TRIP13
-
Official Full Name
thyroid hormone receptor interactor 13 -
Overview
This gene encodes a protein that interacts with thyroid hormone receptors, also known as hormone-dependent transcription factors. The gene product interacts specifically with the ligand binding domain. This gene is one of several that may play a role in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. -
Synonyms
TRIP13;thyroid hormone receptor interactor 13;pachytene checkpoint protein 2 homolog;16E1BP;thyroid receptor interacting protein 13;16E1-BP;Homo sapiens HPV16 E1 protein binding protein mRNA complete cds;HPV16 E1 protein binding protein;HPV16 E1 protein-binding protein;Human papillomavirus type 16 E1 protein binding protein;Human papillomavirus type 16 E1 protein-binding protein;Thyroid receptor-interacting protein 13;TR-interacting protein 13;TRIP-13;TRP13_HUMAN
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- Non
- T7
- Strep
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is TRIP13 Protein?
TRIP13 protein is a bit like a helper molecule found in our cells, playing a significant role in cell division and DNA repair. It's part of the AAA+ family of proteins, which means it's involved in various cellular processes, helping ensure everything runs smoothly. In the context of diseases like cancer, TRIP13 takes on more importance because it can influence how cancer cells grow and spread. Scientists are particularly interested in TRIP13 because changes or increases in its activity have been linked to the development and progression of different types of cancer. So, understanding TRIP13 better could be key in developing new treatment strategies for cancer and possibly other diseases where cell regulation goes haywire.What is the Function of TRIP13 Protein?
TRIP13 protein is like a manager in the cell, overseeing important tasks like fixing DNA and helping with cell division. Part of the AAA+ protein family, it ensures that cells divide properly and that any DNA damage gets repaired, keeping everything in balance. In cancer, TRIP13 seems to kick into overdrive, helping cancer cells survive by aiding their growth and spread. Scientists are really interested in TRIP13 because it could be a target for new cancer therapies. By figuring out what TRIP13 does, they hope to find ways to shut down its cancer-fueling actions and possibly halt tumor growth altogether.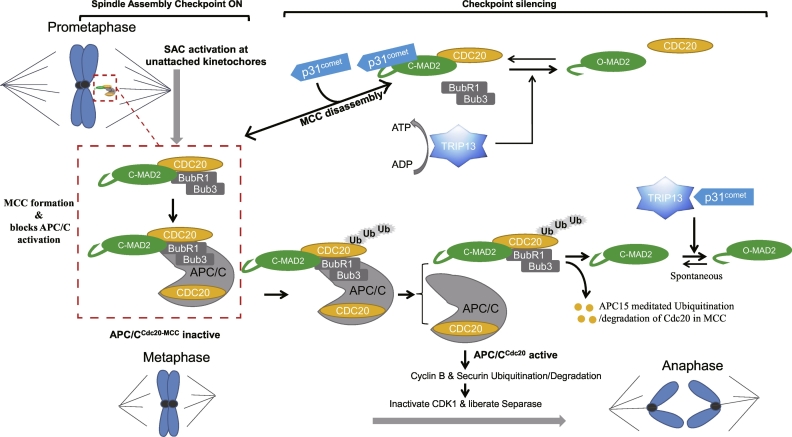
Fig1. Model for the roles of TRIP13 in disassembling the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC) and in promoting mitotic progression. (S Lu, 2019)
TRIP13 Related Signaling Pathway
The TRIP13-related signaling pathway is all about how this protein fits into the bigger picture of cell behavior. TRIP13 is part of various processes, like fixing DNA and helping cells divide properly. It works alongside other proteins to make sure that any DNA damage is patched up and the cell cycle runs smoothly. In cancer, this pathway can get a bit out of whack, with TRIP13 helping cancer cells repair their DNA quickly, making them tougher to kill. This pathway involves interactions with other proteins and molecules that drive cell repair and division. Researchers are digging into these signaling networks to pinpoint where TRIP13 is most active, hoping to develop therapies that can disrupt this pathway in cancer cells. By doing so, they aim to make treatments more effective by slowing down or stopping tumor growth.TRIP13 Related Diseases
