PDYN
-
Official Full Name
prodynorphin -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to form the secreted opioid peptides beta-neoendorphin, dynorphin, leu-enkephalin, rimorphin, and leumorphin. These peptides are ligands for the kappa-type of opioid receptor. Dynorphin is involved in modulating responses to several psychoactive substances, including cocaine. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010] -
Synonyms
PDYN;prodynorphin;ADCA;PENKB;SCA23;proenkephalin-B;rimorphin;leumorphin;leu-enkephalin;preprodynorphin;preproenkephalin B;beta-neoendorphin-dynorphin;neoendorphin-dynorphin-enkephalin prepropeptide
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Pig
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- E.coli
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- KSI
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDYN-149H | Recombinant Human PDYN | Mammalian Cells | Human | His |
|
|
| PDYN-241Z | Recombinant Zebrafish PDYN | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| PDYN-31089TH | Recombinant Human PDYN | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 50 amino acids |
|
| PDYN-3365R | Recombinant Rhesus monkey PDYN Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian Cells | Rhesus macaque | His |
|
|
| PDYN-3316HCL | Recombinant Human PDYN 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| PDYN-3183R | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque PDYN Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| PDYN-3183R-B | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque PDYN Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque |
|
||
| PDYN-3825H | Recombinant Human PDYN Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| PDYN-3825H-B | Recombinant Human PDYN Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Human |
|
||
| PDYN-754P | Recombinant Pig PDYN protein, His-KSI-tagged | E.coli | Pig | His&KSI | 175-184a.a. |
|
Background

Fig1. Locus of human PDYN with targets for transcription factors. (Olga Nosova, 2021)
What is PDYN protein?
PDYN (Prodynorphin) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 20 at locus 20p13. Its protein precursors form a variety of secreted opioid peptides through a process of proteolysis, including β-endorphin, dynorphin, leuco-endorphin, remorphin, and leucomorphin. These peptides play an important role in the body's nervous system, particularly in regulating pain perception, emotional response, stress response and the reward system. The protein precursors of PDYN are expressed in different regions of the brain, particularly in areas associated with pain processing, reward, and emotional regulation, such as the hippocampus, amygdala, and periventricular system. The PDYN protein is consisted of 254 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 28.4 kDa.
What is the function of PDYN protein?
Peptides derived from PDYN play a key role in regulating pain perception. They are involved in pain transmission and modulation in the central nervous system, helping to reduce the perception of pain and influencing the response to pain. The PDYN system plays a role in emotion regulation, stress coping, and reward behavior. These peptides are involved in regulating emotional states, including happiness, pleasure and satisfaction, and are also associated with the ability to cope with stress and adversity. The expression and function of PDYN are associated with drug dependence, such as alcohol and cocaine dependence. These peptides may be involved in the regulation of drug-induced reward and addictive behavior, affecting the individual's craving and dependence on drugs. PDYN and its derived peptides may have neuroprotective effects in some cases, helping to protect neurons from damage and degeneration.
PDYN Related Signaling Pathway
PDYN is a protein that is involved in a variety of signaling pathways. In terms of pain and mood regulation, PDYN exerts an analgesic effect by binding to the μ-opioid receptor (MOR). In addition, it is involved in signaling pathways for reward and addictive behavior. PDYN also plays an important role in the inflammatory response, inhibiting the production of inflammatory factors by binding to the κ-opioid receptor (KOR). In summary, PDYN proteins are involved in signaling pathways including pain and mood regulation, reward and addictive behaviors, and inflammatory responses.
PDYN Related Diseases
Mutations in the PDYN gene are associated with Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 23 (SCA23). It is a rare genetic disorder that presents with progressive motor coordination disorders and ataxia. The PDYN system plays a role in regulating the response to several psychoactive substances, including cocaine. This suggests that the PDYN protein may be involved in the regulation of drug-induced reward and addictive behavior, affecting individuals' craving and dependence on drugs. Variants of the PDYN gene are associated with susceptibility to and response to treatment for Major Depressive Disorder (MDD). The PDYN protein is expressed in different regions of the brain, particularly in areas associated with pain processing, reward, and emotional regulation, such as the hippocampus, amygdala, and periventricular system. Dysfunction in these areas may be associated with certain types of epilepsy.
