RIPK2
-
Official Full Name
receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 2 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the receptor-interacting protein (RIP) family of serine/threonine protein kinases. The encoded protein contains a C-terminal caspase activation and recruitment domain (CARD), and is a component of signaling complexes in both the innate and adaptive immune pathways. It is a potent activator of NF-kappaB and inducer of apoptosis in response to various stimuli. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
RIPK2;receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 2;CCK;RICK;RIP2;CARD3;GIG30;CARDIAK;receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 2;RIP-2;CARD-carrying kinase;growth-inhibiting gene 30;tyrosine-protein kinase RIPK2;receptor-interacting protein 2;CARD-containing IL-1 beta ICE-kinase;CARD-containing interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme (ICE)-associated kinase;receptor-interacting protein (RIP)-like interacting caspase-like apoptosis regulatory protein (CLARP) kinase
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- T7
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIPK2-932H | Recombinant Human RIPK2 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Gln432~Met540 | |
| RIPK2-3761H | Recombinant Human RIPK2 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 221-524 aa | |
| RIPK2-1479H |
Active Recombinant Human RIPK2, GST-tagged
|
Sf9 Cells | Human | GST | 1-299 aa |
|
| RIPK2-419H |
Active Recombinant Human RIPK2, His-tagged
|
Insect Cells | Human | His | amino acids 1-299 |
|
| RIPK2-14244M | Recombinant Mouse RIPK2 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| Ripk2-1795M | Recombinant Mouse Ripk2 protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His&T7 | Met1~Leu294 |
|
| Ripk2-1796R | Recombinant Rat Ripk2 protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | Rat | His&T7 | Met1~Leu294 |
|
| RIPK2-2632C | Recombinant Chicken RIPK2 | Mammalian Cells | Chicken | His |
|
|
| RIPK2-29983TH | Recombinant Human RIPK2 | Human | Non | 1-299 a.a. |
|
|
| RIPK2-418H | Recombinant Human RIPK2, GST-tagged, Active | Sf9 Cells | Human | GST | 1-299 a.a. |
|
| RIPK2-532H | Recombinant Full Length Human RIPK2, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Human | DDK&Myc | Full L. |
|
| RIPK2-711H | Recombinant Human RIPK2, GST-His | Sf9 Cells | Human | GST | 1-299 a.a. |
|
| RIPK2-9761Z | Recombinant Zebrafish RIPK2 | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| RIPK2-2333HCL | Recombinant Human RIPK2 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| RIPK2-5269HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human RIPK2, Flag-tagged | Mammalian Cells | Human | Flag | Full L. |
|
| Ripk2-5522M | Recombinant Mouse Ripk2 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | DDK&Myc |
|
|
| RIPK2-5564H | Recombinant Full Length Human RIPK2 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Full L. 1-540 aa |
|
| RIPK2-5565H | Recombinant Human RIPK2, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST | 1-540 a.a. |
|
| RIPK2-645H | Recombinant Human RIPK2 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 1-540aa |
|
| RIPK2-6505H | Recombinant Human RIPK2 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | HEK293 | Human | DDK&Myc |
|
|
| RIPK2-6660H | Recombinant Human RIPK2 Protein (Gln432-Met540), N-GST tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | Gln432-Met540 |
|
| RIPK2-6795HF | Recombinant Full Length Human RIPK2 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 540 amino acids |
|
| RIPK2-755H | Recombinant Human RIPK2 protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 1-540aa |
|
| RIPK2-7616M | Recombinant Mouse RIPK2 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| RIPK2-7616M-B | Recombinant Mouse RIPK2 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is RIPK2 protein?
RIPK2 (receptor interacting serine/threonine kinase 2) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 8 at locus 8q21. This gene encodes a member of the receptor-interacting protein (RIP) family of serine/threonine protein kinases. The encoded protein contains a C-terminal caspase activation and recruitment domain (CARD), and is a component of signaling complexes in both the innate and adaptive immune pathways. It is a potent activator of NF-kappaB and inducer of apoptosis in response to various stimuli. The RIPK2 protein is consisted of 540 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 61.2 kDa.
What is the function of RIPK2 protein?