TRIP13 is linked to various health problems, especially cancer. When TRIP13 levels get off track, they can help cancer cells repair DNA and grow faster, making the disease harder to tackle. It's involved in many cancers, like lung, breast, and gastric cancer, so researchers are keen to learn more about its role. By targeting TRIP13, they hope to slow or stop cancer growth, offering new treatment options. Since TRIP13 also affects cell repair, it's being studied for other diseases where rapid cell growth or damage is an issue.Bioapplications of TRIP13
TRIP13 isn't just a protein hanging out in cells—it's got some intriguing potential in biotechnology and medicine. Because TRIP13 plays a role in how cells repair DNA and divide, it's a hot topic in cancer research. Researchers are looking into whether tweaking or blocking TRIP13 could stop cancer cells from growing. By getting a clearer picture of how TRIP13 works, they hope to create treatments that specifically mess with its action in tumors, which could make cancer therapies more successful. Beyond cancer, TRIP13's involvement in cell regulation means it could have applications in studying other diseases where cell growth gets out of control. Researchers are also looking at how TRIP13 might be used in diagnostic tests to identify disease progression or treatment responses, making it a versatile tool in the biotech toolkit.Case Study
Case Study 1: Liu W. et al. Sci Rep. 2025
Radiation therapy is a key treatment for lung cancer, but resistance can reduce its effectiveness. Lung cancer cells with more germ cell cancer genes, like TRIP13, repair DNA faster and resist radiation more. TRIP13 boosts resistance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and higher levels lead to worse patient outcomes after treatment. More radiation can increase TRIP13 and resistance, while changing TRIP13 levels affects this resistance. It also improves DNA damage repair with proteins like NBS1 and RAD51 working downstream, but blocking TRIP13 mainly cuts down on homologous recombination repair proteins.-
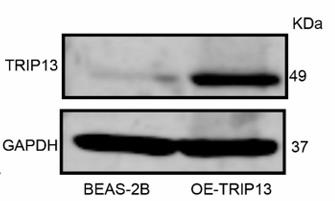 Fig1. Lysates from BEAS-2B (dCas9) and OE-TRIP13 were immunoblotted with anti-TRIP13 and anti-GAPDH as loading control.
Fig1. Lysates from BEAS-2B (dCas9) and OE-TRIP13 were immunoblotted with anti-TRIP13 and anti-GAPDH as loading control. -
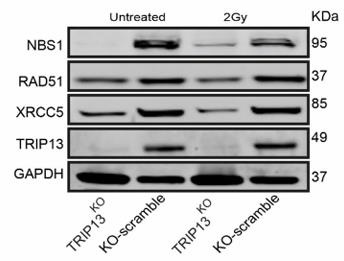 Fig2. NBS1, RAD51, XRCC5 and TRIP13 protein expression in the KO-scramble and TRIP13KO cells.
Fig2. NBS1, RAD51, XRCC5 and TRIP13 protein expression in the KO-scramble and TRIP13KO cells.
Case Study 2: Zhang G. et al. Cell Death Dis. 2024
Gastric cancer, typically adenocarcinoma, is a common and serious cancer that often sneaks in without early symptoms. Finding early markers and new treatment options is key to boosting survival chances. TRIP13, an AAA+ family ATPase, is linked to various tumors and is highly expressed in gastric cancer tissues. It plays a role in cancer cell growth, movement, and spread both in lab settings and in living organisms. TRIP13 works with DDX21, preventing its breakdown and thus fostering cancer progression. Upstream, histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) affects TRIP13, targeting its promoter to boost cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion.-
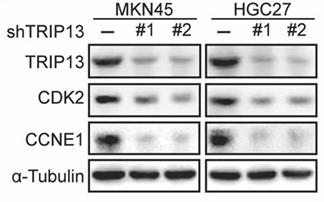 Fig3. Western blot was performed to detect the protein expression of TRIP13, CDK2, and CCNE1 in TRIP13-overexpressing in TRIP13-knockdown gastric cancer cells.
