PREP
-
Official Full Name
Prolyl endopeptidase -
Overview
Proline specific endopeptidase, isolated from Flavobacterium sp., cleaves specifically the peptide bonds on the carboxy side of proline residues1,2. This enzyme is very close, in its properties, to a post-proline cleaving enzyme3-5. The substrates have been found to have the general structure Y-Pro-X, where Y is a peptide or N-protected amino acid and X may be an amino acid, peptide, amide or ester. Much slower hydrolysis is observed when the substrate is Y-Ala-X5. -
Synonyms
Prolyl endopeptidase;Post-proline cleaving enzyme;Post-proline endopeptidase
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Mouse
- Sf21 Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- HEK293
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is PREP protein?
PREP (prolyl endopeptidase) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 6 at locus 6q21. The protein encoded by this gene is a cytosolic prolyl endopeptidase that cleaves peptide bonds on the C-terminal side of prolyl residues within peptides that are up to approximately 30 amino acids long. Prolyl endopeptidases have been reported to be involved in the maturation and degradation of peptide hormones and neuropeptides. The PREP protein is consisted of 710 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 80.7 kDa.
What is the function of PREP protein?
PREP protein, which stands for Prolyl Endopeptidase, is an enzyme that belongs to the serine protease family. It is known for its ability to specifically hydrolyze peptide bonds at the carboxyl-terminal side of proline residues within polypeptide chains. PREP is involved in various physiological and pathological processes, including:
Peptide Maturation and Degradation: It plays a role in the maturation and degradation of peptides.
Inflammation: PREP has been implicated in inflammatory responses, with its activity potentially contributing to the progression of diseases characterized by chronic inflammation.
Oxidative Stress: It is suggested to participate in oxidative stress pathways, possibly affecting the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Autophagy: PREP is also involved in autophagy, a cellular process for the degradation and recycling of cellular components.
Mitochondrial Proteostasis: PREP is also important for mitochondrial function, as it degrades presequence peptides cleaved off from nuclear-encoded proteins, thus maintaining mitochondrial proteostasis.
PREP Related Signaling Pathway
PREP is involved in the modulation of inflammatory responses, potentially influencing the production of cytokines such as interleukin (IL), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and interferon (IFN). PREP's activity has been linked to cell proliferation, and it may contribute to the development and progression of cancer by modulating the activity of proteins involved in these processes. In the brain, PREP is involved in the regulation of neurotransmission, and its altered activity has been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. PREP is important for mitochondrial function, as it degrades presequence peptides cleaved off from nuclear-encoded proteins, thus playing a role in maintaining mitochondrial proteostasis.
PREP Related Diseases
The diseases associated with PREP (Prolyl Endopeptidase) mainly involve neurodegenerative diseases, tumors, and diseases that may be related to inflammation and immune responses. For example, in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, PREP may be involved in regulating disease-related signaling pathways. In the field of oncology, the activity of PREP may be related to the proliferation and survival of tumor cells, affecting tumor development and treatment response. In addition, PREP may also be associated with inflammatory diseases due to its role in immune cells such as macrophages.
Bioapplications of PREP
PREP plays a role in physiological and pathological processes, including the maturation and degradation of peptides, inflammation, oxidative stress, autophagy, cell proliferation, and cancer. Prolyl endopeptidase inhibitors are being investigated for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases due to their neuroprotective, anti-forgetting and cognitive-enhancing properties, as well as their potential therapeutic effects on tumors and hypertension. In addition, inhibitors of PREP contribute to the study of biochemical, cellular, physiological, and pathological mechanisms of PREPL (prolyl endopeptidase-like), especially when exploring therapeutic strategies for hypotonic-cystinuria syndrome (HCS). PREP gene knockout studies have shown an association with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The dual function of PREP, including its proteolytic and non-proteolytic activity, has also been demonstrated in studies of macrophage function.
Case Study
Case Study 1: T Eteläinen, 2021
PREP inhibition has been shown to reduce production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the absence of PREP blocks stress-induced ROS production. However, the mechanism behind PREP-related ROS regulation is not known. As recently discovered PREP's physiological role as a protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) regulator, researchers wanted to characterize PREP inhibition as an approach to reduce OS. They studied the impact of a PREP inhibitor, KYP-2047, on hydrogen peroxide and ferrous chloride induced ROS production and on cellular antioxidant response in HEK-293 and SH-SY5Y cells. In addition, researchers used HEK-293 and SH-SY5Y PREP knock-out cells to validate the role of PREP on stress-induced ROS production. The results showed that absence of PREP almost entirely blocks the stress-induced ROS production in both cell lines. Reduced ROS production and smaller antioxidant response was also seen in both cell lines after PREP inhibition by 10 μM KYP-2047.
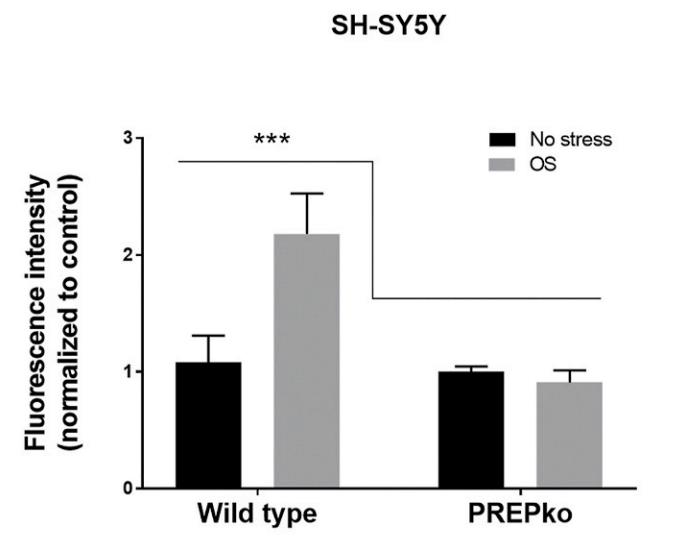
Fig1. Lack of PREP and PREP inhibition reduce ROS production under oxidative stress.