Bioapplications of PDYN
PDYN has a wide range of applications in medical and biological research. As an endogenous peptide substance, it has significant analgesic effects, so it has potential application value in pain management. In addition, it is involved in a variety of biological processes such as neuroendocrine regulation, immune regulation, and inflammatory response, so it can be used to study the mechanisms of these biological processes. Through genetic engineering technology, the PDYN gene can be inserted into the appropriate expression vector, thus achieving efficient recombinant protein production. These recombinant proteins can be used to develop new drugs, study disease pathogenesis, and optimize existing treatments.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Fangyuan Zhou, 2024
To investigate the role of the striatal extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk1/2) and its phosphorylation (p-Erk1/2) in aerobic training to alleviate the development of the L-DOPA induced dyskinesia (LID) in PD mice. A two-point injection of 6-OHDA into the right striatum was used to establish a lateralized injury PD model. PD mice were randomly divided into a PD control group (PD, n=13) and a PD exercise group (PDE, n=16). AIM scores were performed weekly, and mice were assessed for motor function after 4 weeks using the rotarod, open field, and gait tests. Immunohistochemistry was used to test nigrostriatal TH expression, Western blot was used to determine Erk1/2 and p-Erk1/2 protein expression, and immunofluorescence double-labeling technique was used to detect Erk1/2 and p-Erk1/2 co-expression with prodynorphin (PDYN). Compared with Sham, the expression of Erk1/2 protein, the number of positive cells of Erk1/2 and p-Erk1/2 and the number of positive cells co-expressed with PDYN were significantly increased in PD mice (P < 0.05); compared with PD, Erk1/2 protein expression was significantly decreased in PDE mice (P < 0.05), and the number of Erk1/2 and p-Erk1/2 positive cells was significantly reduced (P < 0.05).
.jpg)
Fig1. Schematic diagram of Erk1/2 and PDYN immunofluorescence double-labeling, PDYN immunofluorescence (red).

Fig2. Comparison of Erk1/2 and PDYN co-expression positive cells in each group.
Case Study 2: Fernando Yáñez-Gómez, 2023
The crosstalk between the opioidergic system and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) has a critical role in mediating stress-induced behaviors related to the pathophysiology of anxiety. The present study evaluated the basal status and stress-induced alterations of cortico-thalamic MAPKs and other cell fate-related signaling pathways potentially underlying the anxiogenic endophenotype of PDYN gene-deficient mice. Compared to littermates, PDYN knockout (KO) mice had lower cortical and or thalamic amounts of the phospho-activated MAPKs c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK1/2) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2). Similarly, PDYN-KO animals displayed reduced cortico-thalamic densities of total and phosphorylated (at Ser191) species of the cell fate regulator Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD) without alterations in the Fas receptor. Exposure to acute restraint and chronic mild stress stimuli induced the robust stimulation of JNK1/2 and ERK1/2 MAPKs, FADD, and Akt-mTOR pathways, without apparent increases in apoptotic rates. Interestingly, PDYN deficiency prevented stress-induced JNK1/2 and FADD but not ERK1/2 or Akt-mTOR hyperactivations.