Fig3. Western blot was performed to detect the protein expression of TRIP13, CDK2, and CCNE1 in TRIP13-overexpressing in TRIP13-knockdown gastric cancer cells. -
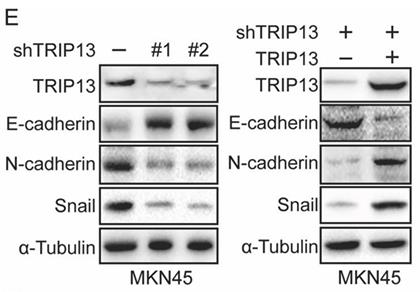 Fig4. Western blot experiments were performed to detect the protein expression of TRIP13.
Fig4. Western blot experiments were performed to detect the protein expression of TRIP13.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TRIP13-3022H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TRIP13-3022H)
Involved Pathway
TRIP13 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TRIP13 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TRIP13 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
-
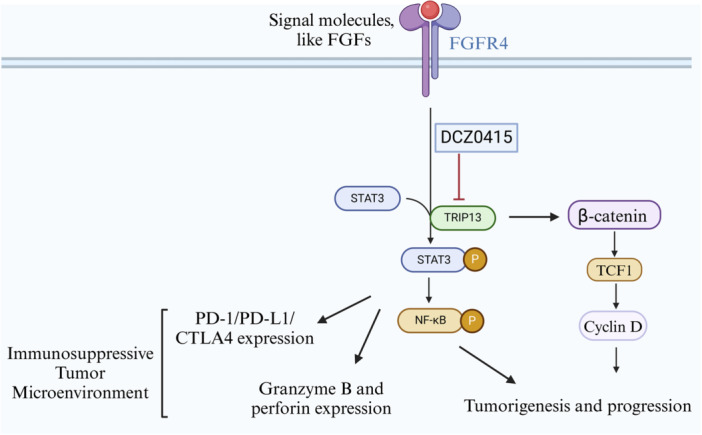 Fig1. Illustration of the mechanism underlying the antitumor effect and immune response of targeting TRIP13. (Shengnan Jing, 2024)
Fig1. Illustration of the mechanism underlying the antitumor effect and immune response of targeting TRIP13. (Shengnan Jing, 2024) -
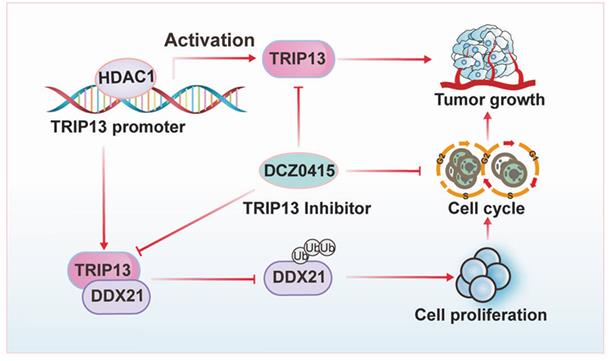 Fig2. HDAC1 mediates TRIP13/DDX21 axis to promote the development of gastric cancer. (Guanghui Zhang, 2024)
Fig2. HDAC1 mediates TRIP13/DDX21 axis to promote the development of gastric cancer. (Guanghui Zhang, 2024)
Protein Function
TRIP13 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,identical protein binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TRIP13 itself. We selected most functions TRIP13 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TRIP13. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| identical protein binding | PSME3,MIEF1,CIDEB,PRKAB2,SH3GLB1,CUBN,TGFB3,CCDC109A,APIP,PICK1 |
| transcription cofactor activity | TFB2M,TADA2A,AIRE,SND1,ZNF671,NFE2L1,BTG1,MED12,MED4,FAM48A |
| protein binding | LAMA1,SEMA4D,TBRG4,FBL,RBP7,TWSG1,NDUFA13,MVK,IQCE,NAP1L1 |
| ATP binding | ABCC1,TRIO,PLK4,PAPD4,DICER1,AACS,P2RY2,UBE2E2,DGKQ,LIMK1 |
Interacting Protein
TRIP13 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TRIP13 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TRIP13.
LASP1;GLYCTK;LOXL4;MAD2L1BP
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


