Pla2
-
Official Full Name
phospholipase A2 -
Overview
Bee venom phospholipase A2 (PLA) is the main allergen in the bee sting allergy. Bee venom phospholipase A2 (BV-PLA2) is a hydrolytic enzyme which specifically cleaves the sn-2 acyl bond of phospholipids at the lipid/water interface. BV-PLA2 is a 14–16-kDa glycoprotein, consisting of 134 amino acids and displaying a single carbohydrate side chain at the residue Asn13. It is also held to be responsible for some systemic anaphylactic reactions in bee venom sensitized individuals. BV-PLA2 presents 3 peptide and a glycopeptide T cell epitopes, which are recognized by both allergic and non-allergic bee venom sensitized subjects. -
Synonyms
Pla2;phospholipase A2;GB13351;allergen Api m 1;phosphatidylcholine 2-acylhydrolase;EC 3.1.1.4
Recombinant Proteins
- Honey bee
- Honey Bee Venom
- E.coli
- Non
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pla2-85A |
Active Native Apis mellifera Phospholipase A2
|
Honey Bee Venom | Honey bee | Non |
|
|
| Pla2-343B | Recombinant Bee Phospholipase A2 | E.coli | Honey bee | Non | 26-162 a.a. |
|
| Kit-0696 | cPLA2 Assay Kit | Non |
|
|||
| Kit-0697 | Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Assay Kit | Non |
|
|||
| Kit-0698 | Phospholipases A2 (calcium-dependent cytosolic) Assay Kit | Non |
|
|||
| Kit-0699 | sPLA2 Activity Assay Kit | Non |
|
|||
| Kit-1082 | Phospholipase A2 Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) | Non |
|
|||
| PLA2-006B | Recombinant Bee PLA2 Protein | E.coli | Honey bee |
|
Background
What is PLA2 Protein?
PLA2 gene is a protein coding gene which encodes Phospholipase A2 (PLA2). This is basically a type of enzyme that chops up phospholipids-those are molecules that make up the protective barrier around our cells-by targeting the fatty acid at the second position. This process releases arachidonic acid, which can be turned into various substances involved in inflammation, like prostaglandins and leukotrienes. You'll find these enzymes hanging out in a bunch of places like mammalian tissues, and even in the venom of things like snakes and bees. They play roles in triggering inflammation and can cause pain when, for example, you get a venomous bite. There are different kinds of PLA2, including ones in our cells and some that are secreted.
What is the Function of PLA2 Protein?
PLA2, is an enzyme that mostly hangs out in our tissues and in things like snake and insect venom. Its main job is to break down fats in phospholipids by cutting off a specific fatty acid, which then releases a substance called arachidonic acid. This acid is pretty busy because it gets turned into different compounds that can either calm inflammation or kick it up a notch. When you're bitten by a snake or stung by an insect, for example, the activity of PLA2 ramps up, releasing more arachidonic acid, which can cause pain and swelling at the bite or sting site. Additionally, this enzyme is part of various protein families and has roles in processes like digestion and inflammation in the body.
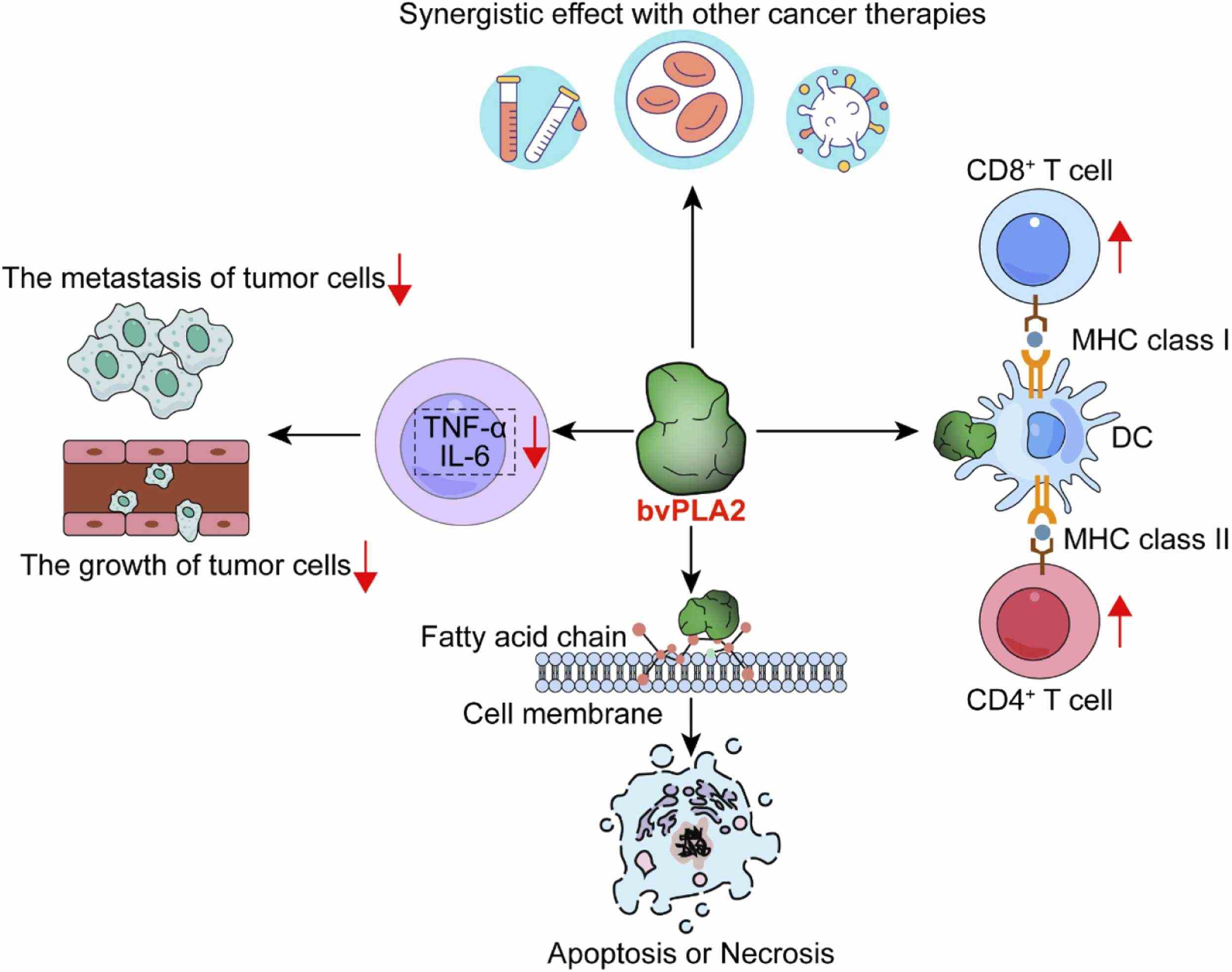
Fig1. Multifaceted mechanisms of bvPLA2 in cancer therapy. (Ziyan Cui, 2024)
PLA2 Related Signaling Pathway
