WRN
-
Official Full Name
Werner syndrome, RecQ helicase-like -
Overview
The RecQ family of DNA and RNA helicases is a family of enzymes that has been shown to be important to genome integrity (1). Members of this family function in several DNA repair processes including double strand break repair, homologous recombination, an -
Synonyms
WRN;Werner syndrome, RecQ helicase-like;Werner syndrome;Werner syndrome ATP-dependent helicase;RECQ3;RECQL2;exonuclease WRN;recQ protein-like 2;DNA helicase, RecQ-like type 3;RECQL3;DKFZp686C2056
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- Non
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
- MBP
- Myc
Background
What is WRN protein?
WRN gene (WRN RecQ like helicase) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 8 at locus 8p12. This gene encodes a member of the RecQ subfamily of DNA helicase proteins. The encoded nuclear protein is important in the maintenance of genome stability and plays a role in DNA repair, replication, transcription and telomere maintenance. This protein contains a N-terminal 3' to 5' exonuclease domain, an ATP-dependent helicase domain and RQC (RecQ helicase conserved region) domain in its central region, and a C-terminal HRDC (helicase RNase D C-terminal) domain and nuclear localization signal. The WRN protein is consisted of 1432 amino acids and WRN molecular weight is approximately 162.5 kDa.
What is the function of WRN protein?
WRN has 3' to 5' helicase activity, which means it can unwind DNA in the 3' to 5' direction. This activity is crucial for processes such as DNA replication, repair, and recombination. The protein plays a significant role in several DNA repair pathways, including nucleotide excision repair (NER), base excision repair (BER), and double-strand break repair (DSBR), particularly through the homologous recombination (HR) pathway. WRN is implicated in the maintenance of telomeres, the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes, which is important for preventing genomic instability associated with aging. The protein may have a role in resolving replication fork stalling and collapse, which can occur during DNA synthesis. WRN interacts with a variety of proteins involved in DNA metabolism, including replication factors, repair enzymes, and other helicases.
WRN Related Signaling Pathway
In DNA repair pathways. WRN is related to Nucleotide Excision Repair, Base Excision Repair and Double-Strand Break Repair. WRN is involved in the resolution of replication fork stalling and collapse, which is essential for preventing genomic instability. Also, this protein is implicated in the maintenance and stabilization of telomeres, which protect the ends of chromosomes from degradation. WRN participates in genetic recombination, which is important for generating genetic diversity during meiosis and for the repair of DNA breaks. It has helicase and exonuclease activities that are essential for various DNA metabolic processes, including replication, repair, and recombination. WRN interacts with cell cycle proteins and may be involved in cell cycle checkpoint control, particularly in response to DNA damage.
WRN Related Diseases
Werner Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the WRN gene that causes patients to experience a much faster than normal aging process. Certain variants of the WRN gene may be associated with other forms of presenily-like symptoms that involve physiological changes that accelerate aging. Due to the role of the WRN protein in DNA repair, loss of its function may increase the risk of cancer, especially those types of cancer associated with defective DNA repair. At the same time, it is also associated with other diseases including: cardiovascular disease, diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases.
