TPH1
-
Official Full Name
tryptophan hydroxylase 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the aromatic amino acid hydroxylase family. The encoded protein catalyzes the first and rate limiting step in the biosynthesis of serotonin, an important hormone and neurotransmitter. Mutations in this gene have been associated with an elevated risk for a variety of diseases and disorders, including schizophrenia, somatic anxiety, anger-related traits, bipolar disorder, suicidal behavior, addictions, and others.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009] -
Synonyms
TPH1;tryptophan hydroxylase 1;TPRH;TRPH;tryptophan 5-hydroxylase 1;L-tryptophan hydroxylase;tryptophan 5-monooxygenase 1;indoleacetic acid-5-hydroxylase;tryptophan hydroxylase (tryptophan 5-monooxygenase)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- Non
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
What is TPH1 Protein?
TPH1 gene (tryptophan hydroxylase 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 10 at locus 10p15. This gene encodes a member of the aromatic amino acid hydroxylase family. The encoded protein catalyzes the first and rate limiting step in the biosynthesis of serotonin, an important hormone and neurotransmitter. Mutations in this gene have been associated with an elevated risk for a variety of diseases and disorders, including schizophrenia, somatic anxiety, anger-related traits, bipolar disorder, suicidal behavior, addictions, and others. The TPH1 protein is consisted of 444 amino acids and TPH1 molecular weight is approximately 51.0 kDa.
What is the Function of TPH1 Protein?
TPH1 is an important enzyme whose primary function is to catalyze the synthesis of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) in vivo, which is the first and rate-limiting step in the serotonin biosynthesis pathway. Serotonin is a key neurotransmitter and hormone that plays an important role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, pain perception and many other physiological functions. At the cellular level, TPH1 protein is mainly located in the cytoplasm, has monomer and tetramer forms, and plays a catalytic role in the cell. At the tissue level, TPH1 is particularly abundant in the brain, intestine, pituitary gland, and stomach, and is expressed at low levels in certain immune cells.
TPH1 Related Signaling Pathway
TPH1 is the rate-limiting enzyme in the serotonin synthesis pathway, responsible for the conversion of tryptophan to 5-hydroxytryptophan, which in turn forms serotonin. This process is crucial to a variety of physiological and psychological processes such as mood, sleep, psychological behavior, and is closely related to the occurrence and development of mental diseases such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. The expression of TPH1 in the gut, especially in enterochromaffin cells (EC cells), plays an important role in the development of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Studies have shown that the clock gene Bmal1 is involved in the occurrence of IBS by regulating EC cells and its TPH1-5 HT signaling pathway. In the gut, 5-HT interacts with PGE2 (prostaglandin E2), and PGE2+ macrophages promote Wnt/β-catenin signaling in ISCs (intestinal stem cells) by binding to the PGE2 receptor EP1/EP4, and 5-HT is a key factor in this process.
TPH1 Related Diseases
Reduced serotonin levels are associated with the emergence of depressive symptoms, and reduced TPH1 activity may lead to insufficient serotonin synthesis, which affects mood regulation. Patients with anxiety disorders may have abnormal serotonin signaling. As a key enzyme in serotonin synthesis, abnormal expression or function of TPH1 may affect anxiety-related behaviors. Abnormal expression of TPH1 may be related to the pathogenesis of schizophrenia, and dysfunction of the serotonin system may affect cognitive and perceptual processes. Seasonal changes may affect serotonin levels, and mutations in the TPH1 gene may be associated with the development of seasonal affective disorder (SAD). The serotonin system is involved in impulse control and mood regulation, and reduced TPH1 activity may be linked to an increased risk of suicide.
