SDC1
-
Official Full Name
syndecan 1 -
Overview
CD138/Syndecan-1 is a transmembrane heparin sulphate proteoglycan which is made up of one core protein and five glycosaminoglycan. CD138 is expected to play a role in cell adhesion. It is expressed on the surface of pre-B cells and plasma cells but is absent from mature B cells. It is lost from the apoptotic myeloma cells. -
Synonyms
SDC1;syndecan 1;syndecan-1;synstatin;Sstn;Synd;CD138;Synd1;syn-1;AA408134;AA409076
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Cattle
- Mus musculus
- Mesocricetus auratus
- Cricetulus griseus
- Oryctolagus cuniculus
- Cynomolgus
- Rabbit
- Golden hamster
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- C-His
- Yeast
- His
- Fc
- T7
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Flag
- SUMO
- Strep II
Background
What is SDC1 protein?
SDC1 gene (syndecan 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2p24. The protein encoded by this gene is a transmembrane (type I) heparan sulfate proteoglycan and is a member of the syndecan proteoglycan family. The syndecans mediate cell binding, cell signaling, and cytoskeletal organization and syndecan receptors are required for internalization of the HIV-1 tat protein. The syndecan-1 protein functions as an integral membrane protein and participates in cell proliferation, cell migration and cell-matrix interactions via its receptor for extracellular matrix proteins. The SDC1 protein is consisted of 310 amino acids and SDC1 molecular weight is approximately 32.5 kDa.
What is the function of SDC1 protein?
SDC1 protein is a kind of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan, which is a component of extracellular matrix and cell membrane. SDC1 interacts with a variety of growth factors, cytokines and extracellular matrix proteins through its heparan sulfate side chain, and is involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, migration, adhesion, apoptosis and angiogenesis. SDC1 is also involved in regulating immune cell function in the tumor microenvironment, including homeostasis of tumor infiltrating regulatory T cells (TREGs). In addition, SDC1 is associated with neoplastic and non-neoplastic diseases.
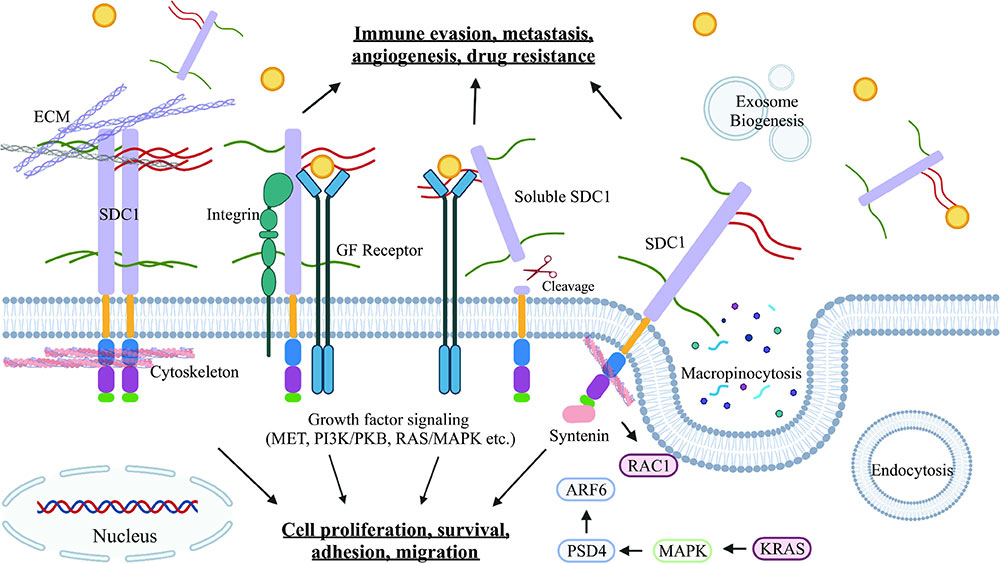
Fig1. Schematic of syndecan-1 (SDC1) interaction and function. (Zecheng Yang, 2022)
SDC1 related signaling pathway
Sdc1-related signaling pathway is a key signal transduction pathway involved in many biological processes. SDC1 is a transmembrane protein belonging to the heparan sulfate proteoglycan family that interacts with extracellular matrix and growth factors through its heparan sulfate chain. SDC1 plays an important role in the process of cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, differentiation and survival, and is involved in the regulation of various signaling pathways, such as Wnt, TGF-β, FGF and VEGF. Abnormal SDC1 expression and function may lead to pathological processes such as tumorigenesis, inflammatory response, and tissue repair.
SDC1 related diseases
Sdc1-associated diseases involve multiple disease processes, including tumors, inflammation, and tissue repair. In terms of tumor, abnormal expression and function of SDC1 are closely related to the occurrence and development of various cancers. For example, SDC1 expression levels are significantly elevated in tumors such as breast, colorectal, prostate, and ovarian cancers and are associated with the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of tumor cells. SDC1 plays an important role in a variety of inflammatory diseases, such as asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. The expression level of SDC1 is significantly increased during skin wound healing, which is related to neovascularization and cell migration.