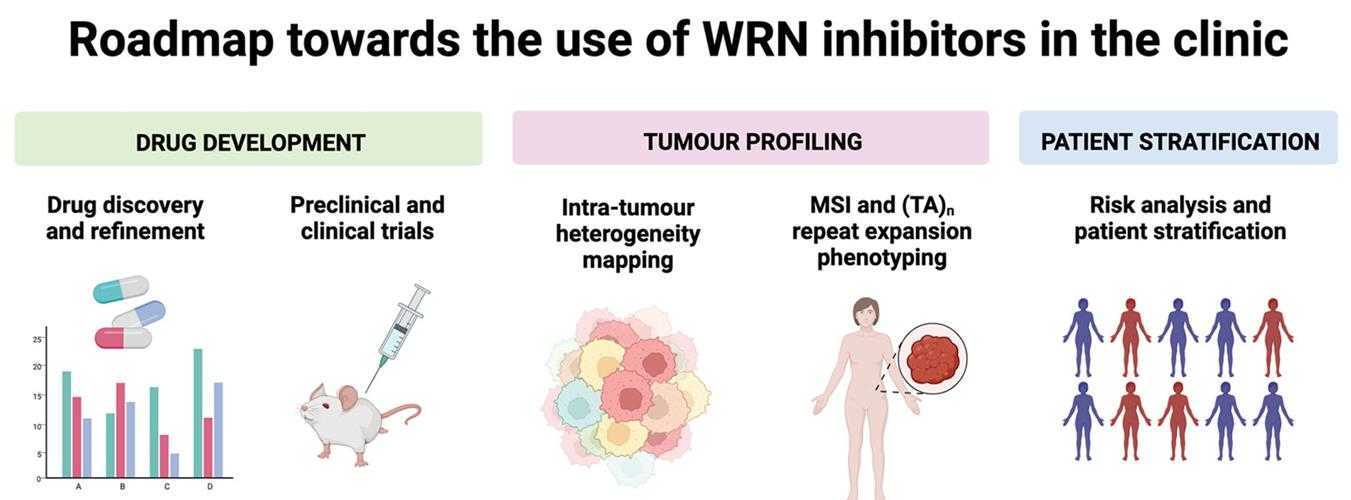
Fig1. Roadmap towards the use of WRN inhibitors in the clinic. (David A Morales-Juarez, 2022)
Bioapplications of WRN
Due to its role in DNA repair and maintenance of genomic stability, WRN protein may play a role in the development of cancer, so it is an important target for cancer biology research. Functional restoration or activation of WRN proteins may help treat diseases associated with WRN deficiency, such as certain types of cancer and symptoms of premature aging, making WRN a potential target for drug screening and development. The functional correction or supplement of WRN gene may be beneficial for the treatment of diseases caused by WRN gene mutation, which provides a possible application direction for gene therapy.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Dali Zong, 2023
Addiction to the WRN helicase is a unique vulnerability of human cancers with high levels of microsatellite instability (MSI-H). However, while prolonged loss of WRN ultimately leads to cell death, little is known about how MSI-H cancers initially respond to acute loss of WRN-knowledge. Here, researchers report the construction of an inducible ligand-mediated degradation system in which the stability of endogenous WRN protein can be rapidly and specifically tuned, enabling to track the complete sequence of cellular events elicited by acute loss of WRN function. WRN degradation leads to immediate accrual of DNA damage in a replication-dependent manner. As a result, WRN-degraded MSI-H cancer cells accumulate DNA damage across multiple replicative cycles and undergo successive rounds of increasingly aberrant mitoses, ultimately triggering cell death. Under conditions of partial WRN degradation, addition of low-dose ATR inhibitor significantly increased their combined efficacy to levels approaching full inactivation of WRN.
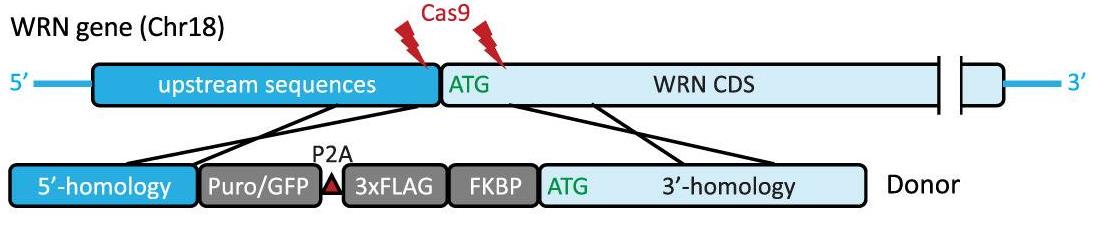
Fig1. Targeting strategy to achieve knock-in of FKBP-WRN at the endogenous human WRN locus.
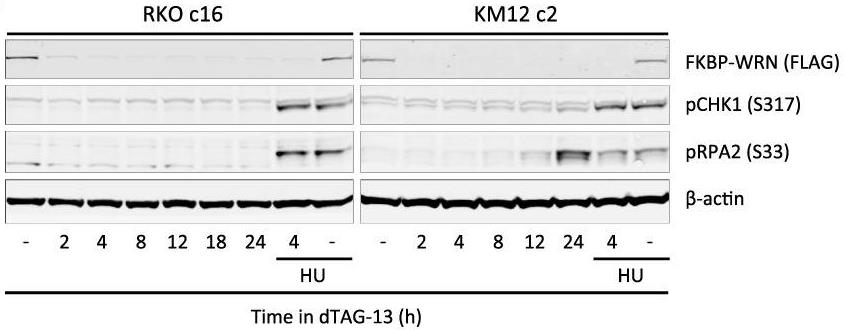
Fig2. Immunoblotting of dTAG-treated RKO FKBP-WRN cells.
