NPC1
-
Official Full Name
Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a large protein that resides in the limiting membrane of endosomes and lysosomes and mediates intracellular cholesterol trafficking via binding of cholesterol to its N-terminal domain. It is predicted to have a cytoplasmic C-terminus, 13 transmembrane domains, and 3 large loops in the lumen of the endosome - the last loop being at the N-terminus. This protein transports low-density lipoproteins to late endosomal/lysosomal compartments where they are hydrolized and released as free cholesterol. Defects in this gene cause Niemann-Pick type C disease, a rare autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by over accumulation of cholesterol and glycosphingolipids in late endosomal/lysosomal compartments. -
Synonyms
NPC1;Niemann-Pick disease, type C1;Niemann-Pick C1 protein;NPC;FLJ98532;Cdig2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- Yeast
- Flag
- His
- Non
- GST
- Myc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPC1-1339H |
Recombinant Human NPC1 protein, His/FLAG-tagged

|
HEK293 | Human | Flag&His | Arg372-Phe622 | |
| NPC1-1338H | Recombinant Human NPC1 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 23-266 aa | |
| NPC1-29132TH | Recombinant Human NPC1 | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 100 amino acids |
|
| NPC1-29133TH | Recombinant Human NPC1, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| NPC1-8054Z | Recombinant Zebrafish NPC1 | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| NPC1-4432H | Recombinant Human NPC1 protein, His-Myc-tagged | Yeast | Human | His&Myc | 23-261aa |
|
| NPC1-4725H | Recombinant Human NPC1 Protein (Gln23-Asp266), N-His tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Gln23-Asp266 |
|
Background
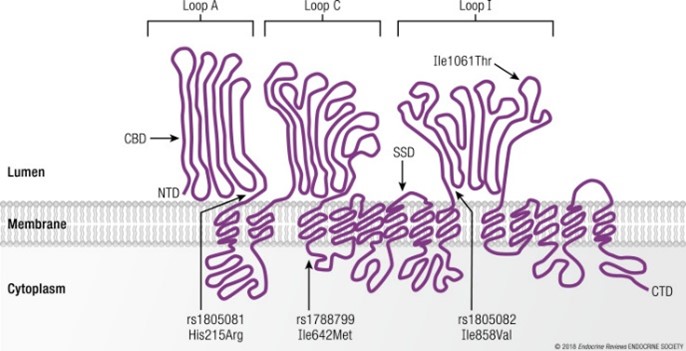
Fig1. The human NPC1 protein and its major structural domains. (Amel Lamri, 2018)
What is NPC1 protein?
NPC1 (NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 18 at locus 18q11. This gene encodes a large protein that resides in the limiting membrane of endosomes and lysosomes and mediates intracellular cholesterol trafficking via binding of cholesterol to its N-terminal domain. It is predicted to have a cytoplasmic C-terminus, 13 transmembrane domains, and 3 large loops in the lumen of the endosome - the last loop being at the N-terminus. This protein transports low-density lipoproteins to late endosomal/lysosomal compartments where they are hydrolized and released as free cholesterol. The NPC1 protein is consisted of 1278 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 142.2 kDa.
What is the function of NPC1 protein?
The NPC1 protein, or Niemann-Pick C1 protein, plays a crucial role in the intracellular transport of cholesterol. It functions in late endosomes and lysosomes to facilitate the egress of unesterified cholesterol, which is essential for maintaining cholesterol homeostasis within the cell. The NPC1 protein is a transmembrane protein that, along with NPC2, is responsible for the egress and recycling of lipoprotein-derived cholesterol. When the function of NPC1 is impaired due to genetic mutations, it can lead to the accumulation of cholesterol in lysosomes, which is associated with Niemann-Pick disease Type C (NPC), a rare genetic disorder characterized by progressive neurodegeneration and other systemic symptoms.
NPC1 Related Signaling Pathway
NPC1 plays an important role in the cholesterol metabolism SREBP (sterol regulatory element binding protein) signaling pathway in the endoplasmic reticulum. NPC1 is responsible for transporting cholesterol from low-density lipoproteins (LDL) into the endoplasmic reticulum, where it is sensed by the SREBP cleavage activating protein (SCAP), thereby regulating cholesterol metabolism. The bioavailability of cholesterol affects the mTORC1 (mammalian target protein Complex 1) signaling pathway, which is involved in cell growth, protein synthesis and many other cellular functions. NPC1 is involved in the regulation of intracellular lipid metabolism, including cholesterol uptake, transport and esterification processes, and is essential for maintaining the integrity and function of cell membranes. The abnormal function of NPC1 may affect the autophagy process and apoptosis pathway of cells, and then affect the survival and death of cells.
NPC1 Related Diseases
The NPC1 protein (Niemann-Pick C1 protein) is closely related to Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC), which is a hereditary neurodegenerative disorder. It is often accompanied by cognitive impairment, physiological disorders, and progressive and disabling neurological symptoms. Mutations in the NPC1 gene cause cholesterol to build up in the lysosomes and not enter cells properly, causing disease. In addition, the abnormal function of NPC1 protein is also associated with cholesterol esterification disorders and cholesterol metabolism disorders, and may affect other diseases related to cholesterol metabolism. NPC1 is also a cellular receptor for Ebola virus, and its abnormalities may be related to the viral infection process.