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) enzymes are like the little cutters in our cells that snip fatty acids from phospholipids, which are special fat molecules in our body. They do this by targeting a specific part of the phospholipid, releasing arachidonic acid and lysophosphatidyl choline. This action is crucial because the released arachidonic acid turns into eicosanoids—compounds that help control inflammation and other bodily processes. These enzymes are found everywhere from human tissues to insect and snake venom, which explains why a bee sting or snake bite can hurt so much; they crank up inflammation by releasing too much arachidonic acid. Additionally, there are different PLA2 enzymes like secreted, cytosolic, and those associated with lipoproteins, each playing unique roles in the body, from digesting dietary fats to participating in cell signaling.
PLA2 Related Diseases
Phospholipase A2, or PLA2, is like a switch that can trigger inflammation in our bodies. When things get out of balance, it can cause or worsen a bunch of diseases. For one, it's tied to some serious heart issues. If there's too much of it, you're more at risk for things like heart attacks because it messes with blood vessels. Plus, in the brain, if PLA2 runs wild, it's linked to Alzheimer's, epilepsy, and multiple sclerosis. It's kind of like pouring gas on a fire when it comes to swelling and pain, such as with arthritis. And even allergies can flare up, thanks to this enzyme. So, it's a tiny thing with a big role in ramping up inflammation and causing or worsening a slew of health problems.
Bioapplications of PLA2
PLA2 enzymes are like tiny molecular scissors that snip fatty acids from phospholipids. This simple action is key to multiple biological processes. For instance, it's a player in our body's inflammation response, which is a big deal when you're injured or fighting an infection. Because of how it works, PLA2 is also tied to medical research in treating conditions like cardiovascular disease and rheumatoid arthritis. Scientists are exploring how manipulating PLA2 levels can help manage these diseases, making it a hot topic in developing new medical treatments.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jacinda Chen, 2023
There's this lipid called BMP in the late endosome/lysosome areas of cells, and it's a big deal for sorting and breaking down stuff, managing cholesterol, and even in cell communication. It's also tied to things like viral infections and brain diseases. Even though BMP has been known about for over fifty years, we're still in the dark about the exact enzymes that make it. The process starts when a phospholipase A2 enzyme turns phosphatidylglycerol (PG) into lysophosphatidylglycerol (LPG). Researchers figured out that lysosomal PLA2 (LPLA2) is this enzyme. This experiment showed that LPLA2 can turn PG into LPG in a test tube setup. Also, when tweaked the levels of LPLA2 in HeLa cells, it changed the BMP levels, affecting things like the shape of LE/Lys and cholesterol levels. In a specific disease model (Niemann-Pick type C), boosting LPLA2 helped reduce cholesterol buildup in cells.