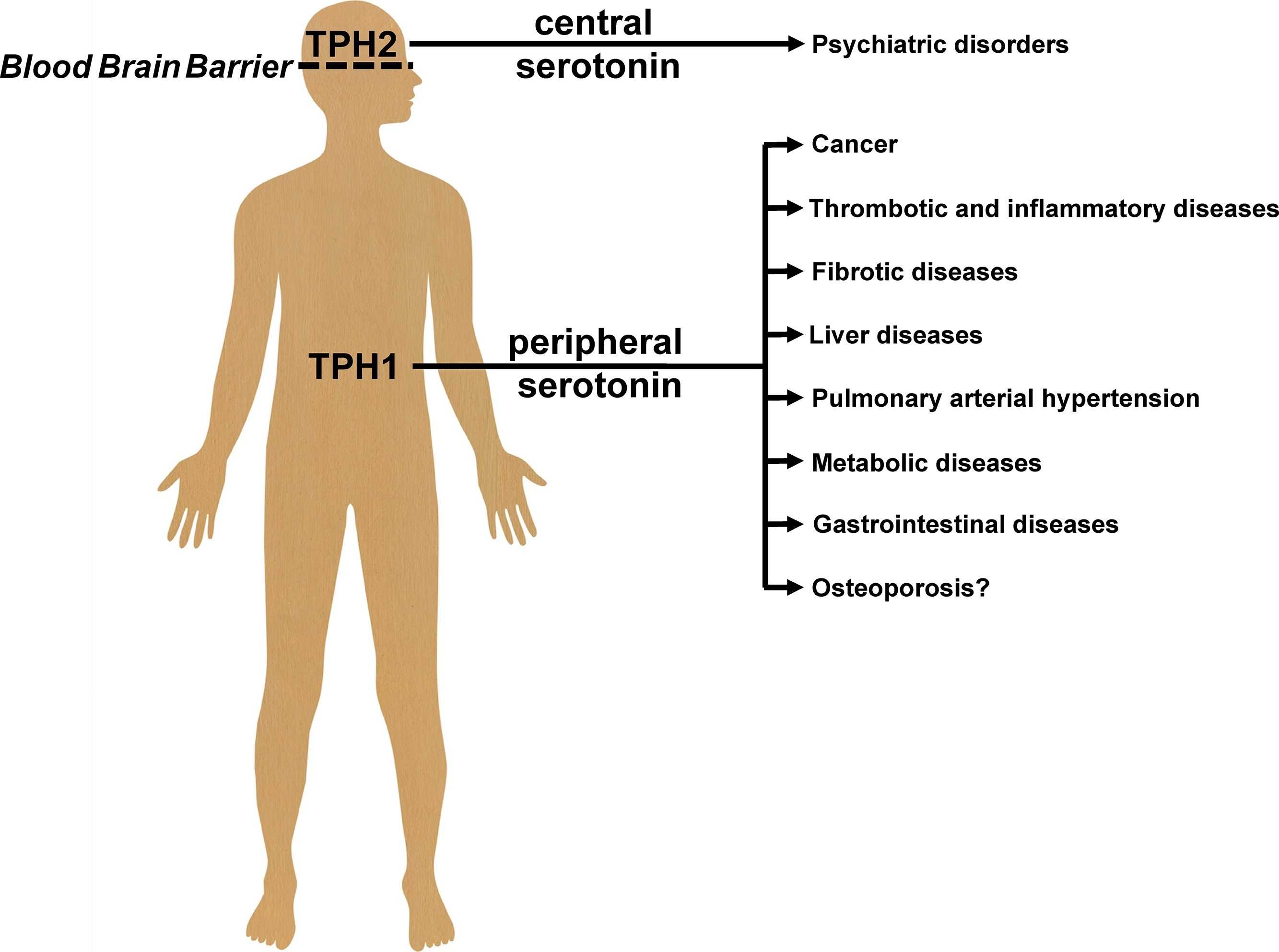
Fig1. Therapeutic options for TPH inhibitors based on the duality of the serotonin system. (Michael Bader, 2020)
Bioapplications of TPH1
Because of TPH1's central role in regulating serotonin levels, drugs that target TPH1 may be effective in treating psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. In digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), regulating TPH1 activity may help improve intestinal function and reduce symptoms. Taking this as an example, both the prevention and treatment of related emotional disorders can be applied. TPH1 is used as a drug target, and the development of its inhibitors or agonists may lead to new therapeutic drugs for the treatment of these diseases. The activity or expression level of TPH1 may serve as a biomarker for psychiatric disorders and other related diseases, which can help in disease diagnosis and monitoring.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jie Zhang, 2022
In the present study, researchers shed light on tumor metabolism and aimed to investigate the role of tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (TPH-1) in the advancement of glioma. The proliferative characteristics and migration ability of TPH-1 overexpressing LN229/T98G cells were evaluated. And they also examined the tumor growth and survival time in a mouse model of glioma treated with chemotherapeutic agents and a TPH-1 inhibitor. The results of both clinical and experimental data showed that excess TPH-1 expression resulted in sustained glioma progression and a dismal overall survival in these patients. Mechanistically, TPH-1 increased the production of serotonin in glioma cells. Taken together, these data suggested that TPH-1 facilitated cellular proliferation, migration, and chemoresistance in glioma through the serotonin/L1CAM/NF-κB pathway.
