UBR4
-
Official Full Name
ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 4 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that interacts with the retinoblastoma-associated protein in the nucleus and with calcium-bound calmodulin in the cytoplasm. The encoded protein appears to be a cytoskeletal component in the cytoplasm and part of the chromatin scaffold in the nucleus. In addition, this protein is a target of the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein. -
Synonyms
UBR4;ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 4;zinc finger, UBR1 type 1 , ZUBR1;E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR4;KIAA0462;KIAA1307;RBAF600;600 kDa retinoblastoma protein associated factor;600 kDa retinoblastoma protein-associated factor;N-recognin-4;p600;Retinoblastoma associated factor 600 like protein;Retinoblastoma associated factor of 600 kDa;Retinoblastoma-associated factor 600;Retinoblastoma-associated factor of 600 kDa;Ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n recognin 4;UBR4_HUMAN;Zinc finger UBR1 type protein 1;Zinc finger UBR1-type protein 1;Zinc finger, UBR1 type 1;ZUBR 1;ZUBR1;OTTHUMP00000002585;retinoblastoma-associated factor 600-like protein;RP5-1126H10.1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- His
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBR4-3562H | Recombinant Human UBR4, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | C-term-349aa | |
| UBR4-32H | Recombinant Human UBR4 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Val124~Arg396 | |
| UBR4-33H | Recombinant Human UBR4 protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 451-799 aa | |
| UBR4-17762M | Recombinant Mouse UBR4 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| UBR4-01H | Recombinant Human UBR4 Protein, GST-Tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| UBR4-9860M | Recombinant Mouse UBR4 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| UBR4-9860M-B | Recombinant Mouse UBR4 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is UBR4 Protein?
UBR4 is a massive protein that's got fingers in a lot of pies. It's a type of enzyme known as an E3 ligase, which plays a big role in tagging other proteins for destruction as part of the N-degron pathway. This pathway is vital for several processes in our bodies, like how our brains develop, how our muscles shrink as we get older, and even how some cancers progress. What's cool about UBR4 is its unique structure, which includes a 'hemiRING' zinc finger and a special N-terminal area that interacts with another enzyme, E2. This setup allows UBR4 to work specifically with E2 partners like UBE2A and UBE2B, making sure that only the right proteins get tagged and broken down at the right speed. It's a finely tuned system that's essential for maintaining cellular balance and function.What is the Function of UBR4 Protein?
UBR4 is like a cellular handyman with a knack for keeping things tidy. Its main gig is working as an E3 ligase in the N-degron pathway, which involves marking certain proteins for cleanup. Think of it as attaching a "throw this out" sticker to old, worn-out proteins, signaling that it's time for them to be broken down and recycled. This process is crucial in a bunch of areas, such as making sure our brains develop properly, how our muscles behave as we age, and even in the dance of cell life and death in cancer. UBR4's unique structure lets it connect effectively with other enzymes, helping to control which proteins get tagged and when. By doing this, UBR4 helps maintain the right balance of proteins inside cells, ensuring everything runs smoothly and efficiently.UBR4 Related Signaling Pathway
