PAEP
-
Official Full Name
progestagen-associated endometrial protein -
Overview
This gene is a member of the kernel lipocalin superfamily whose members share relatively low sequence similarity but have highly conserved exon/intron structure and three-dimensional protein folding. Most lipocalins are clustered on the long arm of chromosome 9. The encoded glycoprotein has been previously referred to as pregnancy-associated endometrial alpha-2-globulin, placental protein 14, and glycodelin, but has been officially named progestagen-associated endometrial protein. Three distinct forms, with identical protein backbones but different glycosylation profiles, are found in amniotic fluid, follicular fluid and seminal plasma of the reproductive system. These glycoproteins have distinct and essential roles in regulating a uterine environment suitable for pregnancy and in the timing and occurrence of the appropriate sequence of events in the fertilization process. A number of alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed at this locus, but the full-length nature of only two, each encoding the same protein, has been determined. -
Synonyms
PAEP;progestagen-associated endometrial protein;glycodelin;alpha uterine protein;GD;GdA;GdF;GdS;glycodelin A;glycodelin F;glycodelin S;MGC138509;MGC142288;PAEG;PEP;PP14;PP14 protein (placental protein 14);pregnancy associated endometrial
Recombinant Proteins
- Rhesus macaque
- Pig
- Human
- Bovine
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Milk
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- T7
- Non
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
- Myc
- DDK
Background
What is PAEP protein?
PAEP (progestagen associated endometrial protein) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 9 at locus 9q34. This gene is a member of the kernel lipocalin superfamily whose members share relatively low sequence similarity but have highly conserved exon/intron structure and three-dimensional protein folding. Most lipocalins are clustered on the long arm of chromosome 9. The encoded glycoprotein has been previously referred to as pregnancy-associated endometrial alpha-2-globulin, placental protein 14, and glycodelin, but has been officially named progestagen-associated endometrial protein. Three distinct forms, with identical protein backbones but different glycosylation profiles, are found in amniotic fluid, follicular fluid and seminal plasma of the reproductive system. These glycoproteins have distinct and essential roles in regulating a uterine environment suitable for pregnancy and in the timing and occurrence of the appropriate sequence of events in the fertilization process. The PAEP protein is consisted of 180 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 20.6 kDa.
What is the function of PAEP protein?
PAEP is a glycoprotein that plays a role in regulating critical steps during fertilization. It has different glycoforms, including glycodelin-S, -A, -F, and -C, which have distinct biological activities in reproductive tissues. PAEP has immunomodulatory effects. For example, glycodelin-A has been reported to possess contraceptive and immunosuppressive activities, while glycodelin-C stimulates the binding of spermatozoa to the zona pellucida. Glycodelin-F, a glycoform of PAEP, inhibits the binding of spermatozoa to the zona pellucida and suppresses the progesterone-induced acrosome reaction of spermatozoa. Glycodelin-S found in seminal plasma is involved in maintaining the uncapacitated state of human spermatozoa.
PAEP Related Signaling Pathway
PAEP has been reported to have immunomodulatory effects, which can be important for maintaining a healthy uterine environment during pregnancy. PAEP is associated with progestogen signaling. Progestogens, such as progesterone, play a crucial role in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy, and PAEP's expression is regulated by these hormones. PAEP may be involved in cell proliferation and differentiation processes, which are essential for tissue growth and repair, including in the endometrium during the menstrual cycle. The expression of PAEP may be influenced by inflammatory processes, and it could potentially play a role in modulating the inflammatory response in the endometrium.
PAEP Related Diseases
PAEP is associated with Kleefstra Syndrome, a rare genetic disorder characterized by intellectual disability, delayed development, and distinctive facial features. PAEP has been linked to ectopic pregnancy, a condition where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. PAEP may play a role in endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, causing pain and sometimes fertility problems. PAEP has been found to be expressed in endometrial cancer, a type of cancer that arises from the lining of the uterus. PAEP may be associated with recurrent pregnancy loss, which is the loss of three or more pregnancies in a row. PAEP has been studied for its potential as a biomarker for the early diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer, with its expression linked to immune infiltration.
Bioapplications of PAEP
PAEP is involved in the regulation of fertilization and embryo implantation processes. It is expressed in the endometrium during the secretory phase and early pregnancy, suggesting its importance in creating a suitable uterine environment for pregnancy. Given its role in endometrial receptivity and embryo implantation, PAEP could be a potential biomarker for assessing the likelihood of successful pregnancy in fertility treatments. PAEP could serve as a diagnostic marker for certain conditions related to the reproductive system, including endometrial disorders and possibly even some types of cancer.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Riccardo Focarelli, 2018
Glycodelin-A (GdA) has been proposed to represent a potential biomarker of endometrial function, but little is known about its expression during the different phases of the menstrual cycle and under pathological conditions. In the light of its potential importance also in embryo implantation, this study aimed to evaluate the expression profile of GdA as well as the presence of different glycosylated glycoforms and the immunolocalization in endometrial tissue from women with endometriosis and in women with proven fertility, at different times during the menstrual cycle. The results showed that GdA is synthesized by endometrial epithelial and stromal cells, both in healthy endometrium and eutopic endometrium from women with endometriosis, with a profile including several glycosylated glycoforms, differentially expressed in each phase of the menstrual cycle. During the secretory phase, a significant increase in GdA protein expression, with a different glycoforms profile, was observed in endometriotic eutopic endometrium. Protein localization in eutopic endometrial tissue resulted significantly different in comparison with endometrium from women with proven fertility.