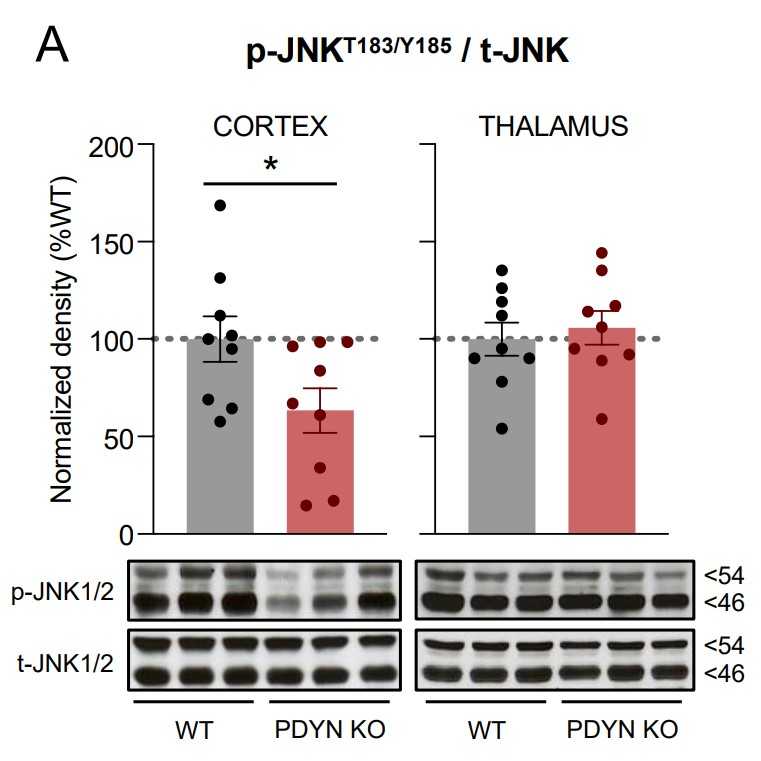
Fig3. Immunodensities of activated JNK1/2 in cortical and thalamic brain tissue samples from WT and PDYN-KO mice.
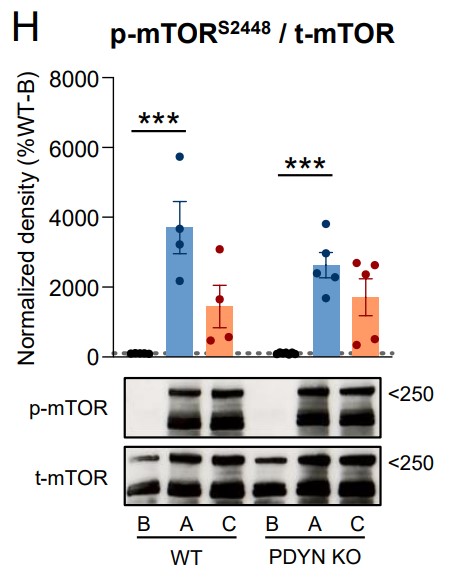
Fig4. Cortical immunodensities of activated p-Ser2448 mTOR in WT and PDYN-KO mice exposed to acute restraint.
Involved Pathway
PDYN involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PDYN participated on our site, such as Cocaine addiction,Alcoholism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PDYN were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Alcoholism | MAPK3,GNG3,HIST2H2AA2,SHC1,CREB3L1,CREB3,HIST3H2BB-PS,HIST2H2AA4,GRIN2B,HIST1H4D |
| Cocaine addiction | PRKACG,GNAI1,CREB3,GRIN2C,DRD2,CREB3L4,MAOB,GRIN2B,FOSB,NFKB1 |
Protein Function
PDYN has several biochemical functions, for example, opioid peptide activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PDYN itself. We selected most functions PDYN had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PDYN. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| opioid peptide activity | PENK,ZFP106,CDC42EP2,PNOC |
Interacting Protein
PDYN has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PDYN here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PDYN.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Reed, B; Fang, N; et al. CHROMATIN ALTERATIONS IN RESPONSE TO FORCED SWIMMING UNDERLIE INCREASED PRODYNORPHIN TRANSCRIPTION. NEUROSCIENCE 220:109-118(2012).
- Hanrieder, J; Ljungdahl, A; et al. L-DOPA-induced Dyskinesia is Associated with Regional Increase of Striatal Dynorphin Peptides as Elucidated by Imaging Mass Spectrometry. MOLECULAR & CELLULAR PROTEOMICS 10:-(2011).