The UBR4-related signaling pathway is like a busy highway in our cells where proteins get the green light to head for recycling. At its core, it involves the N-degron pathway, with UBR4 acting as one of the main traffic cops. Its job is to tag specific proteins that need to be taken out of circulation. This tagging process tells the cell's clean-up crew it's time to break these proteins down and reuse their parts. It's a crucial part of cell maintenance, helping to regulate everything from brain development to muscle integrity as we age, and even playing roles in how cancer cells behave. By working in concert with other molecules and pathways, UBR4 ensures that proteins are properly managed, making sure the cell functions aren't disrupted by too many worn-out or unnecessary proteins lingering around. It's a sophisticated form of quality control that keeps our cellular machinery running smoothly.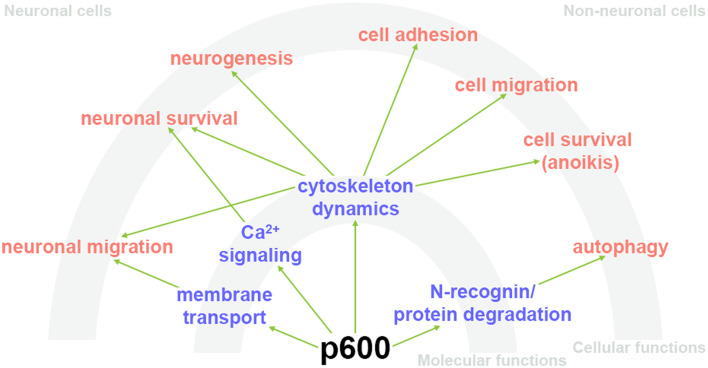
Fig1. Molecular and cellular functions of p600 in neuronal and non-neuronal cells. (Kari Parsons, 2015)
UBR4 Related Diseases
UBR4 is connected to a variety of health issues because of its crucial role in managing protein life cycles within cells. When UBR4 doesn't work as it should, it can lead to a range of diseases. For instance, in neurodevelopmental disorders, if UBR4 fails to remove damaged proteins, it might interfere with how the brain forms and functions. As we age, issues in the UBR4 pathway could contribute to muscular atrophy, where muscles weaken and shrink because they're not getting rid of faulty proteins efficiently. In cancer, when UBR4 isn't doing its job right, it might mess up the process of normal cell death. This means cancer cells can stick around longer than they should, which could help tumors grow. Since UBR4 is involved in so many cellular tasks, problems with it can spread throughout the body, highlighting just how crucial it is for keeping us healthy.Bioapplications of UBR4
UBR4 is proving to be quite the versatile player in the world of biotechnology and medicine. Given its role in tagging proteins for degradation, it's becoming a target of interest in developing therapies for conditions where protein regulation goes haywire. For instance, researchers are exploring ways to tweak UBR4 activity to help treat neurodegenerative diseases where protein build-up in brain cells leads to damage. In cancer research, since UBR4 can influence cell survival, scientists are looking into how modulating its activity might help in designing treatments that encourage cancer cells to self-destruct. Additionally, in regenerative medicine, understanding UBR4's role in cell growth and development could pave the way for novel approaches to tissue engineering and healing. By leveraging UBR4's functions, we could unlock a host of new bioapplications aimed at tackling some of the most challenging health problems.Case Study
Case Study 1: Nakatani Y. et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005
This article examines p600, a unique protein binding with the retinoblastoma protein and calmodulin. In the nucleus, it forms a chromatin scaffold; in the cytoplasm, it structures with clathrin to shape the cytoskeleton and membranes. Reducing p600 disrupts integrin-aided ruffled membrane formation and survival pathways, making cells more prone to apoptosis when detached. These insights reveal how membrane activities might be regulated in tumor development.-
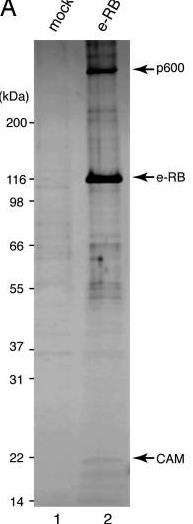 Fig1. Silver staining of the purified RB complex.
Fig1. Silver staining of the purified RB complex. -
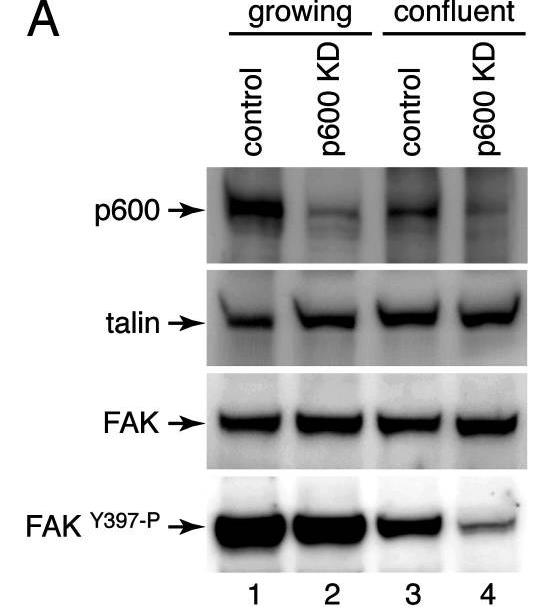 Fig2. Analysis of FAK phosphorylation by Western blotting.