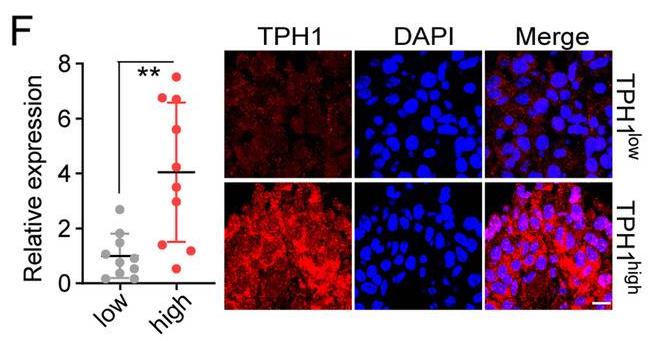
Fig1. Immunofluorescence staining of TPH-1 in TPH-1high and TPH-1low glioma tissues from patients.
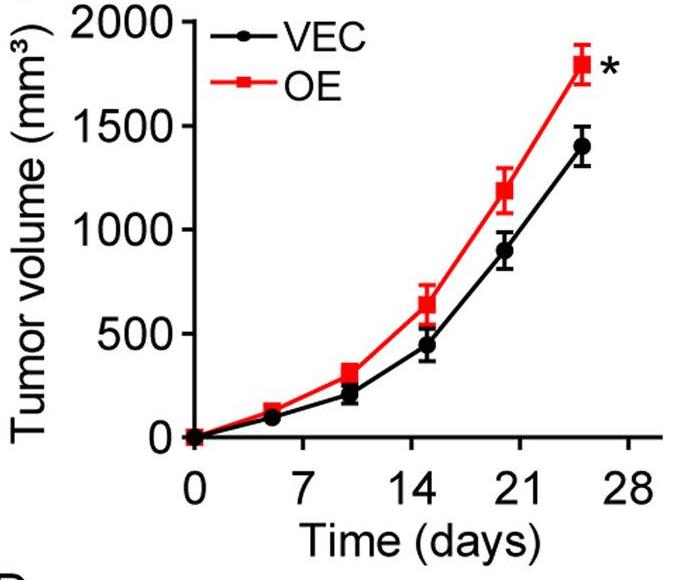
Fig2. LN229 (VEC) and TPH-1 overexpressing LN229 cells (OE) were subcutaneously injected into mice.
Case Study 2: Prakash Chaudhary, 2021
In the present study, the regulatory mechanisms underlying overexpression of EZH2, tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (TPH1), and 5-HT7, in relation to gemcitabine resistance and CSC survival in PDAC cells. In aggressive PANC-1 and MIA PaCa-2 cells, knock-down (KD) of EZH2, TPH1, or HTR7 induced a decrease in CSCs and recovery from gemcitabine resistance, while preconditioning of less aggressive Capan-1 cells with 5-HT induced gemcitabine resistance with increased expression of EZH2, TPH1, and 5-HT7. Such effects of the gene KD and 5-HT treatment were mediated through PI3K/Akt and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways. EZH2 KD or GSK-126 (an EZH2 inhibitor) inhibited activities of these signaling pathways which altered nuclear level of NF-kB, Sp1, and p-STAT3, accompanied by downregulation of TPH1 and 5-HT7. Co-immunoprecipation with EZH2 and pan-methyl lysine antibodies revealed that auto-methylated EZH2 served as a scaffold for binding with methylated NF-kB and Sp1 as well as unmethylated p-STAT3. Furthermore, the inhibitor of EZH2, TPH1, or 5-HT7 effectively regressed pancreatic tumor growth in a xenografted mouse tumor model.
