POTEB
-
Official Full Name
POTE ankyrin domain family, member B -
Synonyms
POTEB;POTE ankyrin domain family, member B;A26B1, ANKRD26 like family B, member 1;POTE ankyrin domain family member B;cancer/testis antigen family 104;member 5;CT104.5;POTE 15;POTE15;A26B1;ANKRD26 like family B member 1;cancer/testis antigen family 104, member 5;MGC119371;MGC119373;prostate, ovary, testis expressed protein on chromosome 15;protein expressed in prostate, ovary, testis, and placenta 15;ANKRD26-like family B member 1;ANKRD26-like family B, member 1;prostate, ovary, testis-expressed protein on chromosome 15;POTE-15
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POTEB-1864H | Recombinant Human POTEB, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 1-381aa |
Background
What is POTEB Protein?
POTEB (POTE Ankyrin Domain Family Member B) is a human protein encoded by the POTEKP gene, primarily linked to cancer progression and cellular signaling pathways. Structurally characterized by its ankyrin repeat domains, POTEB interacts with key regulatory proteins like Akt and NF-κB, influencing apoptosis, cell proliferation, and tumor metastasis. Recent studies highlight its overexpression in breast, prostate, and ovarian cancers, positioning it as a potential biomarker for early detection and prognosis. Researchers are investigating POTEB’s role in drug resistance mechanisms and its utility in targeted cancer therapies. With advancements in proteomics and precision medicine, POTEB continues to gain traction in oncology research, offering insights into innovative diagnostic tools and personalized treatment strategies. Keywords: POTEB protein function, cancer research biomarkers, targeted cancer therapies, ankyrin repeat domains, precision medicine in oncology.What is the Function of POTEB Protein?
The POTEB protein, a member of the POTE ankyrin domain family, plays critical roles in modulating cellular processes such as apoptosis, proliferation, and signal transduction. Its ankyrin repeat domains enable interactions with kinases like Akt and transcription factors such as NF-κB, regulating pathways linked to tumor growth and metastasis. Studies show POTEB influences drug resistance by altering DNA repair mechanisms and survival signaling in cancers like breast and ovarian malignancies. Emerging research also suggests its involvement in immune evasion, making it a focus for immunotherapy strategies. As a biomarker, POTEB aids in predicting treatment response and disease progression, driving interest in targeted therapies and precision oncology. Keywords: POTEB protein function, apoptosis regulation, cancer drug resistance, NF-κB signaling pathway, precision oncology biomarkers.POTEB Related Signaling Pathway
The POTEB protein is intricately involved in the Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways, which regulate critical cellular functions such as survival, proliferation, and inflammation. By binding to Akt, POTEB enhances phosphorylation cascades that suppress apoptosis and promote tumor cell growth. Simultaneously, its interaction with NF-κB amplifies inflammatory responses and metastasis through upregulated cytokine production. Dysregulation of these pathways is linked to aggressive cancers, including triple-negative breast cancer and advanced prostate tumors. Recent studies explore POTEB’s crosstalk with PI3K/mTOR pathways, revealing its role in therapy resistance. Targeting POTEB-associated signaling nodes, such as kinase inhibitors or anti-inflammatory agents, emerges as a promising strategy for precision oncology. Keywords: POTEB signaling pathway, Akt/NF-κB crosstalk, cancer therapy targets, PI3K/mTOR inhibition, metastatic cancer mechanisms.POTEB Related Diseases
POTEB protein dysregulation is strongly implicated in malignancies such as breast, prostate, and ovarian cancers, where its overexpression correlates with aggressive tumor behavior and poor prognosis. By disrupting Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways, POTEB promotes uncontrolled cell proliferation, metastasis, and resistance to chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Emerging evidence also links POTEB to pancreatic and colorectal cancers, suggesting broader oncogenic roles. Beyond oncology, preliminary studies explore its potential involvement in inflammatory disorders due to its interaction with cytokine networks. As a biomarker, POTEB aids in stratifying high-risk patients and predicting therapeutic responses. Current research prioritizes inhibitors targeting POTEB-associated pathways to combat treatment-resistant cancers. Keywords: POTEB-related diseases, cancer biomarkers, Akt/NF-κB signaling, chemotherapy resistance, inflammatory disorders.Bioapplications of POTEB
The POTEB protein has emerged as a pivotal tool in oncology, with bioapplications spanning cancer diagnostics, therapeutic development, and personalized medicine. Its overexpression in tumors like breast and ovarian cancers enables its use as a non-invasive biomarker for early detection via liquid biopsies. In therapeutics, POTEB’s role in Akt/NF-κB pathways drives research into inhibitors that disrupt tumor survival and metastasis, particularly in drug-resistant cancers. Additionally, POTEB-based assays aid in screening compounds for precision oncology drug discovery. Recent innovations explore its utility in CAR-T cell engineering to enhance immune targeting of solid tumors. As proteomic technologies advance, POTEB continues to bridge translational research and clinical innovation. Keywords: POTEB bioapplications, cancer diagnostics, targeted therapy development, precision medicine innovations, CAR-T cell engineering.Case Study
Case Study 1: Bera TK. et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002
The POTE gene, found on chromosome 21, is expressed in normal and cancerous prostate tissues, as well as in testis, ovary, and placenta. It spans about 32 kb of the chromosome 21q11.2 region and encodes a 66 kDa protein with seven ankyrin repeats. POTE has ten paralogs spread across eight chromosomes, showing recent duplication but rapid divergence. In situ hybridization reveals POTE expression in normal prostate epithelium and some prostate cancers. Its limited expression in normal tissues and presence in prostate cancer make it a potential immunotherapy target. The POTE gene family's rapid divergence and expression pattern suggest a significant role in reproductive processes.-
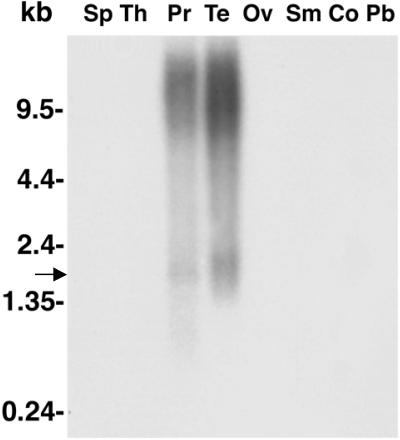 Fig1. Northern blot analysis of POTE transcript in different normal tissues.
