TIPARP
-
Official Full Name
TCDD-inducible poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase superfamily. Studies of the mouse ortholog have shown that the encoded protein catalyzes histone poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation and may be involved in T-cell function. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. -
Synonyms
TIPARP;TCDD-inducible poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase;TCDD-inducible poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase;DDF1;DKFZP434J214;DKFZp686N0351;PARP 1;PARP 7;PARP7;pART14;RM1;poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 7;FLJ40466;DKFZp686P1838
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mammalian Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- Insect Cells
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- Insect cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HEK293
- His
- Non
- GST
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIPARP-16803M | Recombinant Mouse TIPARP Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| TIPARP-29527TH | Recombinant Human TIPARP | Human | Non | Full L. |
|
|
| TIPARP-4093Z | Recombinant Zebrafish TIPARP | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| TIPARP-436H | Active Recombinant Full Length Human TIPARP, GST-tagged | Sf9 Cells | Human | GST | Full L. |
|
| TIPARP-298H | Active Recombinant Human TIPARP Protein, Flag-tagged | Insect Cells | Human | Flag | 400-657 |
|
| TIPARP-33H | Recombinant Human TIPARP Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST | 1-657 a.a. |
|
| TIPARP-5443H | Recombinant Human TIPARP protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 1-657aa |
|
| TIPARP-5633H | Recombinant Human TIPARP protein, His-tagged | Insect cells | Human | His | 1-657aa |
|
| TIPARP-6797HF | Recombinant Full Length Human TIPARP Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 166 amino acids |
|
| TIPARP-9227M | Recombinant Mouse TIPARP Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| TIPARP-9227M-B | Recombinant Mouse TIPARP Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is TIPARP Protein?
TIPARP gene (TCDD inducible poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3q25. TIPARP is part of the PARP family and helps transfer mono-ADP-ribose from something called NAD+ to other molecules, a process known as mono-ADP-ribosylation. It's pretty key in a bunch of body functions like controlling genes, responding to viruses, and managing the cell's scaffolding or structure. Abnormal regulation of TIPARP may lead to neurodevelopmental disorders, abnormal antiviral responses, certain types of cancer, and dioxin-induced fatty liver disease. Therefore, TIPARP protein plays a key role in physiological and pathological processes and is an important target for the study and treatment of related diseases. The TIPARP protein is consisted of 657 amino acids and TIPARP molecular weight is approximately 76.2 kDa.
What is the Function of TIPARP Protein?
TIPARP, a member of the PARP family, is primarily responsible for transferring a single ADP ribonucleotide from nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to other molecules in a process called mono-ADP-ribonucleation. Although it may sound technical, in short, TIPARP is involved in regulating some important physiological processes, such as gene regulation, response to viruses, and cytoskeleton regulation. TIPARP plays an important role in both defending against viruses and regulating the internal structure of cells.
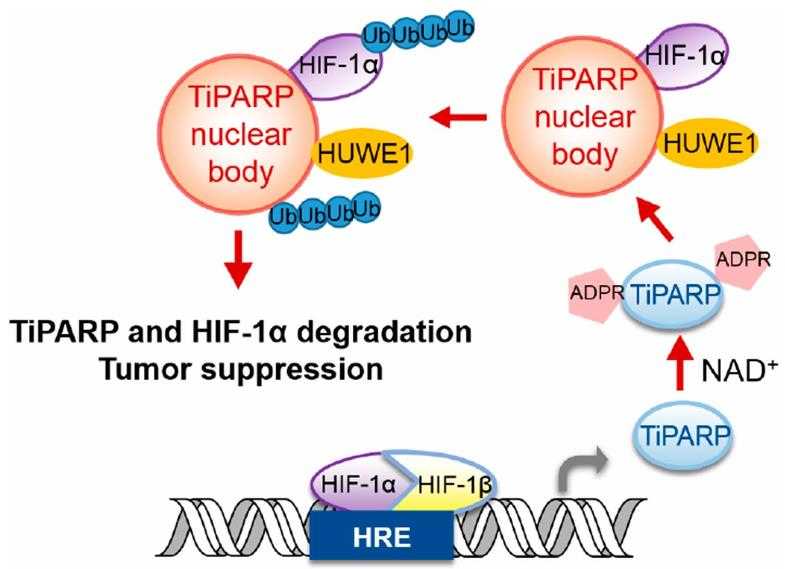
Fig1. Proposed model depicting the negative-feedback loop regulation of HIF-1α via TiPARP nuclear bodies. (Lu Zhang, 2020)
TIPARP Related Signaling Pathway
TIPARP, a protein in the PARP family, is like a tiny engine that transfers a component called mono-ADP-ribose from NAD+ onto various molecular targets in our cells. This action, known as mono-ADP-ribosylation, is key to supporting many physiological roles. For one, TIPARP is involved in controlling how genes get switched on and off, which is crucial for responding to changes inside and outside the body. It's also part of the defense strategy against viruses, helping the body to respond when it detects an intruder. Furthermore, TIPARP helps in managing the structure and movement of cells by regulating the cytoskeleton. This multifaceted protein is essential for maintaining cellular order and adapting to new challenges.