RIPK2 plays a role in a variety of cellular processes, including immune response, cell proliferation, and cell death. It consists of several key domains, including a kinase domain (KD), an intermediate domain (INTD), and a hemipascaspase activation and recruitment domain (CARD). The activation of RIPK2 can occur in a variety of ways, including autophosphorylation and ubiquitination, which leads to the activation of downstream signaling pathways, such as the NF-κB and MAPK pathways, which trigger the production and release of inflammatory cytokines.
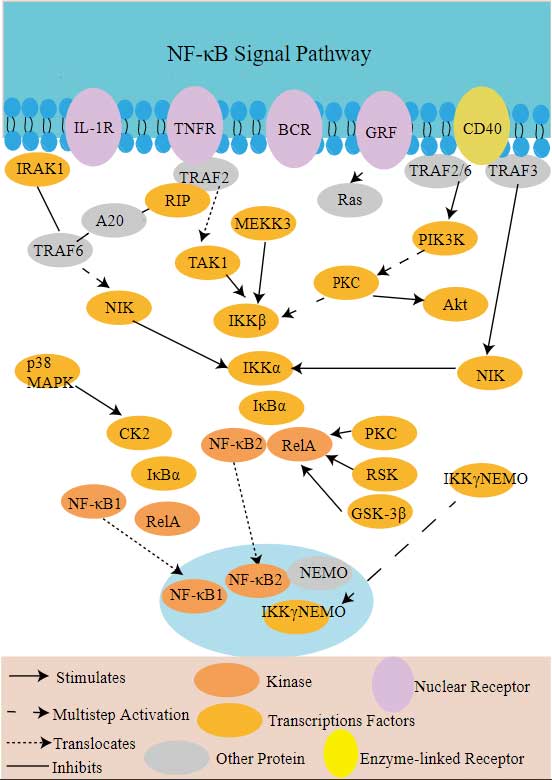
RIPK2 Related Signaling Pathway
RIPK2 has a role in both classical and non-classical NF-κB activation pathways and is involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses and anti-apoptotic processes. As a member of the NOD-like receptor family, RIPK2 is able to bind to NLRP1 and activate downstream inflammatory responses, thereby promoting caspase-1 activation and the maturation and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β. Studies have shown that RIPK2 plays a role in regulating TNF-induced apoptosis and programmed necrosis, and may interact with other proteins such as RIPK1 and MLKL. As part of innate immunity, RIPK2 is also involved in recognizing pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and DAMPs (damage associated molecular patterns), which in turn activate downstream signaling cascades.
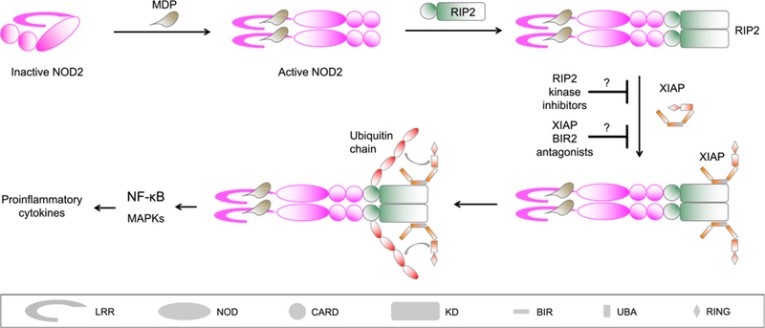
Fig1. Mechanism of NOD2 Signaling Blockade by RIP2 Kinase Inhibitors and XIAP BIR2 Antagonists. (Shiyu Xia, 2018)
RIPK2 Related Diseases
Abnormal RIPK2 function has been linked to a variety of diseases, including: autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), in which RIPK2 may play a key role in regulating inflammation and joint damage. Inflammatory bowel diseases include Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Due to its role in the immune system, RIPK2 is also important in responding to bacterial, viral, and other pathogen infections. Certain types of tumors are associated with alterations in the expression or function of RIPK2, which may affect cell survival and proliferation. There are also cardiovascular diseases, metabolic diseases and so on.
