TRAF4
-
Official Full Name
TNF receptor-associated factor 4 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF) family. TRAF proteins are associated with, and mediate signal transduction from members of the TNF receptor superfamily. The encoded protein has been shown to interact with neurotrophin receptor, p75 (NTR/NTSR1), and negatively regulate NTR induced cell death and NF-kappa B activation. This protein has been found to bind to p47phox, a cytosolic regulatory factor included in a multi-protein complex known as NAD(P)H oxidase. This protein thus, is thought to be involved in the oxidative activation of MAPK8/JNK. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed but the full-length nature of only one has been determined. -
Synonyms
TRAF4;TNF receptor-associated factor 4;CART1;MLN62;RNF83;MLN 62;malignant 62;RING finger protein 83;metastatic lymph node gene 62 protein;tumor necrosis receptor-associated factor 4A;cysteine-rich domain associated with ring and TRAF domain;cys
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRAF4-3387H | Recombinant Human TRAF4, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 35-307AA | |
| TRAF4-558H | Recombinant Human TRAF4 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Gln193~Asp444 | |
| TRAF4-17289M | Recombinant Mouse TRAF4 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| TRAF4-31602TH | Recombinant Human TRAF4, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 207-406 a.a. |
|
| TRAF4-550H | Recombinant Human TRAF4 Protein, GST-His-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST&His |
|
|
| TRAF4-820HCL | Recombinant Human TRAF4 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| TRAF4-6711H | Recombinant Human TRAF4 Protein (Gln193-Asp444), His tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Gln193-Asp444 |
|
| TRAF4-9558M | Recombinant Mouse TRAF4 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| TRAF4-9558M-B | Recombinant Mouse TRAF4 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is TRAF4 Protein?
TRAF4 (TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 4) is a multifunctional adaptor protein involved in regulating immune responses, cell survival, and stress signaling pathways. Structurally, it contains a RING domain and TRAF-binding motifs, enabling interactions with receptors like TNFR and kinases such as MAPK. TRAF4 modulates NF-κB and JNK pathways, influencing inflammation, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis. Overexpressed in breast, lung, and esophageal cancers, it correlates with metastasis and therapy resistance by stabilizing oncogenic proteins. Recent studies highlight its role in embryonic development and immune evasion, driving interest in TRAF4 inhibitors for targeted cancer treatment. Emerging applications include diagnostic biomarkers and CRISPR-based therapeutic strategies. Keywords: TRAF4 protein function, NF-κB signaling pathway, cancer metastasis mechanisms, TRAF4 inhibitors, immune evasion biomarkers.What is the Function of TRAF4 Protein?
