NUP93
-
Official Full Name
nucleoporin 93kDa -
Overview
Nuclear pore complex protein Nup93 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUP93 gene. -
Synonyms
NUP93;nucleoporin 93kDa;nuclear pore complex protein Nup93;KIAA0095;nucleoporin Nup93;93 kDa nucleoporin;NIC96;MGC21106
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is NUP93 Protein?
NUP93 is a vital part of the nuclear pore complex (NPC), which helps manage the movement of large molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. It's a big player in keeping the NPC's structure intact and ensuring it works properly, as well as being involved in how genes get expressed. In endothelial cells, NUP93 acts like a shield by holding back Yap activity, which helps stave off early aging of these cells and slows down the aging of blood vessels. In cardiac cells, NUP93 influences gene transcription by directly interacting with chromatin, highlighting its importance in heart cell function.What is the Function of NUP93 Protein?
NUP93 is a key player in the nuclear pore complex (NPC), helping to control how large molecules move between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. It's really important for gene regulation, as it can activate or repress gene transcription by interacting directly with chromatin. In endothelial cells, NUP93 helps out by holding back Yap activity, which slows down aging in these cells and the blood vessels. Meanwhile, in heart muscle cells, it steps in to protect against damage from low oxygen levels by managing gene transcription. With these roles, NUP93 is essential for keeping cells functioning well and protecting against age-related diseases.NUP93 Related Signaling Pathway
NUP93 is involved in several critical signaling pathways, mainly through its role in the nuclear pore complex to regulate cell functions. By directly interacting with chromatin, NUP93 can kickstart gene transcription, affecting how cells grow and move. It also plays a key part in immune responses, especially in fighting off viruses, by boosting TBK1 activity and helping IRF3 move into the nucleus to regulate type I interferon genes. When cells are stressed, lowering NUP93 levels can activate the NF-κB signaling pathway, leading to increased expression of genes related to inflammation and immunity. These actions make NUP93 crucial in processes like cell growth, immune responses, and disease development.NUP93 Related Diseases
NUP93 protein is linked to various diseases, notably playing a significant role in kidney disorders. Mutations in the NUP93 gene can lead to steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS), a genetic condition that often presents as focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) and can progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Beyond kidney issues, NUP93 mutations are also connected with other conditions like juvenile papillomatosis of the breast. These findings highlight NUP93's essential role in keeping the nuclear pore complex working properly and managing material exchange between the nucleus and cytoplasm, with its dysfunction potentially leading to the onset and progression of several diseases.
Fig1. Model depicting proposed regulatory roles for validated GPCR/cAMP mediators. (Khairunnisa Mentari Semesta, 2020)
Bioapplications of NUP93
NUP93 protein has a wide range of applications in research, industry, and clinical studies. In research, it's a crucial part of the nuclear pore complex, often studied for its role in moving materials between the nucleus and cytoplasm and regulating genes. Its role in protecting endothelial cells makes it an important target for studying blood vessel health and aging. In industry, scientists use recombinant NUP93 to create experimental reagents and tools to better understand its role in cells. Clinically, NUP93 is considered a potential target for treating diseases like breast and bladder cancer, where its levels are linked to how aggressive or severe the tumors are. It also holds potential in addressing age-related blood vessel conditions.Case Study
Case Study 1: Sonawane PJ. et al. Protein Sci. 2020
The central transport channel (CTC) inside nuclear pore complexes is built from three nucleoporins: Nup62, Nup58, and Nup54. We're still figuring out exactly how these nucleoporins come together to form the CTC. By studying various species, we found that their unique biochemical traits are evolutionarily conserved. Our analysis showed different stoichiometric mixes of Nup62, Nup54, and Nup58 working together. Specifically, the N-terminal domain of mammalian Nup93 plays a key role in attaching and positioning the CTC in the NPCs. We successfully reconstituted and purified the mammalian CTC·Nup93 complex by co-expressing Nup93 with the CTC. Using small angle X-ray scattering and electron microscopy, we discovered that the CTC·Nup93 complex forms a "V" shape.-
 Fig1. A pull‐down assay with either anti‐GFP‐nanobody (GFPNB) or GST (as a control) was performed using various Nup93 constructs transfected to HEK293F cells.