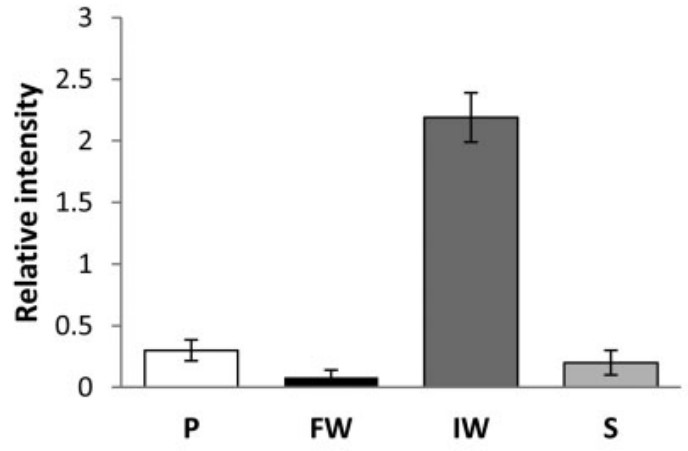
Fig1. Computer-assisted semiquantitative analysis of the overall relative intensity of the GdA reactive spots.
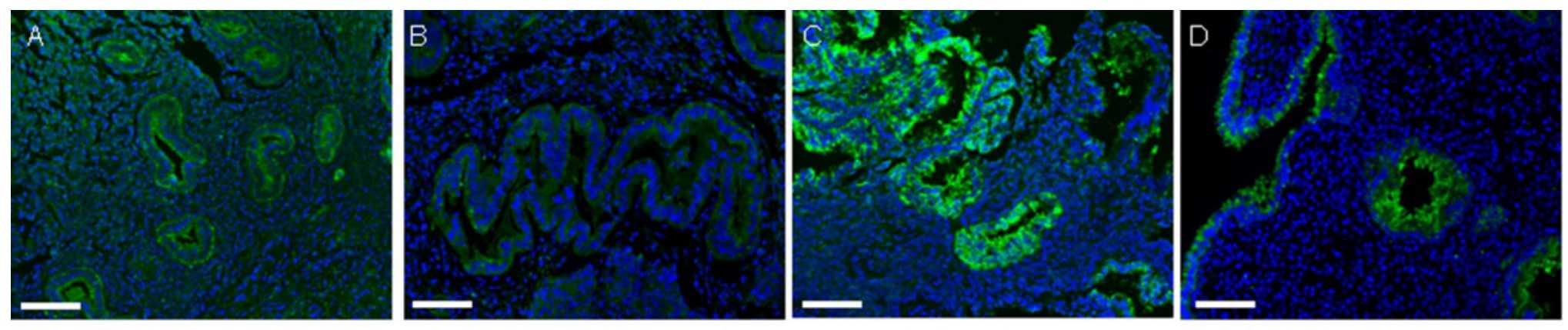
Fig2. Representative microphotographs of GdA staining in endometrium in proliferative phase.
Case Study 2: Marc A Schneider, 2015
In recent years, immune therapeutic strategies against non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) based on tissue-derived biomarkers, for example PD1/PD-L1 (CD274), have evolved as novel and promising treatment options. However, the crosstalk between tumor and immune cells is poorly understood. Glycodelin (gene name PAEP), initially described in the context of pregnancy and trophoblastic implantation, is a secreted immunosuppressive glycoprotein with an as-of-yet largely unknown function in lung cancer. In this study, the researchers characterized the expression and role of glycodelin in NSCLC through mRNA and protein expression analyses, functional knockdown experiments, and correlations with clinicopathologic parameters. Overall survival (OS) was significantly reduced in NSCLC with high glycodelin mRNA levels in women but not in men. Glycodelin was detected in the sera of patients, and the levels correlated with recurrence and metastatic disease. Knockdown of glycodelin with siRNAs in NSCLC cell lines resulted in significant upregulation of immune system modulatory factors such as PDL1, CXCL5, CXCL16, MICA/B, and CD83 as well as proliferation stimulators EDN1 and HBEGF.