Fig2. Analysis of FAK phosphorylation by Western blotting.
Case Study 2: Barnsby-Greer L. et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024
UBR4 is a key E3 ligase in the N-degron pathway, affecting brain development, age-related muscle loss, and cancer. Researchers identified an E3 module in human UBR4 with a 'hemiRING' zinc finger, a UZI subdomain, and an N-terminal area for E2 binding. The E2-E3 complex structure shows how hemiRING targets UBE2A/UBE2B. The UZI boosts the activity of the E2~Ub. This combo works with UBE2A's high lysine reactivity for precise substrate targeting and fast degradation. These findings explain how UBR4 functions and works with UBE2A, highlighting the diversity in its structure.-
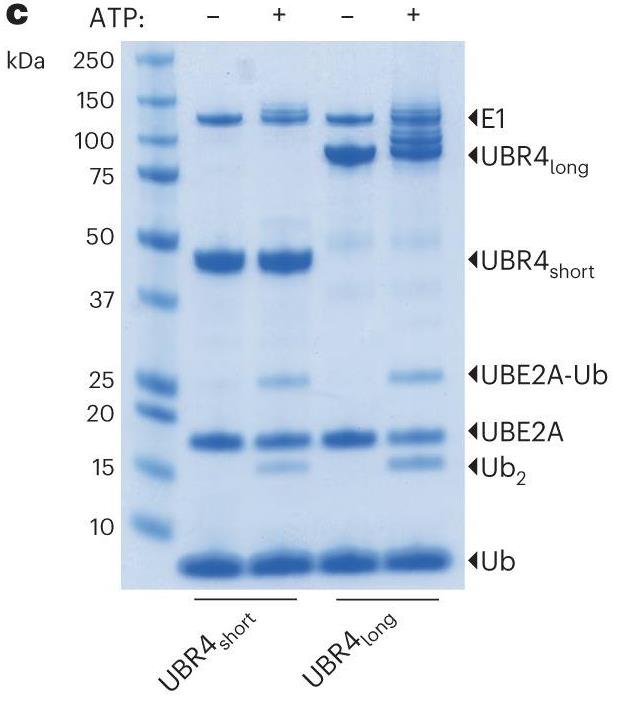 Fig3. Activity assessment of UBR4short and UBR4long with UBE2A.
Fig3. Activity assessment of UBR4short and UBR4long with UBE2A. -
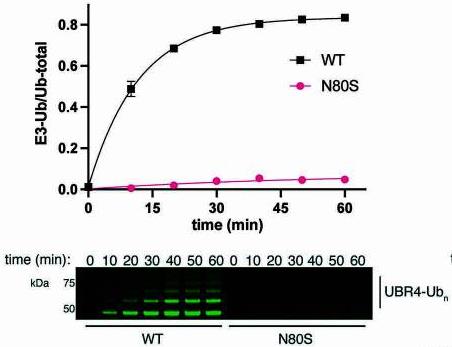 Fig4. Quantitative UBR4 autoubiquitination assay comparing UBE2A WT with UBE2A Asn80Ser under single turnover E2∼Ub discharge conditions.