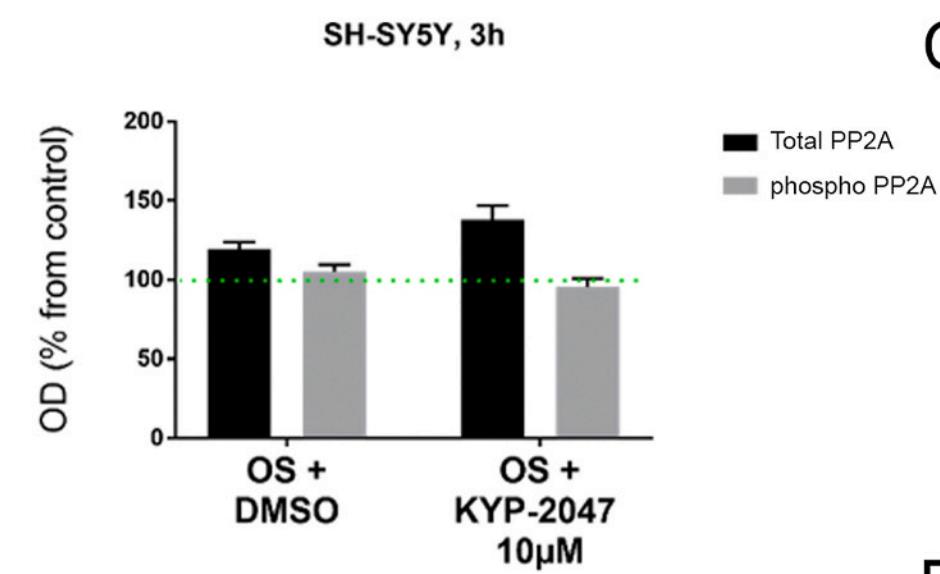
Fig2. PREP inhibition reduces OS induced p47phox phosphorylation.
Case Study 2: Jue Chen, 2014
The mitochondrial presequence protease (PreP) is a member of the pitrilysin class of metalloproteases. It degrades the mitochondrial targeting presequences of mitochondria-localized proteins as well as unstructured peptides such as amyloid-β peptide. The specific activity of PreP is reduced in Alzheimer patients and animal models of Alzheimer disease. The loss of activity can be mimicked in vitro by exposure to oxidizing conditions, and indirect evidence suggested that inactivation was due to methionine oxidation. Researchers performed peptide mapping analyses to elucidate the mechanism of inactivation. None of the 24 methionine residues in recombinant human PreP was oxidized. They present evidence that inactivation is due to oxidation of cysteine residues and consequent oligomerization through intermolecular disulfide bonds. The most susceptible cysteine residues to oxidation are Cys34, Cys112, and Cys119. Most, but not all, of the activity loss is restored by the reducing agent dithiothreitol.
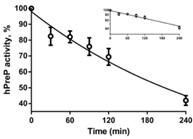
Fig3. Kinetics of inactivation of hPreP by 500 μM hydrogen peroxide at pH 8.2.
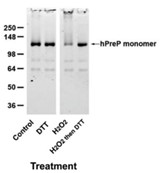
Fig4. Non-reducing SDS-PAGE gel of hPreP subjected to varying treatments.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PREP-3430H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PREP-542H)
Involved Pathway
PREP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PREP participated on our site, such as Renin-angiotensin system, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PREP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Renin-angiotensin system | ACE,KLK1B22,CTSA,MRGPRD,KLK2,KLK1B9,KLK1B3,ATP6AP2,CMA1,THOP1 |
Protein Function
PREP has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,serine-type endopeptidase activity,serine-type exopeptidase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PREP itself. We selected most functions PREP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PREP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| serine-type peptidase activity | FURINA,HTRA1B,Gzmg,KLK11,ELA2,FAP,PLAUB,KLK5,HTRA1,KLK15 |
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | PRSS40,TMPRSS5,CFD,KLK9,PCSK7,HGF,CELA2A,PRSS54,GZMC,TMPRSS11F |
| protein binding | COL1A2,ASAP3,KRTAP2-3,GDF7,FAM13C,SOX17,ORAI1,HSPBP1,SKA3,HFE |
| serine-type exopeptidase activity | HPN,PREPL |
Interacting Protein
PREP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PREP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PREP.
GAPDH;HLA-B;PRKAB1;TRAF6;SUCO
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Sun, ZW; Wang, Q; et al. Intranasal Administration of Maleic Anhydride-Modified Human Serum Albumin for Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. VIRUSES-BASEL 7:798-819(2015).
- Roush, DJ; Myrold, A; et al. Limits in Virus Filtration Capability? Impact of Virus Quality and Spike Level on Virus Removal with Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus. BIOTECHNOLOGY PROGRESS 31:135-144(2015).


