PFKL
-
Official Full Name
phosphofructokinase, liver -
Overview
Phosphofructokinase (PFK) catalyzes the phosphorylation of fructose-6-phosphate in glycolysis. There are three isozymes: muscle-type, liver-type, and platelet-type. The liver-type PFK (PFKL) is the predominant subunit of PFK found in the liver . Research -
Synonyms
PFKL;phosphofructokinase, liver;6-phosphofructokinase, liver type;phosphohexokinase;phosphofructokinase 1;liver-type 1-phosphofructokinase;phosphofructo-1-kinase isozyme B;PFK-B;FLJ30173;FLJ40909;DKFZp686G1648;DKFZp686L2097
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- T7
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFKL-1657H | Recombinant Human PFKL, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 424-780aa | |
| PFKL-12664M | Recombinant Mouse PFKL Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| PFKL-1658H | Recombinant Human PFKL protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST | 1 a.a. - 827 a.a. |
|
| PFKL-4394R | Recombinant Rat PFKL Protein | Mammalian Cells | Rat | His |
|
|
| Pfkl-8012R | Recombinant Rat Pfkl protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | Rat | His&T7 | Ala2~His390 |
|
| PFKL-3272HCL | Recombinant Human PFKL 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| PFKL-3273HCL | Recombinant Human PFKL 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| PFKL-2581H | Recombinant Human PFKL Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Ala2-His390 |
|
| PFKL-4054R | Recombinant Rat PFKL Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| PFKL-4054R-B | Recombinant Rat PFKL Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| PFKL-568HF | Recombinant Full Length Human PFKL Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 827 amino acids |
|
| PFKL-6653M | Recombinant Mouse PFKL Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| PFKL-6653M-B | Recombinant Mouse PFKL Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is PFKL Protein?
PFKL, short for phosphofructokinase-1 liver type, is an enzyme crucial for our body's energy management. It's a vital part of glycolysis, the process that breaks down glucose to produce energy. Predominantly active in the liver, PFKL serves as a checkpoint in this energy pathway, adjusting the speed of glycolysis depending on the body's requirements. Because of its critical role in energy management, PFKL can affect cell growth and how cells meet their energy demands. Changes in its activity are sometimes linked to diseases, including cancer. Scientists are interested in PFKL because by understanding it deeper, they hope to unlock new ways to address metabolic issues and develop treatments.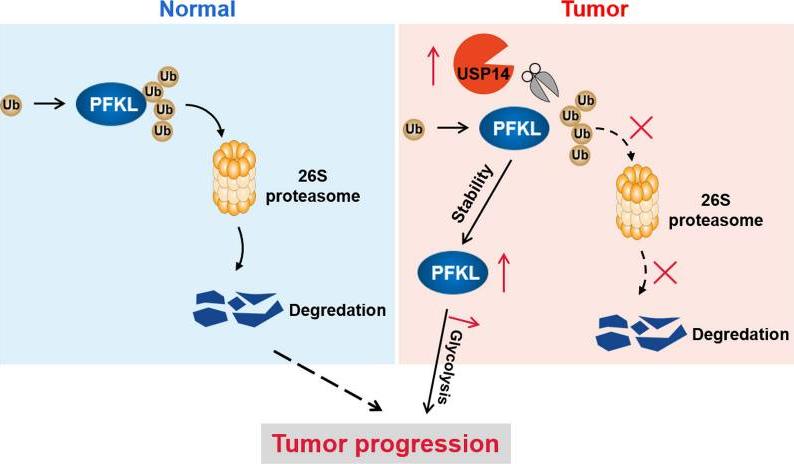
Fig1. Diagram illustrating the USP14-mediated deubiquitylation and stabilization of PFKL. (Xingming Zhang, 2024)
What is the Function of PFKL Protein?