Bioapplications of RIPK2
Small molecule inhibitors targeting RIPK2 and PROTACs (protein degradation targeting chimeras) have shown potential in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. These molecules are able to inhibit the activity of RIPK2 or promote its degradation, thereby reducing the inflammatory response and improving disease symptoms.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Xiao-Liang Wang, 2022
This study aimed to investigate the role of receptor-interacting protein 2 (RIP2) in regulation of stemness of glioma cells and chemotherapy resistance. Plasmid transfection was used to overexpress RIP2. Chemical inhibitors were used to inhibit RIP2 or NF-κB activity. Cancer stemness of glioma cells was investigated by sphere formation assays, clone formation assays, and xenograft tumor formation assays. The expression of RIP2, p-NF-κB, IκBα, CD133, or SOX-2 was detected by Western blotting and immunofluorescence. Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry. Immunohistochemical staining was used to detect the expression of RIP2, CD133, and SOX-2 in xenograft tumor tissue. Transfection with RIP2 plasmid enhanced the sphere formation capability of U251 cells, clone formation capability, and xenograft tumor formation capability. RIP2 could mediate TMZ resistance by upregulating the expression of CD133 and SOX-2 by activating the NF-κB pathway. Both RIP2 inhibitor GSK583 and the NF-κB inhibitor SC75741 could reverse the resistance of U251 cells to TMZ.
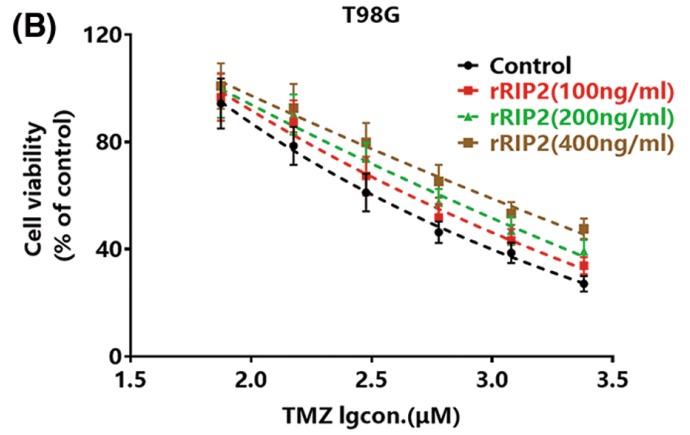
Fig1. Different glioma cells were treated with gradient concentrations of rRIP2 for 24 h and then TMZ was added for 72 h, and cell viability was detected by CCK-8 assay.
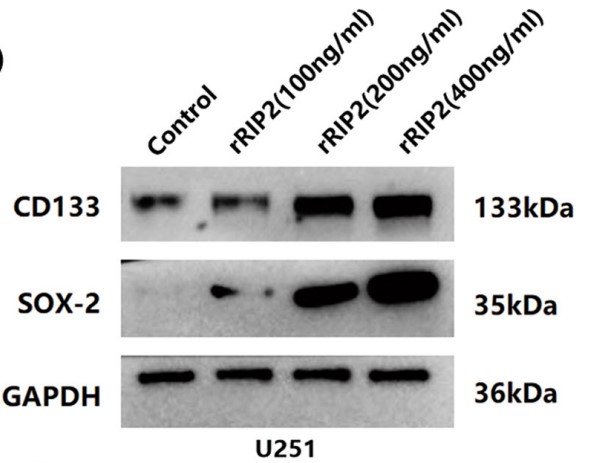
Fig2. U251 cells were treated with 100, 200, and 400 ng/mL rRIP2 for 24 h, and the expressions of CD133 and SOX-2 were detected by Western blotting.
Case Study 2: Yiwu Yan, 2022
Despite progress in prostate cancer (PC) therapeutics, distant metastasis remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality from PC. Thus, there is growing recognition that preventing or delaying PC metastasis holds great potential for substantially improving patient outcomes. This study shows receptor-interacting protein kinase 2 (RIPK2) is a clinically actionable target for inhibiting PC metastasis. RIPK2 is amplified/gained in ~65% of lethal metastatic castration-resistant PC. Its overexpression is associated with disease progression and poor prognosis, and its genetic knockout substantially reduces PC metastasis. Multi-level proteomics analyses reveal that RIPK2 strongly regulates the stability and activity of c-Myc (a driver of metastasis), largely via binding to and activating mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7 (MKK7), which we identify as a direct c-Myc-S62 kinase. RIPK2 inhibition by preclinical and clinical drugs inactivates the noncanonical RIPK2/MKK7/c-Myc pathway and effectively impairs PC metastatic outgrowth.