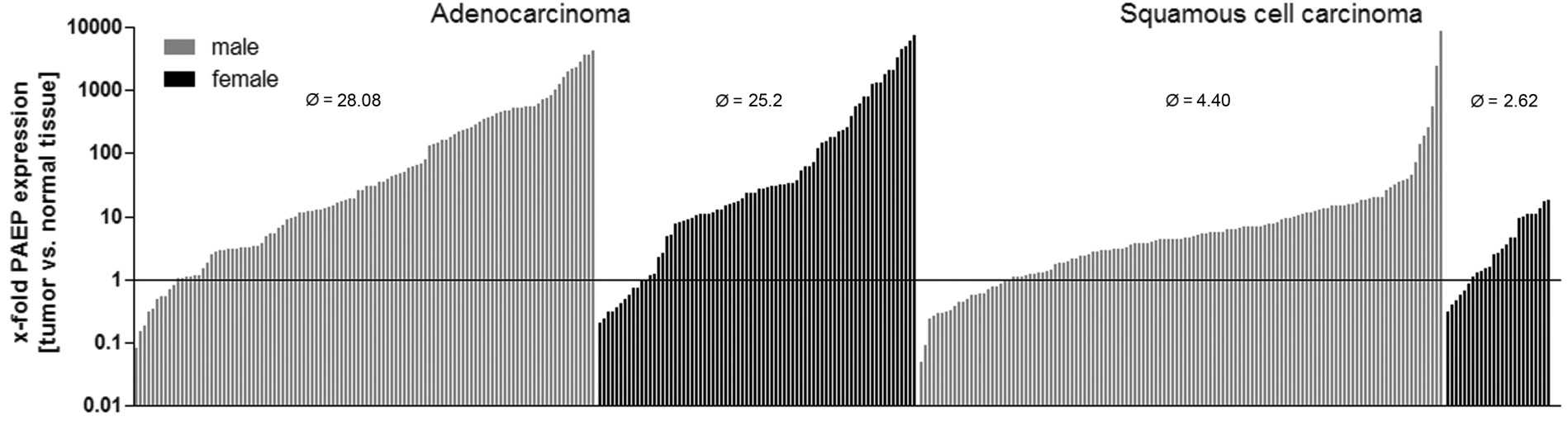
Fig3. PAEP-expression in 336 lung tumor.
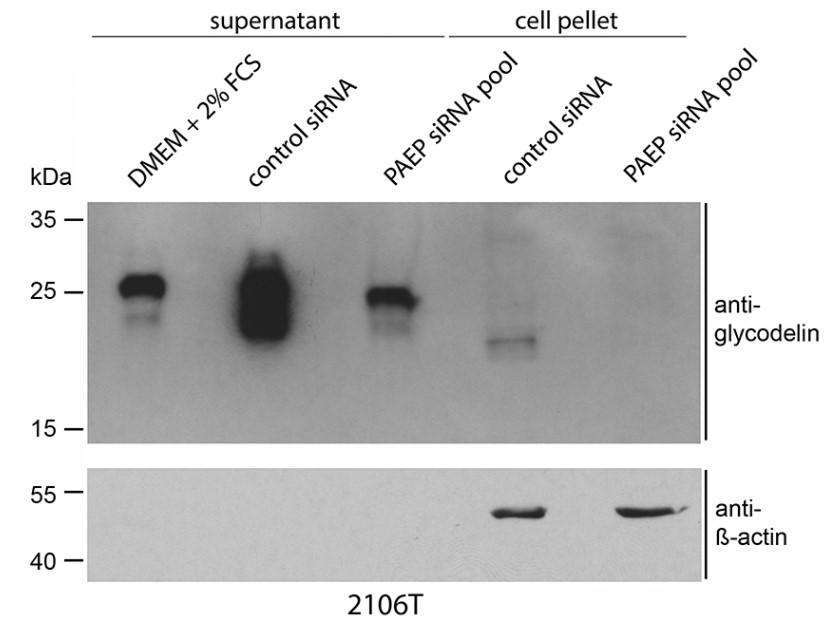
Fig4. 2106T were transfected with a pool of four different PAEP-specific siRNAs for 72h.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PAEP-6549H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PAEP-5048H)
Involved Pathway
PAEP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PAEP participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PAEP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
PAEP has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,small molecule binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PAEP itself. We selected most functions PAEP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PAEP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | SDPR,FAM96A,RAPGEF3,CD79A,UQCC2,BOC,SNF8,PRKRIP1,CREB3,NEDD9 |
| small molecule binding | RBP4L,LCN15,APODA.2,PTGDSA,AMBP,MUP17,LCN2,MUP3,LCN5,MUP20 |
Interacting Protein
PAEP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PAEP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PAEP.
GRAMD3;XRCC6;UBE2E1;EEF1A1;RIF1;COPS6;IGSF21;ESYT2;SLC25A12;DNAJB5;UBL4A;DDOST;SMAD3;GTF3C2;ZFP91
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