Fig4. Quantitative UBR4 autoubiquitination assay comparing UBE2A WT with UBE2A Asn80Ser under single turnover E2∼Ub discharge conditions.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (UBR4-32H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (UBR4-32H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (UBR4-33H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (UBR4-33H)
Involved Pathway
UBR4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways UBR4 participated on our site, such as Viral carcinogenesis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with UBR4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Viral carcinogenesis | GRB2,POLB,MAPK1,KAT2A,HIST2H4,H2-Q10,MAD1L1,ACTN4,YWHAZ,HIST1H4B |
-
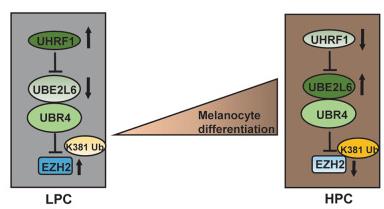 Fig1. Proposed model for UHRF1/UBE2L6/UBR4-mediated regulation of EZH2 and thereby melanocytic differentiation phenotypes in melanoma. (Gamze Kuser-Abali, 2023)
Fig1. Proposed model for UHRF1/UBE2L6/UBR4-mediated regulation of EZH2 and thereby melanocytic differentiation phenotypes in melanoma. (Gamze Kuser-Abali, 2023) -
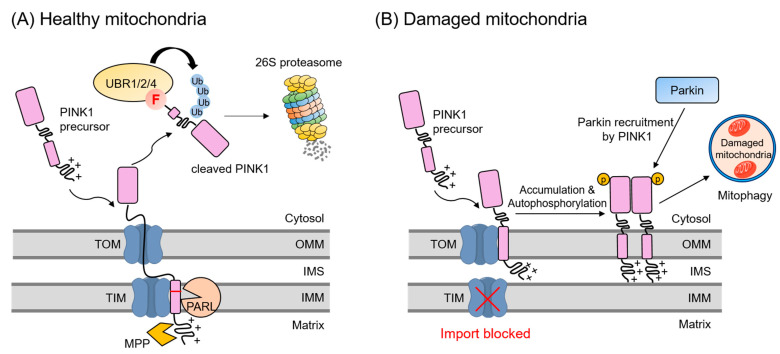 Fig2. A schematic model describing mitochondrial quality control mediated by UBR1/2/4 in response to the mitochondrial damage. (Jung Gi Kim, 2021)
Fig2. A schematic model describing mitochondrial quality control mediated by UBR1/2/4 in response to the mitochondrial damage. (Jung Gi Kim, 2021)
Protein Function
UBR4 has several biochemical functions, for example, calmodulin binding,ligase activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by UBR4 itself. We selected most functions UBR4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with UBR4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | DZIP3,WWP2,HECTD3,FBXW2,RNF151,BRAP,FBXL5,RNF141,FBXO11,RCHY1 |
| calmodulin binding | MYH10,CAMK2B1,PHKB,TRPC2,NRGNA,PHKG1A,MYH1E,REM1,PHKG1,TRPV5 |
| protein binding | GAGE1,SFMBT1,CSNK2B,STAC3,UNC13A,CHCHD3,IRS4,ASB3,SAP30BP,GDAP2 |
| ligase activity | TNFAIP3,UBR1,HECW1,CDC34A,RNF123,MARCH2,RAD18,HUWE1,RNF115,MUL1 |
| zinc ion binding | PNMA3,AMFR,MMP28,SHARPIN,NR1H5,TRIM10,MORC1,ZSWIM3,MARCH5,TTF2 |
Interacting Protein
UBR4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with UBR4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of UBR4.
E7;VCAM1;gag-pol;E7;E7;MCRS1;PRPF40A;SRGN;UBE2A;UBE2B;Smad6;Nsfl1c
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Parsons, K; Nakatani, Y; et al. p600/UBR4 in the central nervous system. CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR LIFE SCIENCES 72:1149-1160(2015).
- Aoyagi, N; Watanabe, M; et al. Optical properties of tetravalent uranium complexes in non-aqueous media. JOURNAL OF RADIOANALYTICAL AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY 303:1095-1098(2015).