TIPARP Related Diseases
TIPARP, a protein involved in adding a single ADP-ribose unit to other proteins, plays a significant role in various body functions like how genes are regulated, responding to viruses, and organizing the structure inside cells. Changes or issues with TIPARP can be linked to several health conditions. For instance, it's involved in eye conditions like glaucoma, where controlling the pressure inside the eye goes awry. TIPARP also interacts with cancer-related processes by breaking down certain factors that can promote tumor growth. By influencing these biological pathways, TIPARP has a broader connection to diseases beyond just these examples, highlighting its importance in maintaining normal physiological balance.
Bioapplications of TIPARP
Recombinant TIPARP proteins are pretty handy in the scientific and research fields, as well as in industrial production. In research, it helps scientists dig into the nitty-gritty of cellular processes like gene regulation and response to environmental stress. In the industrial scene, these proteins can be utilized for developing or testing new drugs, especially for diseases linked to TIPARP malfunction. Plus, they play a role in creating targeted therapies by understanding how TIPARP influences various biological pathways. So, it's a versatile tool that's quite valuable across multiple domains.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Youjia Zhang, 2022
High eye pressure is a big risk for glaucoma, but exactly what causes this pressure is still a bit of a mystery, making treatment tough. We looked into TIPARP, a specific enzyme, and found it's all over the human eye, like in the cornea and retina. People with primary open-angle glaucoma had higher levels of TIPARP in their blood and specific eye parts compared to those without the disease. When TIPARP was up, certain genes linked to the eye's structure were lower, but when TIPARP was down, proteins like collagen increased, changing the eye's framework. Blocking TIPARP in rats made their eye pressure go up, showing TIPARP might control eye pressure by tweaking the eye's cellular makeup.

Fig1. Western blot confirmed that the expression of TIPARP protein was downregulated in the TIPARP siRNA-treated HTM cells
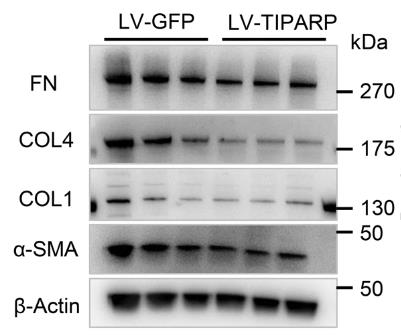
Fig2. Western blot and quantitative analyses showed fibronectin, collagen type IV, and α-SMA expression decreased in the LV-TIPARP-treated HTM cells.
Case Study 2: Lu Zhang, 2020
Keeping transcription factors in check is key for our body's functions. Once these factors, like HIF-1, do their job, they need to be turned off properly. HIF-1 and other cancer-related transcription factors get switched off by a protein called TiPARP. HIF-1 kicks off the creation of TiPARP, which then gathers into nuclear areas to deactivate HIF-1. It pulls in both HIF-1α and an enzyme called HUWE1, leading to HIF-1α's breakdown. TiPARP does the same to other cancer-linked proteins like c-Myc and the estrogen receptor, showing strong anticancer effects in lab and animal studies. Essentially, TiPARP acts like a self-regulating brake for these factors, hinting at a new angle for cancer treatments by boosting TiPARP.
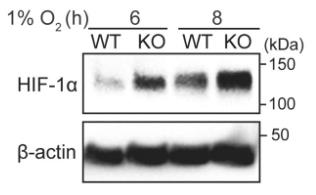
Fig3. Western blot of HIF-1α in HAP-1 WT or TiPARP KO cells after 6 and 8 h of hypoxia (1% O2) treatment.
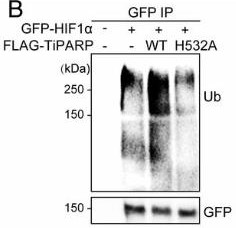
Fig4. HEK 293T cells cotransfected with GFP-HIF1α and empty vector, Flag-tagged WT, or H532A mutant TiPARP.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TIPARP-298H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TIPARP-5633H)
Involved Pathway
TIPARP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TIPARP participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TIPARP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
TIPARP has several biochemical functions, for example, NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase activity,enhancer binding,metal ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TIPARP itself. We selected most functions TIPARP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TIPARP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase activity | TNKS2,PARP14,PARP11,GIG2Q,PARP1,GIG2L,PARP8,GIG2G,PARP12A,PARP15 |
| enhancer binding | AHR,MESP1,SOX9,LEF1,FOXH1,TCF12,TCF3,SMAD3,ARNT,ELL3 |
| metal ion binding | ZNF266,PDP1,COL2A1,APLF,ERCC5,CYP2X8,DEM1,ZRSR2,ZNF280B,ZEB1B |
Interacting Protein
TIPARP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TIPARP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TIPARP.
XRN2
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- MacPherson, L; Ahmed, S; et al. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Repressor and TiPARP (ARTD14) Use Similar, but also Distinct Mechanisms to Repress Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCES 15:7939-7957(2014).
- Diani-Moore, S; Zhang, S; et al. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation by Dioxin Targets Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase (PEPCK) for ADP-ribosylation via 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD)-inducible Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase (TiPARP). JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 288:21514-21525(2013).