Case Study 2: Venkateswarlu Popuri, 2010
NEIL1, the mammalian homolog of Escherichia coli endonuclease VIII, is a DNA glycosylase that repairs ring-fragmented purines, saturated pyrimidines and several oxidative lesions like 5-hydroxyuracil, 5-hydroxycytosine, etc. Previous studies from our laboratory have shown that Werner Syndrome protein (WRN), one of the five human RecQ helicases, stimulates NEIL1 DNA glycosylase activity on oxidative DNA lesions. The goal of this study was to extend this observation and analyze the interaction between NEIL1 and all five human RecQ helicases. The DNA substrate specificity of the interaction between WRN and NEIL1 was also analyzed. The results indicate that WRN is the only human RecQ helicase that stimulates NEIL1 DNA glycosylase activity, and that this stimulation requires a double-stranded DNA substrate.
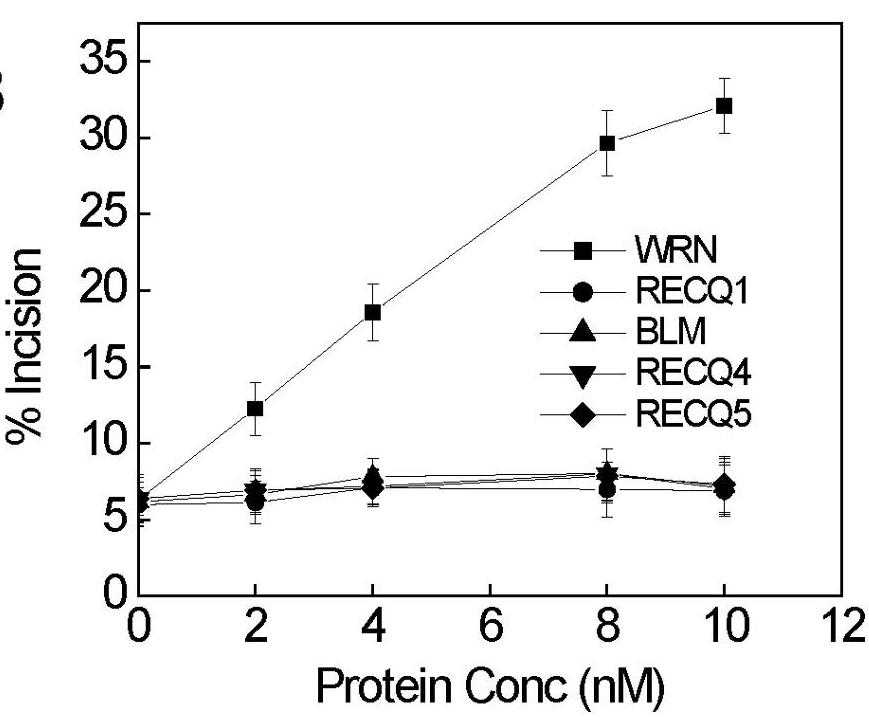
Fig3. Stimulation of NEIL1 incision activity on duplex substrate with FapyA lesions specifically by WRN.
