover the precise roles of Tie-2 signaling in different contexts and to translate these findings into clinically relevant applications that can benefit patients with angiogenesis-related diseases.
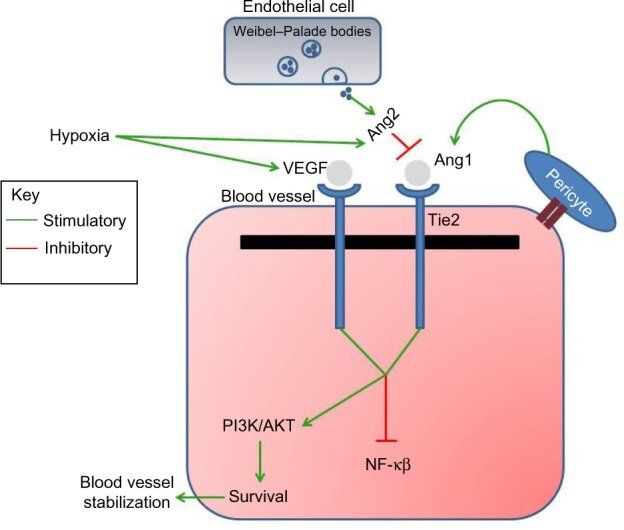 Fig.2 Schematic showing the signal transduction with Tie2 and Ang1/2. (Bupathi M, et al., 2014)
Fig.2 Schematic showing the signal transduction with Tie2 and Ang1/2. (Bupathi M, et al., 2014)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Saharinen P, Eklund L, Alitalo K. Therapeutic targeting of the angiopoietin-TIE pathway. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(9):635-661.
- Gillen J, Richardson D, Moore K. Angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 inhibitors: Clinical Development. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019;21(3):22.
- Bupathi M, Kaseb A, Janku F. Angiopoietin 2 as a therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: current perspectives. Onco Targets Ther. 2014;7:1927-1932.
