ROBO1
-
Official Full Name
roundabout, axon guidance receptor, homolog 1 (Drosophila) -
Overview
Bilateral symmetric nervous systems have special midline structures that establish a partition between the two mirror image halves. Some axons project toward and across the midline in response to long-range chemoattractants emanating from the midline. The product of this gene is a member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily and encodes an integral membrane protein that functions in axon guidance and neuronal precursor cell migration. This receptor is activated by SLIT-family proteins, resulting in a repulsive effect on glioma cell guidance in the developing brain. A related gene is located at an adjacent region on chromosome 3. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009] -
Synonyms
ROBO1;roundabout, axon guidance receptor, homolog 1 (Drosophila);SAX3;DUTT1;roundabout homolog 1;deleted in U twenty twenty
Recombinant Proteins
- Rat
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Yeast
- Fc
- His
- Non
- Avi
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is ROBO1 protein?
ROBO1 gene (roundabout guidance receptor 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3p12. Bilateral symmetric nervous systems have special midline structures that establish a partition between the two mirror image halves. Some axons project toward and across the midline in response to long-range chemoattractants emanating from the midline. The product of this gene is a member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily and encodes an integral membrane protein that functions in axon guidance and neuronal precursor cell migration. This receptor is activated by SLIT-family proteins, resulting in a repulsive effect on glioma cell guidance in the developing brain. The ROBO1 protein is consisted of 1651 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 180.9 kDa.
What is the function of ROBO1 protein?
ROBO1 acts as a receptor for SLIT family proteins, such as SLIT1 and SLIT2, mediating cell response to molecular guidance cues, playing a role in cell migration, including axon navigation in the ventral midline of the neural tube and the projection of axons to different regions during neurodevelopment. ROBO1 interacts with the intracellular domain of FLRT3, promoting axon attraction to NTN1-expressing cells. ROBO1 plays a role in cell migration through its interaction with MYO9B, inhibiting the activity of RHOA GTPase mediated by MYO9B, resulting in increased levels of active GTP-binding RHOA. ROBO1 may play an important role in lung development.
ROBO1 Related Signaling Pathway
Slit-robo signaling pathway is a signaling system composed of secreted glycoprotein Slit and its receptor Roundabout (Robo), originally discovered as a neuronal axon-directing factor. Slit-Robo signaling pathway regulates axonal rejection and is involved in angiogenesis, tumor angiogenesis, inflammation, leukocyte chemotaxis, and vascular leakage during neurodevelopment. ROBO1 plays a key role in nervous system development, especially in axon guidance and neuronal precursor cell migration. ROBO1 performs its biological functions through a variety of different downstream signal transduction pathways, including signaling pathways associated with cytoskeleton and cell movement.
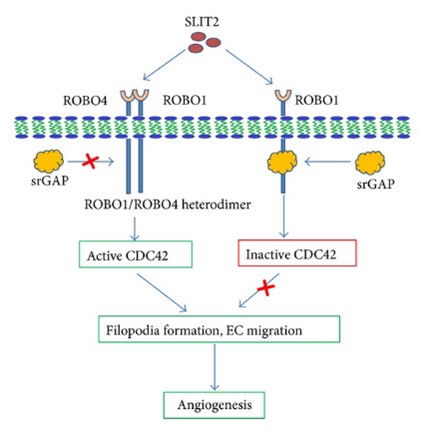
Fig1. SLIT2 mediated proangiogenic or antiangiogenic activity is dependent on recruitment of srGAP. (Suresh Singh Yadav, 2014)
ROBO1 Related Diseases
ROBO1 gene mutation has been associated with a variety of diseases, including pituitary stalk blocking syndrome (PSIS), a rare congenital polypituitary hormone deficiency disorder characterized by ocular defects, hypoglycemia, and growth retardation. Neurodevelopmental disorders, such as cerebellar atrophy, developmental delay, and epilepsy; Glioma, which may involve the migration and invasion of tumor cells; Schizophrenia, affecting neuropsychiatric function; And tumor-related diseases, including osteofibrosarcoma, osteosarcoma, and myelodysplastic syndrome. ROBO1 has also been linked to familial hypercholesterolemia, macular degeneration, lung, colon and breast cancer, demonstrating its wide-ranging role in human health and disease.