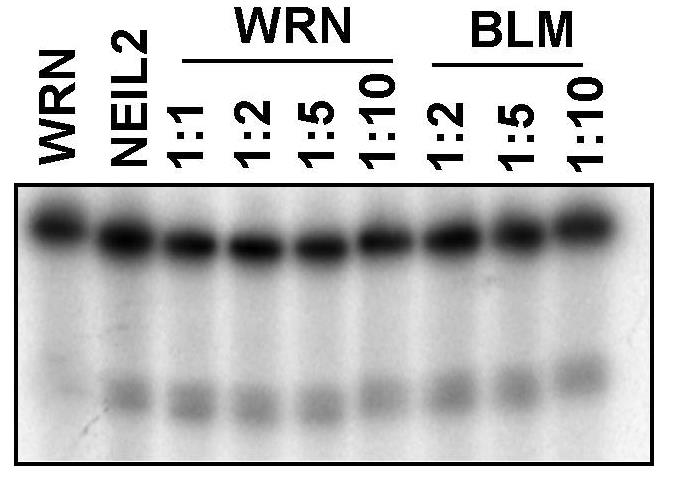
Fig4. WRN can't stimulate NEIL2.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (WRN-1388H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (WRN-1387H)
Involved Pathway
WRN involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways WRN participated on our site, such as DNA Double-Strand Break Repair,DNA Repair,HDR through Homologous Recombination (HR) or Single Strand Annealing (SSA), which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with WRN were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| HDR through Homologous Recombination (HR) or Single Strand Annealing (SSA) | UIMC1,TOPBP1,HUS1,PPP4R2B,RTEL1,RAD51AP1,TIPIN,PPP4CB,EME1,TIMELESS |
| HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) | TOPBP1,RHNO1 |
| HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) | RAD51AP1,EME1,RAD9B,RHNO1,FUZ,HUS1,RBBP8,GEN1,TOPBP1,RAD9 |
| DNA Double-Strand Break Repair | RBBP8,EME1,KIAA0146,PPP4R2A,PPP4R2B,CLSPN,PARP1,DNA2,EME2,BABAM1 |
| Integrated Pancreatic Cancer Pathway | GPRC5A,NOXA1,BRF1,CD82,PPP1R13L,RAPGEF3,FKBP1B,AGA,FKBP3,CST3 |
| Homology Directed Repair | EME1,TIPIN,RHNO1,RNF4,PPP4CB,TIMELESS,TOPBP1,EME2,RTEL1,RAD51AP1 |
| Homologous DNA Pairing and Strand Exchange | TOPBP1,RHNO1,RAD51AP1 |
| DNA Repair | RAD51AP1,ASCC2,EME2,COPS7B,DDB1,SMARCA5,TFPT,DCLRE1A,TDP1,ZBTB32 |
Protein Function
WRN has several biochemical functions, for example, 3-5 DNA helicase activity,3-5 exonuclease activity,ATP binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by WRN itself. We selected most functions WRN had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with WRN. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| 3-5 DNA helicase activity | ERCC3,CDC45,FBXO18,GINS1 |
| Y-form DNA binding | MEN1,RAD18,MSH3,MSH2 |
| protein complex binding | ATP6V1B1,RRAS,CDKN1B,ABI2,HNF1B,WASF1,TMED10,IST1,ITPR1,KIF11 |
| protein homodimerization activity | PDE2A,XDH,SMAD2,MAPK4,RXRB,HSF2,VEGFB,TPD52L2,XPNPEP1,P2RX4 |
| protein binding | RBPMS,ITGB1BP3,VANGL1,RNF5,NRIP3,FBXL15,AEN,LSM8,SCNN1G,MAPK11 |
| DNA helicase activity | FBXO18,PEO1,MCM3L,MCM6L,ATRX,RAD54B,DNA2,RUVBL1,MCM5,RECQL5 |
| ATP-dependent 3-5 DNA helicase activity | BLM,ASCC3,RECQL4 |
| ATP-dependent DNA helicase activity | DDX3X,FBXO18,BRIP1,ERCC2,RUVBL2,XRCC6,GTF2H4,CHST13,CHD4,CHD2 |
| ATP binding | KIF12,EHD1,ACTA1,CAMK1GB,PFKP,ABCB5,PRKCBB,RARS2,HELQ,ATP2B1 |
Interacting Protein
WRN has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with WRN here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of WRN.
XRCC5;XRCC6;RPA1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Goto, M; et al. Anti-WRN(RecQ3 DNA/RNA helicase) antibodies in systemic sclerosis.. ARTHRITIS AND RHEUMATISM 52:S368-S369(2005).
- Bordi, L; Amendola, A; et al. Expression of Werner and Bloom syndrome genes is differentially regulated by in vitro HIV-1 infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL IMMUNOLOGY 138:251-258(2004).