Bioapplications of NPC1
NPC1 protein has important applications in medical and biological research. First, the key role of NPC1 protein in intracellular cholesterol transport and homeostasis regulation makes it an important target for studying cholesterol metabolism and related diseases, helping to develop new strategies for treating diseases with abnormal cholesterol metabolism such as Niemann-Pick C disease. Secondly, as a cellular receptor of pathogens such as Ebola virus, the study of NPC1 structure and function is of great significance for understanding the mechanism of virus invasion and developing antiviral drugs and vaccines. In addition, the structural biology of NPC1 protein has promoted the understanding of the structure and dynamics of membrane proteins, providing a basis for related drug design and disease mechanism research. Finally, drug researches are responding to medical needs including NPC1 inhibitors, NPC1 antibody and small molecular drugs.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Pavlo Gilchuk, 2018
Ebolaviruses cause severe disease in humans, and identification of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that are effective against multiple ebolaviruses are important for therapeutics development. Here researchers describe a distinct class of broadly neutralizing human mAbs with protective capacity against three ebolaviruses infectious for humans: Ebola (EBOV), Sudan (SUDV), and Bundibugyo (BDBV) viruses. They isolated mAbs from human survivors of ebolavirus disease and identified a potent mAb, EBOV-520, which bound to an epitope in the glycoprotein (GP) base region. EBOV-520 efficiently neutralized EBOV, BDBV, and SUDV and also showed protective capacity in relevant animal models of these infections by performing cell surface displayed GPCL soluble purified NPC1-C binding inhibition assay. EBOV-520 mediated protection principally by direct virus neutralization and exhibited multifunctional properties. This study identified a potent naturally occurring mAb and defined key features of the human antibody response that may contribute to broad protection.
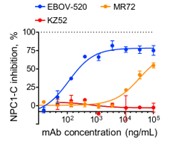
Fig1. Capacity of mAbs to inhibit NPC1-C binding to GPCL.
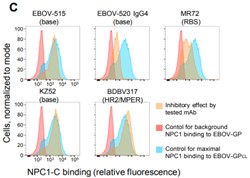
Fig2. Capacity to inhibit receptor binding.
Case Study 2: Maria Casas, 2023
Lysosomes communicate through cholesterol transfer at endoplasmic reticulum (ER) contact sites. At these sites, the Niemann Pick C1 cholesterol transporter (NPC1) facilitates the removal of cholesterol from lysosomes, which is then transferred to the ER for distribution to other cell membranes. Mutations in NPC1 result in cholesterol buildup within lysosomes, leading to Niemann-Pick Type C (NPC) disease, a progressive and fatal neurodegenerative disorder. The molecular mechanisms connecting NPC1 loss to NPC-associated neuropathology remain unknown. Here researchers show both in vitro and in an animal model of NPC disease that the loss of NPC1 function alters the distribution and activity of voltage-gated calcium channels (CaV). Underlying alterations in calcium channel localization and function are KV2.1 channels whose interactions drive calcium channel clustering to enhance calcium entry and fuel neurotoxic elevations in mitochondrial calcium. Targeted disruption of KV2-CaV interactions rescues aberrant CaV1.2 clustering, elevated mitochondrial calcium, and neurotoxicity in vitro.
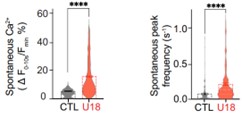
Fig3. Loss of NPC1 function increases voltage-dependent Ca2+ entry.
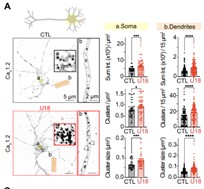
Fig4. Loss of NPC1 function alters voltage-dependent CaV1 channel distribution.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (NPC1-4725H)
Involved Pathway
NPC1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways NPC1 participated on our site, such as Lysosome, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with NPC1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Lysosome | ARSG,LAPTM4A,ATP6V0CB,ACP5B,AP1S3,NAGLU,IGF2R,SCARB2,CD63,ACP5A |
Protein Function
NPC1 has several biochemical functions, for example, cholesterol binding,hedgehog receptor activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by NPC1 itself. We selected most functions NPC1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with NPC1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | MDFIC,VAMP7,ORC4L,SERPINC1,ZNRF1,C5orf30,DNAI1,EHD3,TSEN54,BRAP |
| receptor activity | TREM2,CCR6,NLGN2A,EXTL3,TNFRSF9,EPHB6,CD226,CHRM3,PVRL3,RTN4RL1 |
| hedgehog receptor activity | DISP1,PTCH1,B9D1,PTCHD3,PTCH2,PTCHD4,PTCHD1 |
| transmembrane signaling receptor activity | Cd79a,FCGR2C,NRXN2,NPR2,GHRHRL,CLEC2D,NCR2,TLR4,KLRC2,OR12D2 |
| cholesterol binding | APOA4A,ERLIN2,APOA4B.2,PROM2,ABCG1,NR1H3,APOA4B.1,STARD6,TSPO2,APOD |
| virus receptor activity | HAVCR1,ITGB6,XPR1,ICAM1,PVRL1,CR2,MOG,PVRL2,ITGB1,ITGAV |
| sterol transporter activity | C20orf79,SCP2,SCP2A,OSBP |
Interacting Protein
NPC1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with NPC1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of NPC1.
cholesterol;b3xyc5_sollc;cona_canen;TMEM173;Unc93b1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Kwiatkowska, K; Marszalek-Sadowska, E; et al. Visualization of cholesterol deposits in lysosomes of Niemann-Pick type C fibroblasts using recombinant perfringolysin O. ORPHANET JOURNAL OF RARE DISEASES 9:-(2014).
- Lennemann, NJ; Rhein, BA; et al. Comprehensive Functional Analysis of N-Linked Glycans on Ebola Virus GP1. MBIO 5:-(2014).