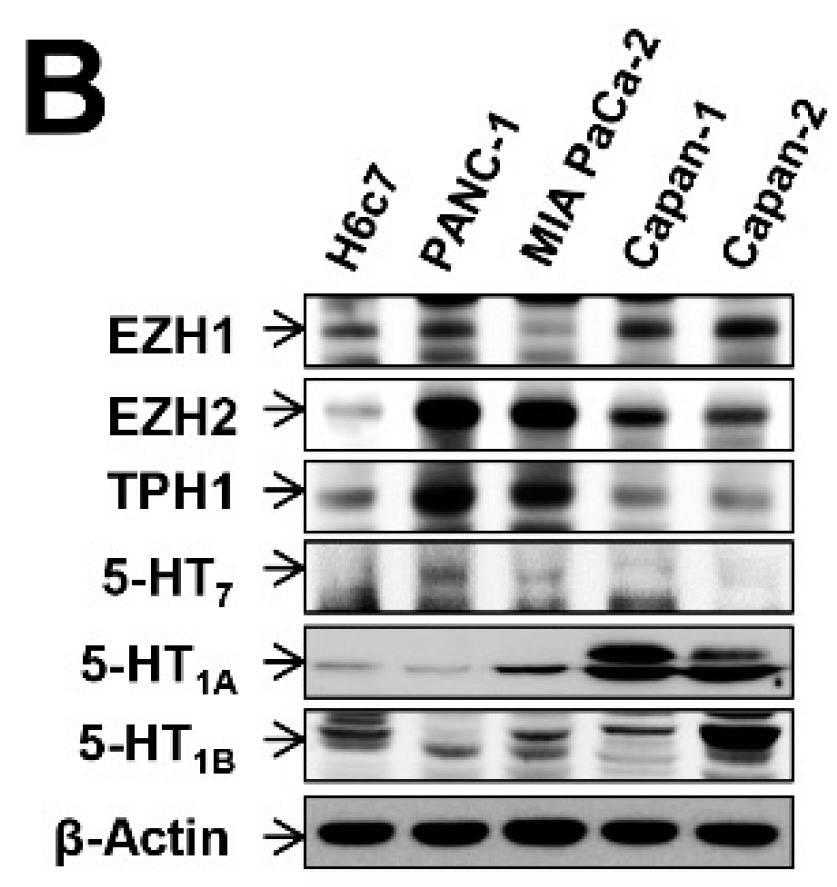
Fig3. Expression levels of EZH1, EZH2, TPH1, and 5-HT receptors.