The PFKL protein, or phosphofructokinase-1 liver type, has a pivotal function in our body’s energy machinery. It’s a major player in glycolysis, the process where glucose is broken down to create energy. Primarily found in the liver, PFKL acts like a traffic signal for this pathway, telling the process to speed up or slow down based on what the body needs. By managing the flow of glycolysis, it helps balance energy production according to the body's supply and demand. This balancing act is crucial, as it influences everything from how fast cells grow to how they respond to energy shortages or surpluses, linking PFKL to metabolic health and potentially to diseases like cancer if things go awry.PFKL Related Signaling Pathway
PFKL, or phosphofructokinase-1 liver type, is deeply involved in a crucial signaling pathway linked to metabolism. It’s a key component of glycolysis, the pathway that breaks down glucose to produce energy. Acting like a gatekeeper, PFKL regulates the rate at which glycolysis occurs, depending on the energy needs of the body. This regulation is essential not only for maintaining energy balance but also for responding to different metabolic signals that the body sends out. When cells need more energy, PFKL can ramp up glycolysis, and when less energy is needed, it can slow it down. This ability to respond to signals makes PFKL an important player in how cells manage resources, influence growth, and react to changes, especially under conditions like stress or nutrient scarcity, and it might even be linked to disease processes like cancer if its regulation is disrupted.PFKL Related Diseases
PFKL, known as phosphofructokinase-1 liver type, is tied to a range of diseases because of its critical role in energy metabolism. As a major player in glycolysis, problems with PFKL can lead to energy imbalances in cells. When PFKL malfunctions, it can disrupt normal energy production, potentially contributing to metabolic disorders like diabetes. Moreover, since cancer cells often depend heavily on glycolysis to meet their high energy needs, changes in PFKL activity can be associated with cancer development. Researchers are investigating these links to see if targeting PFKL pathways could open up new treatments for diseases where energy metabolism goes awry.Bioapplications of PFKL
PFKL, known as phosphofructokinase-1 liver type, offers promising possibilities in bioapplications due to its crucial role in energy metabolism. Being a central part of glycolysis—the pathway that breaks down glucose to generate energy—PFKL might be targeted to develop treatments for metabolic disorders such as diabetes, where cellular energy use is impaired. Additionally, because cancer cells heavily rely on glycolysis for their fast growth, altering PFKL activity could pave the way for innovative cancer therapies. Researchers are also considering PFKL in the context of biotechnological applications, where tweaking energy production pathways might improve industrial processes involving cell growth and product formation. Unraveling more about PFKL's role could pave the way for innovative treatments and technologies that exploit its central role in cellular energy management.Case Study
Case Study 1: Amara N. et al. Cell. 2021
In neutrophils, NADPH from the pentose phosphate pathway powers NOX2 to make reactive oxygen species to fight pathogens. However, too much NOX2 can worsen inflammation, like in ARDS. Researchers used chemical proteomic strategies and found that LDC7559 and a stronger analog, NA-11, cut NOX2 activity by activating the glycolytic enzyme PFKL, reducing pentose phosphate pathway activity. Neutrophils treated with NA-11 showed lower NOX2 outputs, reducing NETosis and tissue damage. NA-11 binds to the AMP/ADP activation site of PFKL, but doesn't affect other phosphofructokinase types like PFKP or PFKM.-
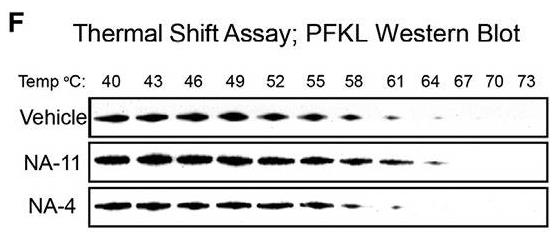 Fig1. Western blots of THP-1 lysates heated for 3 min.
Fig1. Western blots of THP-1 lysates heated for 3 min. -
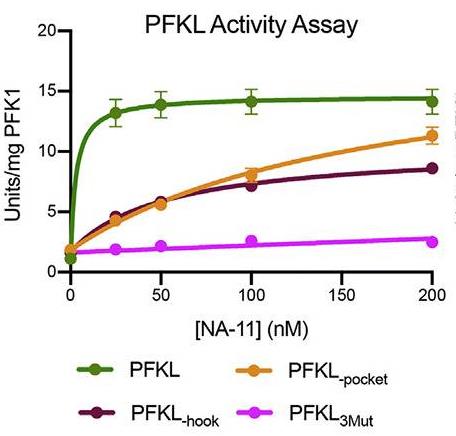 Fig2. Activity of wild-type and mutant forms of PFKL.