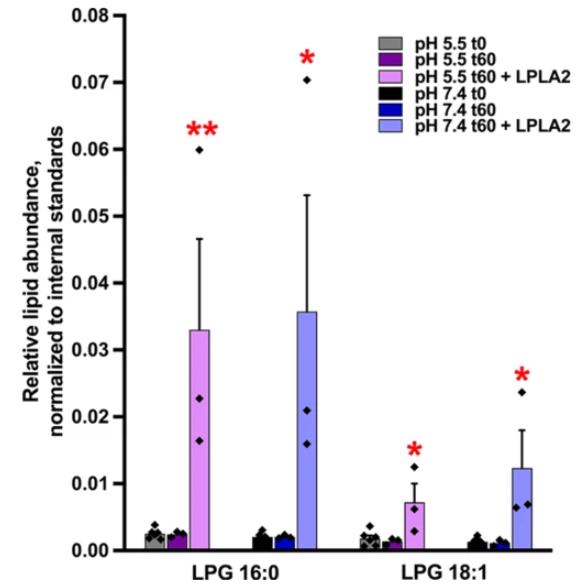
Fig1. LC-MS/MS results for the detection of LPG 16:0 and LPG 18:1.
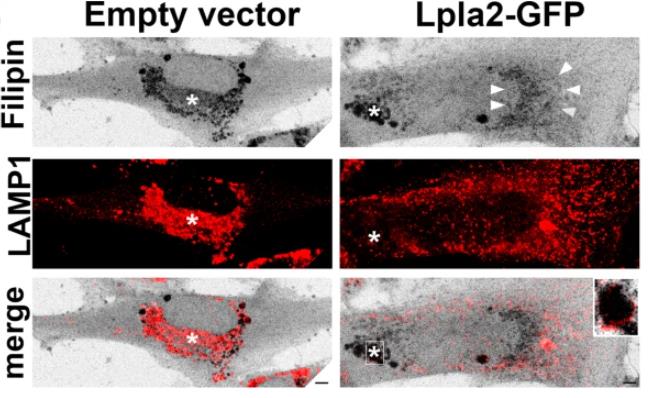
Fig2. Representative maximum intensity projections of human NPC fibroblasts expressing GFP or Lpla2-GFP stained with filipin (gray) and immunolabeled for LAMP1 (red).
Case Study 2: Francis H C Tsao, 2024
The body's response to infection leads to sepsis, causing a domino effect of cell death that eventually results in organ failure. In an attempt to understand this, a study looked into how inflammatory response players like serum secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) and albumin behave in septic patients. By checking serum samples collected over several days, researchers discovered that as sPLA2 activity went up, albumin's ability to bind to membranes went down, especially as sepsis complications worsened. Interestingly, patients on a permissive underfeeding diet showed quicker normalization of these protein activities compared to those on standard feeding. The interplay between rising sPLA2 and dropping albumin hints at a complex relationship managing cell membrane phospholipid balance during sepsis. The findings suggest that albumin's role changes, likely due to pre-bound fatty acids, affecting its structure and function. Therefore, monitoring these two proteins together might help gauge if nutritional strategies are effectively aiding the immune recovery in those severely affected by sepsis.