Fig1. A pull‐down assay with either anti‐GFP‐nanobody (GFPNB) or GST (as a control) was performed using various Nup93 constructs transfected to HEK293F cells. -
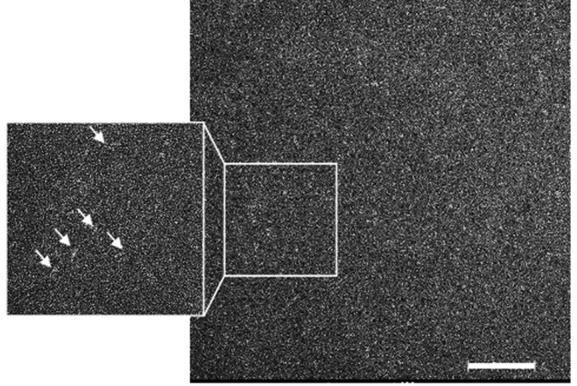 Fig2. A representative micrograph of purified CTC·Nup93(1–819) complex stained with 2% uranyl acetate.
Fig2. A representative micrograph of purified CTC·Nup93(1–819) complex stained with 2% uranyl acetate.
Case Study 2: Lin CS. et al. Cancer Lett. 2022
The nuclear pore complex (NPC) is the key channel for moving large molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm, playing vital roles in cell function. However, its role in cancer, like hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), isn't fully understood. Researchers studied 729 HCC cases and found that Nup93 was often elevated, especially in metastatic tumors, correlating with worse outcomes. Lowering Nup93 stopped HCC growth and spread, while higher levels did the opposite. Nup93 aids HCC metastasis by affecting β-catenin's movement, directly interacting with it without importin. LEF1 and β-catenin also enhance Nup93's role in HCC through a feedback loop.-
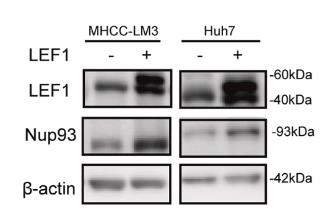 Fig3. Western blotting (WB) analysis showing Nup93 protein expression after transfection with LEF1.
Fig3. Western blotting (WB) analysis showing Nup93 protein expression after transfection with LEF1. -
 Fig4. Cell proliferation rates after Nup93 silencing were examined for 5 consecutive days.
Fig4. Cell proliferation rates after Nup93 silencing were examined for 5 consecutive days.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (NUP93-509H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (NUP93-509H)
Involved Pathway
NUP93 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways NUP93 participated on our site, such as RNA transport, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with NUP93 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| RNA transport | THOC4,SEC13,EIF2B4,FMR1,UBE2IA,SMN1,SUMO2B,PABPC1L2A,NUP107,SENP2 |
-
 Fig1. Patterns revealed the correlation between Nup93, β-catenin, and LEF1. (Cen-Shan Lin, 2022)
Fig1. Patterns revealed the correlation between Nup93, β-catenin, and LEF1. (Cen-Shan Lin, 2022) -
 Fig2. Schematic representation of the spatiotemporal organization and function of the HOXA gene locus during differentiation. (Ajay S Labade, 2021)
Fig2. Schematic representation of the spatiotemporal organization and function of the HOXA gene locus during differentiation. (Ajay S Labade, 2021)
Protein Function
NUP93 has several biochemical functions, for example, structural constituent of nuclear pore. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by NUP93 itself. We selected most functions NUP93 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with NUP93. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| structural constituent of nuclear pore | NUP54,NUP62,NUP98,NUP153,NDC1,NUP107,NUP62L,NUP205,NUP155,TMEM33 |
Interacting Protein
NUP93 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with NUP93 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of NUP93.
MYC;Nup188;Nup214;SAP18;GIPC1;AIRE;PTP4A3;CIAO1;CHM;CASP4;ARF6;CLN3;ILK;TSC22D1;PAN2;AHCTF1;PNKP
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Kim, DI; Birendra, KC; et al. Probing nuclear pore complex architecture with proximity-dependent biotinylation. PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA 111:E2453-E2461(2014).
- Vollmer, B; Antonin, W; et al. The diverse roles of the Nup93/Nic96 complex proteins - structural scaffolds of the nuclear pore complex with additional cellular functions. BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 395:515-528(2014).