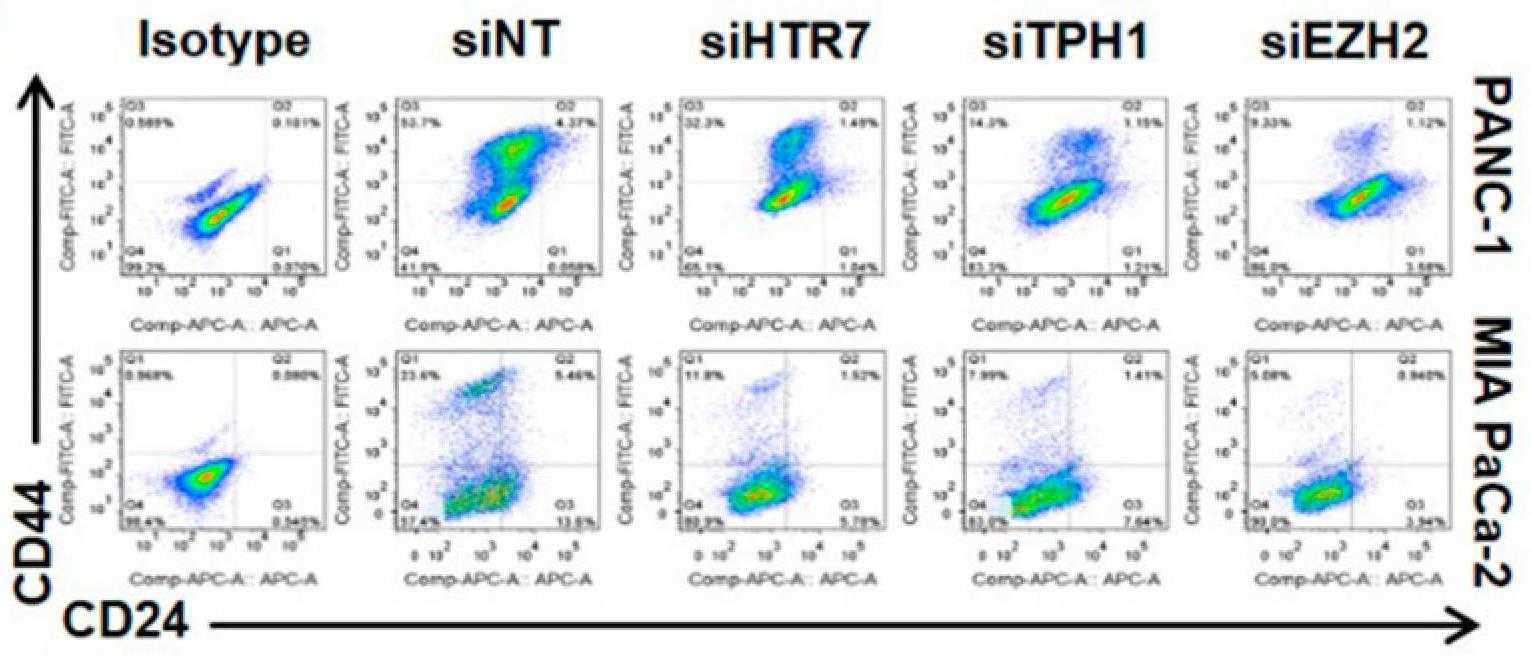
Fig4. Relative number of CD24+CD44+ population after KD of HTR7, TPH1, or EZH2.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TPH1-1706H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TPH1-1723M)
Involved Pathway
TPH1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TPH1 participated on our site, such as Tryptophan metabolism,Metabolic pathways,Serotonergic synapse, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TPH1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Tryptophan metabolism | AOC1,OGDHA,AOX4,HADHA,MAOB,TDO2B,ALDH3A2,AADAT,CMTM2A,KMO |
| Metabolic pathways | TSTA3,FUT1,PYCRL,GALCA,ALDH2.1,NME5,G6PCA.1,ctaG,NT5E,GLUD2 |
| Serotonergic synapse | GNB3,PRKCA,CYP2D10,TPH2,PTGS2,GNB1,GNAS,PLCB3,GNAI2,GNG7 |
Protein Function
TPH1 has several biochemical functions, for example, amino acid binding,iron ion binding,tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TPH1 itself. We selected most functions TPH1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TPH1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| iron ion binding | MSMO1,CYP2X9,CYP2A6,CYP7A1A,CYP4F3,ALOX5B.2,CYP27B1,CYP17A1,HBD,CYP2C70 |
| amino acid binding | GOT2,AARS2,GCHFR,OTC,TPH1B,KARS,AGXT,SHMT2,TH,TPH2 |
| tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activity | TPH1B,TPH1A,TPH2,TH2 |
Interacting Protein
TPH1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TPH1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TPH1.
MYC
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Oberkofler, CE; Limani, P; et al. Systemic Protection Through Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Is Spread by Platelet-Dependent Signaling in Mice. HEPATOLOGY 60:1409-1417(2014).
- Patrick, RP; Ames, BN; et al. Vitamin D hormone regulates serotonin synthesis. Part 1: relevance for autism. FASEB JOURNAL 28:2398-2413(2014).