Fig2. Activity of wild-type and mutant forms of PFKL.
Case Study 2: Zhang X. et al. J Transl Med. 2024
Overactive USP14 has been spotted in several cancers, like oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). This study shows that high USP14 levels link to bad outcomes and features in OSCC patients, suggesting it might drive tumor growth. Researchers discovered USP14 as a deubiquitinating enzyme for PFKL, a key enzyme in glycolysis. By interacting with and stabilizing PFKL, USP14 boosts glycolysis, promoting cell growth and cancer spread in OSCC. This work establishes USP14 as a crucial player in glycolysis and a new pathway for tumor growth and metastasis in OSCC.-
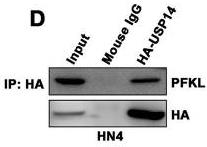 Fig3. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) analysis of the interactions between exogenous USP14 and endogenous PFKL.
Fig3. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) analysis of the interactions between exogenous USP14 and endogenous PFKL. -
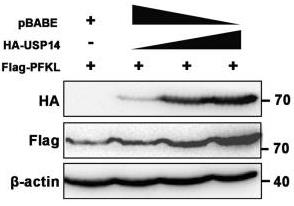 Fig4. Increasing amounts of HA-USP14 plasmids were co-transfected with Flag-PFKL plasmid into HEK293T cells and the indicated proteins were examined by Western blotting.
Fig4. Increasing amounts of HA-USP14 plasmids were co-transfected with Flag-PFKL plasmid into HEK293T cells and the indicated proteins were examined by Western blotting.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PFKL-2581H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PFKL-2581H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PFKL-8012R)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PFKL-8012R)
Involved Pathway
PFKL involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PFKL participated on our site, such as Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis,Pentose phosphate pathway,Fructose and mannose metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PFKL were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Galactose metabolism | PFKMA,HKDC1,HK2,G6PCA.2,PFKP,AKR1B1L,UGP2A,PFKMB,G6PCA.1,GALE |
| Pentose phosphate pathway | TALDO1,DERA,PFKMA,TKTL2,PGD,GPIB,PRPS1B,ALDOAA,deoC,GPI |
| Fructose and mannose metabolism | ALDOAA,PMM2,ALDOB,PFKFB2A,ALDOAB,PFKFB2,GMPPA,AKR1B10,FBP2,AKR1B1L |
| Biosynthesis of amino acids | ALDOCB,PKLR,PGAM1,PGAM1A,BCAT2,PYCR1A,IDH3B,ACO1,AADAT,IDH3A |
| AMPK signaling pathway | IRS1,ELAVL1,INS2,INS1,CCND1,PFKFB4,STK11,PPP2R2B,EEF2,STRADB |