Bioapplications of ROBO1
As a key receptor for axon guidance, ROBO1 plays a central role in neural development and axon pathway selection, and is an important molecule in the study of neurodevelopmental mechanisms. The abnormal expression of ROBO1 in certain tumors, particularly in glioma and lung cancer, makes it a potential target for the study of tumorigenesis, progression, and metastasis. Because of ROBO1's role in a variety of diseases, drug development targeting ROBO1 may help treat related diseases, especially in the field of oncology therapy. The development of related ROBO1 antibody will help promote relevant clinical studies. The change of ROBO1 expression level may be used as a biomarker for some diseases, which is helpful for early diagnosis and treatment monitoring of diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Xiaoxiao Liu, 2024
Recently shown to regulate cardiac development, the secreted axon guidance molecule SLIT3 maintains its expression in the postnatal heart. Despite its known expression in the cardiovascular system after birth, SLIT3's relevance to cardiovascular function in the postnatal state remains unknown. As such, the objectives of this study were to determine the postnatal myocardial sources of SLIT3 and to evaluate its functional role in regulating the cardiac response to pressure overload stress. Researchers performed in vitro studies on cardiomyocytes and myocardial tissue samples from patients and performed in vivo investigation with SLIT3 and ROBO1 (roundabout homolog 1) mutant mice undergoing transverse aortic constriction to establish the role of SLIT3-ROBO1 in adverse cardiac remodeling. They determined that ROBO1 was the most highly expressed roundabout receptor in cardiomyocytes and that ROBO1 mediated SLIT3's hypertrophic effects in vitro. Furthermore, α-MHC+ cardiomyocyte-specific deletion of ROBO1 also preserved left ventricular function and abrogated hypertrophy, but not fibrosis, after transverse aortic constriction.
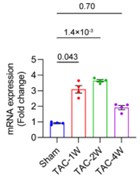
Fig1. Transcript levels of Robo1 in mice heart tissue subjected to sham or transverse aortic constriction (TAC) surgery.
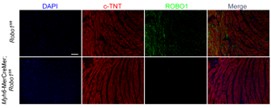
Fig2. Immunofluorescence staining using anti-ROBO1 antibody (green).
Case Study 2: Lihua Wang, 2022
Exosomal miR-29b reportedly plays a role during cancer metastasis. However, its exact function and underlying mechanism during pancreatic cancer (PC) have not been investigated. Exosomes from PC cells were prepared and identified. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and confocal microscopy were used to examine structural characteristics of the exosomes and verify their internalization by human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). GW4869 was used to suppress exosome release. Luciferase reporter assays were performed to verify the predicted interaction of miR-29b with ROBO1 and SRGAP2 mRNA. The downregulation of ROBO1 and SRGAP2 in cocultured HUVECs was also reduced after additional treatment with GW4869. Luciferase reporter assays verified the interaction of miR-29b with ROBO1 and SRGAP2. That interaction was also supported by rescue assays showing that overexpression of ROBO1 and SRGAP2 also reduced the antiangiogenic effect of exosomal miR-29b in HUVECs.
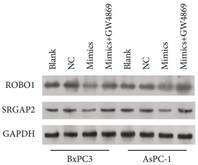
Fig3. Western blot study to determine the expression of ROBO1 and SRGAP2 proteins.
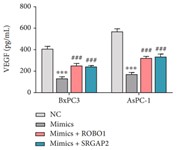
Fig4. ELISA detection of VEGF levels in HUVECs.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ROBO1-4672H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ROBO1-2415M)
Involved Pathway
ROBO1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ROBO1 participated on our site, such as Axon guidance, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ROBO1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Axon guidance | NEFLB,PEA15A,CAP2,MET,NRP1A,SEMA7A,CSF2,RGS3,EPHA1,RASA1 |
Protein Function
ROBO1 has several biochemical functions, for example, LRR domain binding,axon guidance receptor activity,identical protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ROBO1 itself. We selected most functions ROBO1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ROBO1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| LRR domain binding | LRRFIP2,STK11,POLR2J,KRAS,ZXDC |
| protein binding | SPSB4,PFDN5,GNB1B,TTC23L,OOEP,RND3,STX10,KRTAP10-9,NOTCH3,UROD |
| identical protein binding | MLL1,EIF2AK3,C1QL4,IGF1R,RASSF3,PRNP,FAM108A1,THG1L,SORD,SMURF2 |
| axon guidance receptor activity | EPHB1,SEMA5A,GFRA3,EPHB3,EPHA7,ROBO2 |
Interacting Protein
ROBO1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ROBO1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ROBO1.
ROBO4;ROBO2;TUBB4A;BRK1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Nakayama, T; Mizohata, E; et al. Structural features of interfacial tyrosine residue in ROBO1 fibronectin domain-antibody complex: Crystallographic, thermodynamic, and molecular dynamic analyses. PROTEIN SCIENCE 24:328-340(2015).
- Qi, CL; Lan, HM; et al. Slit2 promotes tumor growth and invasion in chemically induced skin carcinogenesis. LABORATORY INVESTIGATION 94:766-776(2014).