Fig1. Northern blot analysis of POTE transcript in different normal tissues. -
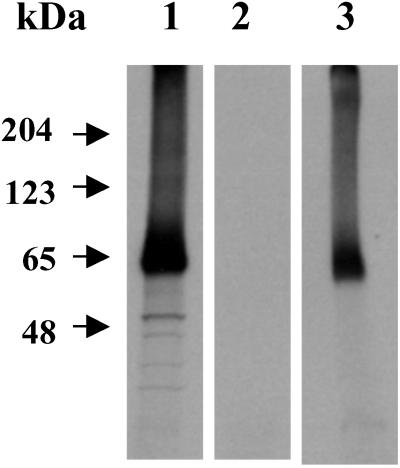 Fig2. Analysis of the protein encoded by POTE mRNA.
Fig2. Analysis of the protein encoded by POTE mRNA.
Case Study 2: Ise T. et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008
The POTE gene family includes 13 paralogs highly expressed in prostate, ovary, testis, and placenta. Researchers developed 10 monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) targeting three POTE paralogs: POTE-21, POTE-2gammaC, and POTE-22. One MAb reacted with all three, six with POTE-2gammaC and POTE-22, and three were specific to POTE-21. All epitopes were in the cysteine-rich repeats (CRRs) at the N-terminus. Differences in cross-reactivity were observed among MAbs. Using MAbs HP8 and PG5, a POTE-actin fusion protein was detected in human testis via immunoprecipitation and Western blotting. Immunohistochemistry showed POTE expression in primary spermatocytes, suggesting a role in spermatogenesis.-
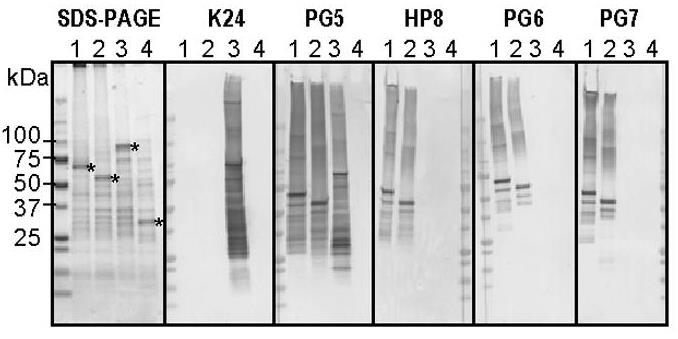 Fig3. Twenty ng of GST-POTE paralogs or GST-PRAC2 fusion proteins were blotted on a PVDF membrane.
Fig3. Twenty ng of GST-POTE paralogs or GST-PRAC2 fusion proteins were blotted on a PVDF membrane. -
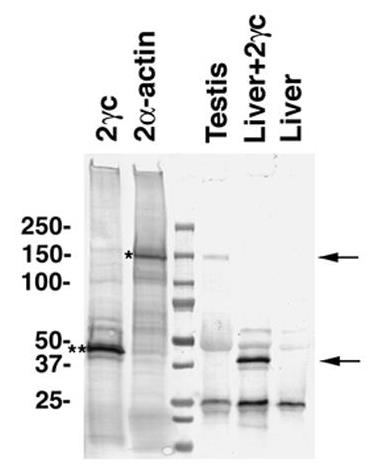 Fig4. Detection of POTE-2α-actin protein by immunoprecipitation.
Fig4. Detection of POTE-2α-actin protein by immunoprecipitation.
Involved Pathway
POTEB involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways POTEB participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with POTEB were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
POTEB has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by POTEB itself. We selected most functions POTEB had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with POTEB. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
POTEB has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with POTEB here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of POTEB.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