TRAF4 (TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 4) functions as a critical regulator of cellular signaling, primarily influencing immune responses, stress adaptation, and oncogenic processes. It mediates interactions between TNF receptors and intracellular kinases, modulating NF-κB and JNK pathways to control inflammation, apoptosis, and cell survival. Structurally, its RING domain facilitates ubiquitination, while TRAF-binding motifs anchor signaling complexes. In cancer, TRAF4 overexpression drives metastasis in breast and lung cancers by enhancing cell migration and therapy resistance through stabilization of oncoproteins like β-catenin. Recent studies also link TRAF4 to embryonic development and immune evasion via PD-L1 regulation. Emerging therapies targeting TRAF4’s signaling nodes aim to disrupt tumor progression and improve immunotherapy efficacy. Keywords: TRAF4 protein function, NF-κB signaling in cancer, immune evasion mechanisms, TRAF4 ubiquitination, metastatic cancer therapy.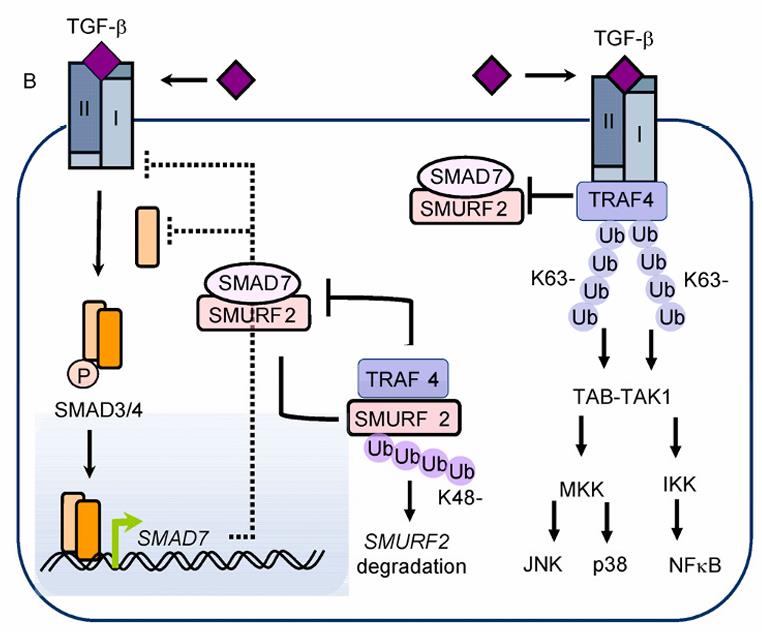
Fig1. TRAF4-involved regulation of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β/SMAD (SMA- and MAD-related protein) signaling and SMAD-independent signaling in cancer progression. (FangFang Zhou, 2014)
TRAF4 Related Signaling Pathway
TRAF4 (TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 4) orchestrates key signaling networks, including NF-κB, JNK, and Wnt/β-catenin pathways, driving cancer progression and immune evasion. Through its RING domain and TRAF-binding motifs, TRAF4 interacts with receptors like TNFR and EGFR, amplifying pro-survival signals and inflammatory responses. It stabilizes β-catenin via ubiquitination, promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis in breast and lung cancers. TRAF4 also suppresses Hippo pathway activity, enhancing YAP/TAZ-driven tumor growth. In the tumor microenvironment, TRAF4 upregulates PD-L1 to inhibit T-cell function, facilitating immune escape. Targeting TRAF4-linked pathways, such as with small-molecule inhibitors or monoclonal antibodies, shows promise in overcoming therapy resistance. Emerging research explores its diagnostic potential as a biomarker for aggressive cancers. Keywords: TRAF4 signaling pathway, NF-κB activation, cancer metastasis mechanisms, Wnt/β-catenin regulation, Hippo pathway crosstalk.TRAF4 Related Diseases
TRAF4 (TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 4) dysregulation is implicated in multiple diseases, particularly cancers such as breast, lung, and esophageal malignancies, where its overexpression drives metastasis and chemotherapy resistance. By stabilizing β-catenin and activating NF-κB pathways, TRAF4 promotes tumor cell survival, invasion, and immune evasion via PD-L1 upregulation. Beyond oncology, TRAF4 is linked to inflammatory disorders like rheumatoid arthritis by amplifying cytokine production through JNK signaling. Rare genetic mutations in TRAF4 are associated with developmental abnormalities, including neural tube defects. Current research focuses on TRAF4 as a diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target, with inhibitors blocking its ubiquitination activity showing promise in preclinical trials. Emerging strategies also explore CRISPR-based editing to modulate TRAF4-driven pathways. Keywords: TRAF4-related diseases, cancer metastasis mechanisms, NF-κB inflammation, TRAF4 inhibitors, immune checkpoint biomarkers.Bioapplications of TRAF4