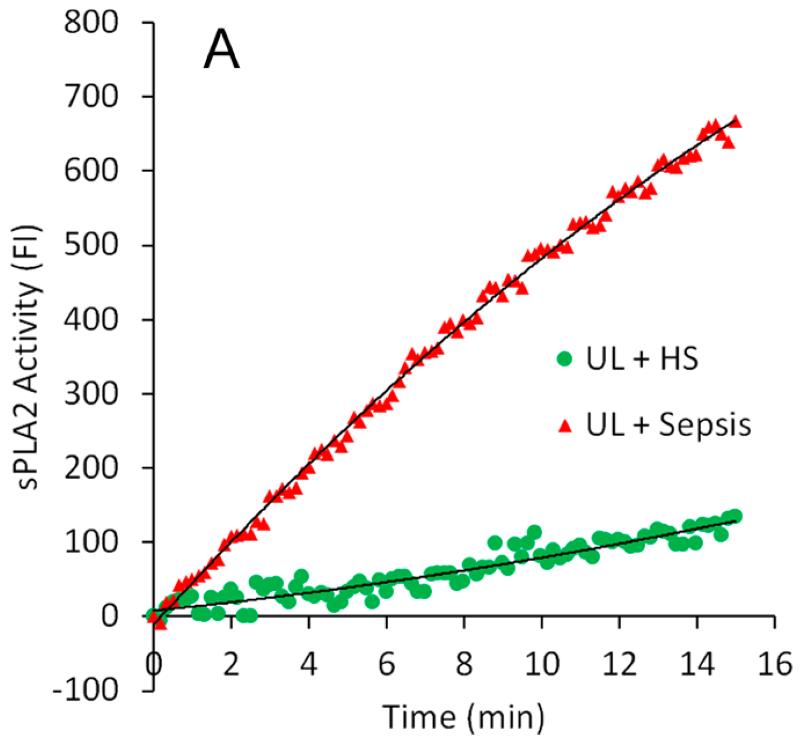
Fig3. Examples of real-time measurement of sPLA2 activity in the serum.
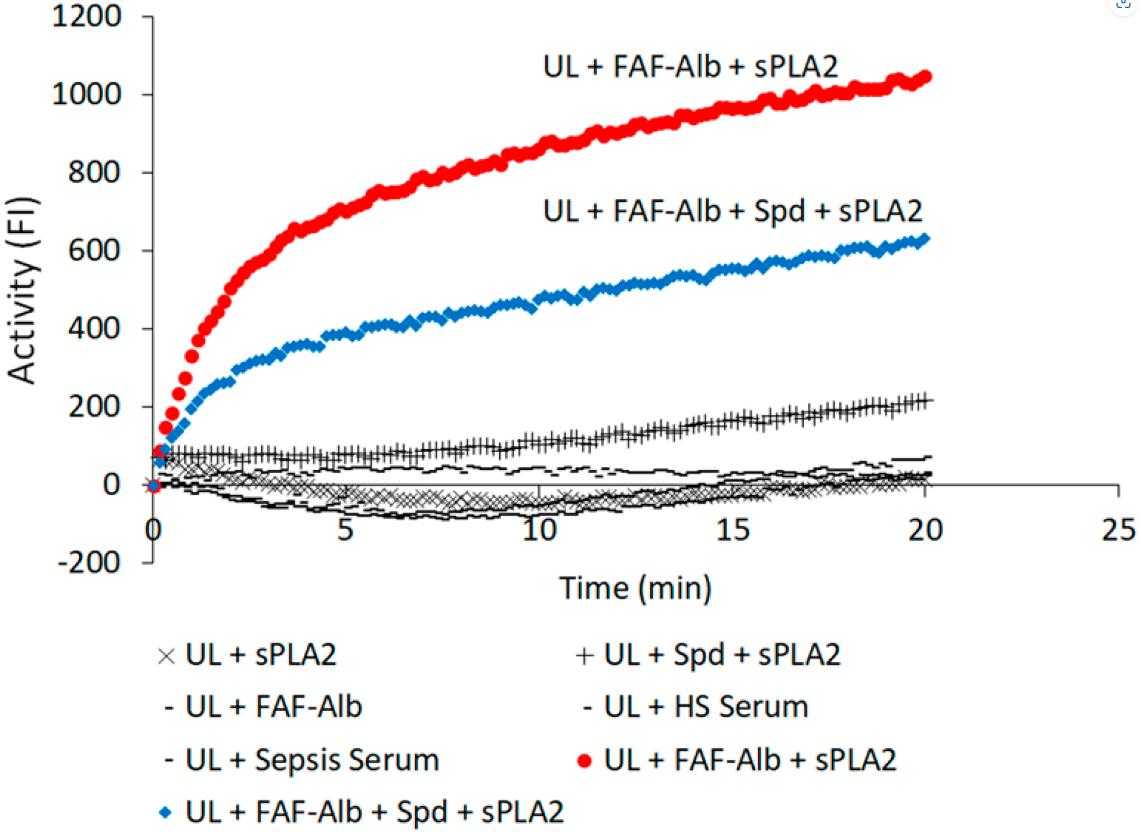
Fig4. Effect of spermidine on albumin–FA binding activity (Alb-FA-BA) of purified human fatty acid-free (FAF) albumin determined by the Alb-FA-BA assay.
Involved Pathway
Pla2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Pla2 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Pla2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
Pla2 has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Pla2 itself. We selected most functions Pla2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Pla2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
Pla2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Pla2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Pla2.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