| Carbon metabolism | PGK1,MCEE,ACAT2,ACSS2L,PGAM1,ENO3,HADHA,TKTB,G6PDX,GPI1 |
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | PDK1,PIK3CA,G6PDX,MAPK3,MAPK1,PIK3R2,HRAS,RET,PDHB,PTEN |
| HIF- signaling pathway | IGF1R,MKNK2,RPS6KB2,NOX1,PIK3CD,AKT2,IFNGR2,CAMK2B,ERBB2,HMOX1 |
| RNA degradation | ENO1B,WDR61,EXOSC1,LSM3,PFKMB,CNOT8,XRN1,PAN2,CNOT2,DIS3 |
-
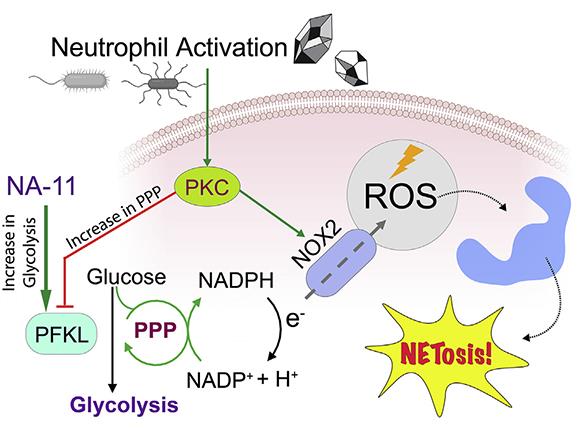 Fig1. NA-11 represents a tool for selective activation of PFKL, the main phosphofructokinase-1 isoform expressed in immune cells. (Neri Amara, 2021)
Fig1. NA-11 represents a tool for selective activation of PFKL, the main phosphofructokinase-1 isoform expressed in immune cells. (Neri Amara, 2021) -
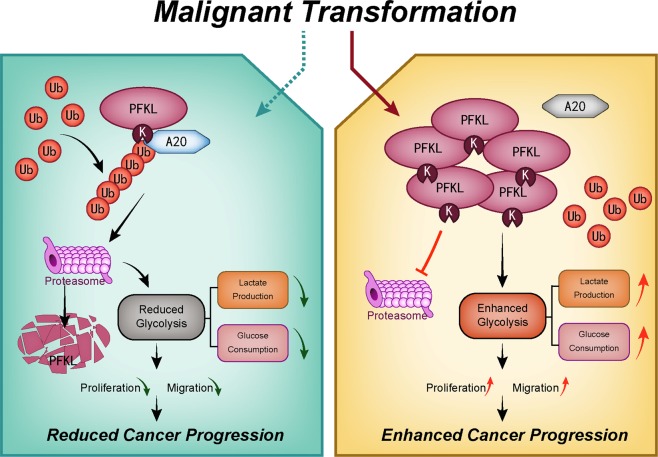 Fig2. A20 upregulation promotes PFKL degradation through UPS. (Yilu Feng, 2020)
Fig2. A20 upregulation promotes PFKL degradation through UPS. (Yilu Feng, 2020)
Protein Function
PFKL has several biochemical functions, for example, 6-phosphofructokinase activity,contributes_to 6-phosphofructokinase activity,ATP binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PFKL itself. We selected most functions PFKL had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PFKL. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| identical protein binding | CBS,TPCN2,SMN1,GCC2,SNCAIP,RIPK3,ALS2CL,EDC3,VEGFA,PRNP |
| ATP binding | SNRK,MYH8,ACVR2AA,KIF6,NLK2,FICD,ATP1A1A.3,MAPK12B,RUVBL1,NSF |
| fructose binding | PFKM,ALDOB,ALDOA |
| 6-phosphofructokinase activity | PFKMB,PFKLB,PFKMA,PFKM,PFKP |
| kinase binding | SP100,PPP2R5A,PRDX3,JAKMIP1,RB1,CEBPB,STX1A,HPCA,BCL10,TENC1 |
| metal ion binding | CBS,PRUNE,FXC1,ADI1,ZNF560,ZFP879,ZNF222,NPEPPS,SORBS2,ARHGEF38 |
| fructose-6-phosphate binding | PFKFB1,GCKR |
| protein binding | CA4,ECE1,CDKAL1,FAM151B,ATL2,CWC15,UNG,ASL,PNMA2,DUT |
Interacting Protein
PFKL has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PFKL here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PFKL.
PFKM;KRTAP5-9;KRTAP10-7;GTPBP3;1-phosphatidyl-1d-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Shin, JH; Krapfenbauer, K; et al. Mass-spectrometrical analysis of proteins encoded on chromosome 21 in human fetal brain. AMINO ACIDS 31:435-447(2006).
- Peled-Kamar, M; Degani, H; et al. Altered brain glucose metabolism in transgenic-PFKL mice with elevated L-phosphofructokinase: in vivo NMR studies. BRAIN RESEARCH 810:138-145(1998).