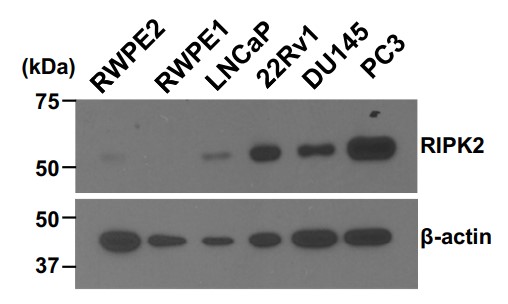
Fig3. Comparison of RIPK2 protein levels in six commonly used prostate cell line models.
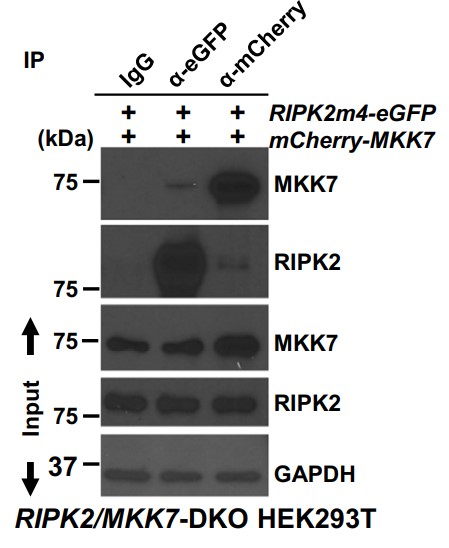
Fig4. Representative images of Co-IP analysis detecting the association of RIPK2 and MKK7 ectopically expressed in RIPK2/MKK7-DKO HEK293T cells.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
RIPK2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RIPK2 participated on our site, such as NOD-like receptor signaling pathway,Neurotrophin signaling pathway,Shigellosis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RIPK2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Tuberculosis | H2-AA,CD209C,IL10RA,FCGR2C,RAB5B,ITGB2,IL12B,CD14,NFKB1,IRAK4 |
| Shigellosis | WASL,MAPK12,FBXW11,PFN4,BTRC,ATG5,ITGA5,UBE2D2,ACTB,DIAPH1 |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | RAF1,RPS6KA5,NFKBIB,MAP3K5,TP53,PLCG1,RELA,RAPGEF1,AKT2,RPS6KA3 |
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | MAPK1,NFKBIA,SUGT1,TNF,MAPK12,MAP3K7IP3,CARD8,IL6,NLRC4,NFKBIAA |
Protein Function
RIPK2 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,CARD domain binding,LIM domain binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RIPK2 itself. We selected most functions RIPK2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RIPK2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| CARD domain binding | CARD9,CARD11,C9orf89,MAVS,CARD14,NOD1 |
| receptor binding | IDH1,PLAUR,CADM3,TNFSF9,STOML2,FGF11,LAMA4,PIPOX,APP,HSD17B4 |
| protein homodimerization activity | EEA1,EXT1,SYT10,NRBP1,GAMT,NTRK2,TSC2,C1QB,ADD1,PVRL1 |
| ATP binding | ACTR1B,PAK1,KIF2C,DYNC2H1,XRCC3,ABCA3,CAMK2B,EGFRA,PRKCDA,MAP3K13 |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | WEE2,PTK2,Fert2,FYNB,STK16,FGR,PTK2AA,STYK1,TNK2B,TEC |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | ZNF143B,PAK6,NIM1,MKNK1,TNNI3K,LIMK1,TTBK2,SNRK,CDK11A,STK17A |
| signal transducer activity | TNK1,PTGER1C,NDFIP2,HCAR1-1,PPM1A,TAS2R200.2,OLFR1013,OLFCW1,GNAI2,GPR186 |
| protein binding | ZBTB7A,ATP5B,RPLP1,RUSC2,UQCRH,MYCN,TFCP2,KHDRBS3,MBL2,C5orf13 |
| LIM domain binding | CSRP2BP,ACTN2,LDB2A,LDB2,LDB1,RPH3AL,TLN1,LDB2B,LDB1B,LDB1A |
Interacting Protein
RIPK2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RIPK2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RIPK2.
XIAP;NOD2;TRAF3;BIRC3;BIRC2;TRAF2
RIPK2 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References

.jpg)
.jpg)