TRAF4 (TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 4) is leveraged in diverse bioapplications, particularly in oncology and immunology. As a diagnostic biomarker, its overexpression in tumors like breast and lung cancers enables non-invasive detection via liquid biopsies. In therapeutics, TRAF4-targeted inhibitors disrupt NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin pathways, curbing metastasis and chemotherapy resistance. Researchers exploit TRAF4’s role in immune evasion to design PD-L1-blocking therapies, enhancing checkpoint inhibitor efficacy. CRISPR-based editing of TRAF4 shows potential in reversing oncogenic signaling, while proteomic tools map its interactions for drug discovery. Emerging applications include nanoparticle delivery systems for TRAF4 siRNA, improving precision in solid tumor treatment. These advances position TRAF4 as a cornerstone for next-generation cancer management. Keywords: TRAF4 bioapplications, cancer immunotherapy, diagnostic biomarkers, CRISPR gene editing, targeted drug delivery.Case Study
Case Study 1: Dong X. et al. Cell Death Dis. 2023
TRAF4, an E3 ligase, is often overactive in colorectal cancer (CRC) and tied to tumor growth. This study shows TRAF4 levels are higher in CRC tumors. Knocking down TRAF4 makes CRC cells less aggressive and more sensitive to radiation. Radiation activates a pathway involving JNK and c-Jun, which boosts levels of the anti-death protein Bcl-xL, making cancer cells more resistant. Blocking TRAF4 or Bcl-xL helps radiation kill cancer cells better in lab and animal tests.-
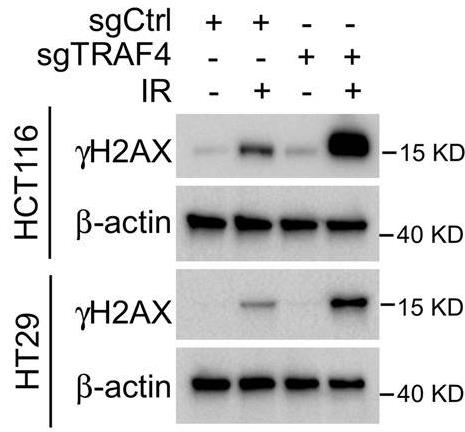 Fig1. Immunoblotting for γ-H2AX expression in sgTRAF4-HCT116 and -HT29 cells with or without IR (4 Gy) treatment.
Fig1. Immunoblotting for γ-H2AX expression in sgTRAF4-HCT116 and -HT29 cells with or without IR (4 Gy) treatment. -
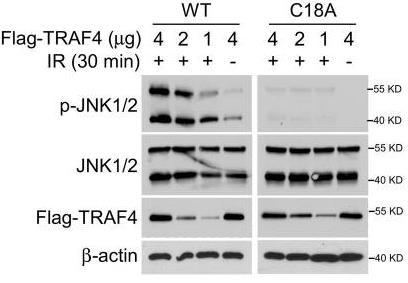 Fig2. TRAF4-knockout HT29 cells were transfected with Flag-TRAF4 WT or Flag-TRAF4 C18A mutant for 48 h, followed by IR (4 Gy) treatment for 30 min.
Fig2. TRAF4-knockout HT29 cells were transfected with Flag-TRAF4 WT or Flag-TRAF4 C18A mutant for 48 h, followed by IR (4 Gy) treatment for 30 min.
Case Study 2: Iyengar PV. et al. Mol Cancer Res. 2022
In bladder cancer, low TRAF4 expression is linked to poor survival. TRAF4 is epigenetically silenced, leading to lower protein levels. It inversely correlates with EMT markers and regulates EMT genes and invasive properties. High TRAF4 enhances BMP/SMAD signaling and inhibits NF-κB by targeting SMURF1 for degradation. Inhibiting SMURF1 reduces migration in aggressive bladder cancer cells.-
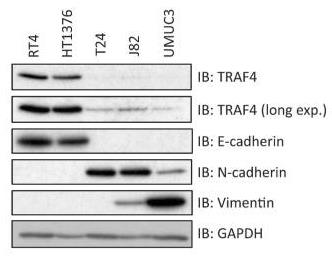 Fig3. Immunoblot analysis showing the expression of TRAF4 and other EMT marker proteins.
Fig3. Immunoblot analysis showing the expression of TRAF4 and other EMT marker proteins. -
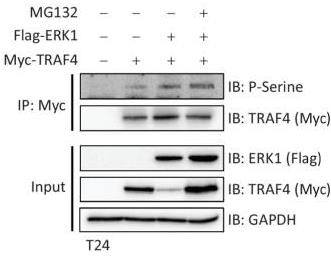 Fig4. Immunoprecipitation of Myc-TRAF4 with or without Flag-ERK1 overexpression, GAPDH, loading control.