Bioapplications of SDC1
rhSDC1 has a wide prospect in biological applications. As an important biomolecule, rhSDC1 can be used to regulate the processes of cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, differentiation and survival, and participate in the activation and inhibition of various signaling pathways. Therefore, rhSDC1 is expected to be used in the fields of tumor therapy, tissue engineering, wound healing and inflammation regulation. For example, using the antitumor activity of rhSDC1, novel cancer treatments can be developed; By promoting cell adhesion and migration, it can be used in tissue engineering and wound healing. Its ability to regulate inflammatory response can be used in the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Ghadah A Karasneh, 2021
Heparan sulfate (HS) and its proteoglycans (HSPGs) play a key role in viral entry for many viruses. Herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) increases the levels of heparanase (HPSE), an enzyme that cleaves HS, which helps the virus exit cells. In this study, more HPSE reduces the formation of viral plaques but aids in virus release. It does not impact how the virus enters cells or spreads from cell to cell. Certain agents and recombinant heparinases can boost HSV-1 release from cells.
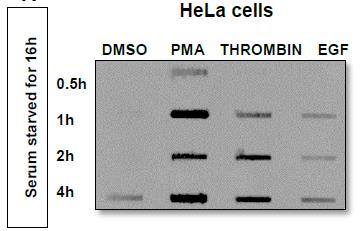
Fig1. Shed syndecan-1 was evaluated by slot blot analysis.

Fig2. Syndecan-1 expression in HeLa cells was measured using flow cytometry.
Case Study 2: Chieh Yu, 2020
Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) can develop into adipocytes or osteoblasts, and imbalances in this process can lead to bone loss. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs), including syndecans (SDCs) and glypicans (GPCs), influence hMSC differentiation, with SDC-1 being a key player in both adipogenesis and osteogenesis. Researchers investigated the role of SDC-1 in hMSCs by knocking it down (KD) using RNA interference. Knocking down SDC-1 in undifferentiated hMSCs led to a pro-adipogenic phenotype and improved osteoblast maturation. In contrast, SDC-1 KD after differentiation promoted adipogenesis and hindered osteogenesis.
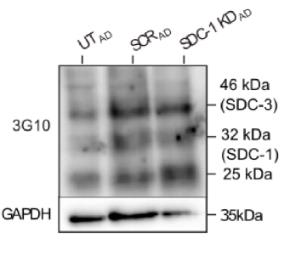
Fig3. Western blot analysis of HS 3G10 epitope in SDC-1 KDAD samples.

Fig4. hMSC SDC-1 KDAD cultures stained with Oil Red O.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SDC1-2033H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SDC1-327H)
Involved Pathway
SDC1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SDC1 participated on our site, such as ECM-receptor interaction,Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs),Malaria, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SDC1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Proteoglycans in cancer | ACTB,ITGAV,PDPK1,KRAS,LUM,HPSE2,PPP1CC,CAV1,ITGB5,TGFB1 |
| ECM-receptor interaction | TNW,COL1A1B,SV2B,GP5,VTNA,THBS1,COL11A2,ITGB3B,COL1A1,FN1A |
| Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | H2-AA,CLDN4,BLB2,ITGAM,ITGB1B.2,NCAM2,CD8B1,HLA-C,MHC1UXA2,CLDNC |
| Malaria | TGFB2,ITGB2L,THBS4,SELE,THBS3,KLRK1,TLR9,IL-8,HBA1,IL18 |
Protein Function
SDC1 has several biochemical functions, for example, glycoprotein binding,protein C-terminus binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SDC1 itself. We selected most functions SDC1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SDC1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein C-terminus binding | PFKM,SIRT1,VGLL3,PRKAA1,VPS4B,TRP53,VPS4A,VIM,CITED1,TOP2A |
| glycoprotein binding | PTBP3,FBXO27,HSPA5,Itgam&Itgb2,FYN,FLNA,TFRC,IDE,B2M,CDH1 |
| protein binding | ZNF593,PKN3,LDHD,SSTR3,PLDN,MED15,MC3R,KDM6B,C7orf50,UBL4A |
Interacting Protein
SDC1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SDC1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SDC1.
PECAM1;q7ci82_yerpe;MNDA;PYHIN1;PDCD6IP
Resources
Research Area
Wnt Signaling ModulatorsSynaptic Proteins
Mesenchymal Cells and EMT
Proteoglycans
Myeloma Cancer Stem Cell Markers
CAR-T Cell Therapy Targets
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Gonzales, JC; Gordts, PLSM; et al. Apolipoproteins E and AV mediate lipoprotein clearance by hepatic proteoglycans. JOURNAL OF CLINICAL INVESTIGATION 123:2742-2751(2013).
- Wang, HY; Jin, HN; et al. Cytoplasmic Domain Interactions of Syndecan-1 and Syndecan-4 with alpha 6 beta 4 Integrin Mediate Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (HER1 and HER2)-dependent Motility and Survival. JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 289:30318-30332(2014).