Fig4. Immunoprecipitation of Myc-TRAF4 with or without Flag-ERK1 overexpression, GAPDH, loading control.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TRAF4-558H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TRAF4-558H)
Involved Pathway
TRAF4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TRAF4 participated on our site, such as Pathways in cancer,Small cell lung cancer, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TRAF4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Pathways in cancer | PTCH1,RARB,LAMA4,RB1,FLT3,Fasl,PRKACG,GNG11,MET,LAMB2 |
| Small cell lung cancer | LAMC2,TRAF1,PTGS2,ITGA2B,PIK3R2,LAMB4,FHIT,PIAS2,TRAF5,MAX |
-
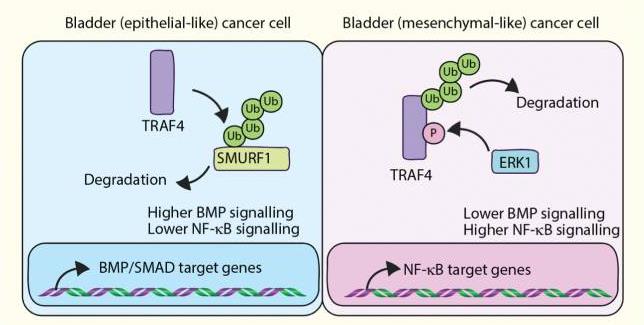 Fig1. Schematic representation of TRAF4 signaling dynamics in epithelial-like and mesenchymal-like bladder cancer cells. (Prasanna Vasudevan Iyengar, 2022)
Fig1. Schematic representation of TRAF4 signaling dynamics in epithelial-like and mesenchymal-like bladder cancer cells. (Prasanna Vasudevan Iyengar, 2022) -
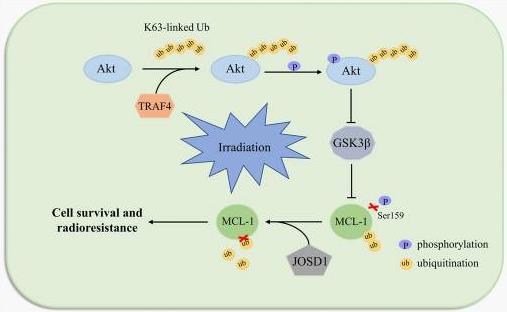 Fig2. The schematic of TRAF4-mediated regulation of MCL-1 expression and radioresistance. (Ming Li, 2022)
Fig2. The schematic of TRAF4-mediated regulation of MCL-1 expression and radioresistance. (Ming Li, 2022)
Protein Function
TRAF4 has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,WW domain binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TRAF4 itself. We selected most functions TRAF4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TRAF4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| tumor necrosis factor receptor binding | TNFSF15,ERAP1,TRAF3,TNFSF10L,TNFSF13B,TNFSF12,TRAP1,TRAF6,LTB,TNFSF4 |
| protein kinase binding | MS4A2,TRAF2,CDK5RAP2,Fert2,PTPRR,C10orf46,EEF1A1,DAXX,SNAP91,SLC12A7 |
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | UBR1,FBXL14A,BRCA1,SIAH1,G2E3,LNX1,RBBP6,KLHL20,UBE2G2,UBE2O |
| zinc ion binding | RSPRY1,RNF34A,KDM5B,Ar,NR1D4A,MARCH9,PHF10,ADAM10B,GM3258,TRIM59 |
| thioesterase binding | HAUS7,RAC1,TRAF1,ADRA2A,TRAF6,TRAF5,CALM2,ARF6,CDC42,CALM3 |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | TSG101,UBE2G1,UBOX5,PDE4D,WASH1,PCBP2,UBE2R2,TMEM173,UBE2K,CUL1B |
| DNA binding | ERG,ZNF334,NUCB1,SCMH1,ZNF786,ZNF556,ZFP692,TTF2,ZFY2,TRERF1 |
| WW domain binding | NFE2,SCNN1G,LITAF,TP63,TCEAL6,SHISA5,NDFIP2,WBP11,PMEPA1,FAM189B |
| protein binding | UFC1,ELK1,ATP6V1F,C7orf25,CBR4,SCRN1,TMEM64,STXBP2,VSNL1,SPRED2 |
Interacting Protein
TRAF4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TRAF4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TRAF4.
WWP2;BYSL;SMURF1;BCL6B;NPIPA7
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


