MED1
-
Official Full Name
mediator complex subunit 1 -
Overview
The activation of gene transcription is a multistep process that is triggered by factors that recognize transcriptional enhancer sites in DNA. These factors work with co-activators to direct transcriptional initiation by the RNA polymerase II apparatus. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the CRSP (cofactor required for SP1 activation) complex, which, along with TFIID, is required for efficient activation by SP1. This protein is also a component of other multisubunit complexes e.g. thyroid hormone receptor-(TR-) associated proteins which interact with TR and facilitate TR function on DNA templates in conjunction with initiation factors and cofactors. It also regulates p53-dependent apoptosis and it is essential for adipogenesis. This protein is known to have the ability to self-oligomerize. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
MED1;mediator complex subunit 1;PBP;CRSP1;RB18A;TRIP2;PPARBP;CRSP200;DRIP205;DRIP230;PPARGBP;TRAP220;mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 1;ARC205;TRIP-2;PPAR binding protein;PPAR-binding protein;PPARG binding protein;TR-interacting protein 2;p53 regulatory protein RB18A;thyroid receptor interacting protein 2;thyroid receptor-interacting protein 2;vitamin D receptor-interacting protein 230 kD;activator-recruited cofactor 205 kDa component;peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-binding protein;vitamin D receptor-interacting protein complex component DRIP205;thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein complex 220 kDa component;thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein complex component TRAP220
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- SUMO
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MED1-800H | Recombinant Human MED1, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 207-556aa | |
| MED1-9679M | Recombinant Mouse MED1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| MED1-01H | Recombiant Human MED1 Protein Lysate | HEK293 | Human |
|
||
| MED1-436H | Recombinant Human MED1 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Met1~Thr212 |
|
| MED1-4421H | Recombinant Human MED1 protein, His-SUMO-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&SUMO | 878-1031aa |
|
| MED1-5440M | Recombinant Mouse MED1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| MED1-5440M-B | Recombinant Mouse MED1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is MED1 Protein?
MED1, also known as Mediator complex subunit 1, is a protein that's really important for gene transcription in humans. It's part of this bigger group called the Mediator complex, which is like an essential team that helps RNA polymerase II do its job of turning genes on. Basically, MED1 acts like a helper or coactivator for various nuclear receptors. These receptors are like switches that need to be turned on for certain genes to get active, and MED1 makes sure this process goes smoothly. Without MED1, the communication between those switches and the genes might not work as it should, affecting how genes express themselves in the body.
What is the Function of MED1 Protein?
Imagine MED1 as a vital cog in the machinery of gene expression. This protein is a part of the Mediator complex, connecting transcription factors to RNA polymerase II, essentially helping switch genes on and off. It's got a big hand in hormone-related actions and plays a role in some cancers, especially breast and prostate, by fueling their growth. MED1's role isn't static; it's tweaked by chemical changes and mingles with other proteins like BAP1 in breast cancer, influencing how cells multiply and spread. Beyond that, it gets involved in immune responses and inflammation by managing cytokine-driven gene activity. So, MED1 is like a master regulator, orchestrating gene expression in reaction to diverse signals, impacting everything from cell behavior to disease.

Fig1. Transcription coactivator MED1 as a central crosstalk point of ER and HER2 pathways. (Gregory Bick, 2022)
MED1 Related Signaling Pathway
MED1 protein is like a jack-of-all-trades in the cell, playing a part in a range of signaling pathways that dictate cell behavior. It's a coactivator with nuclear receptors, crucial for hormone-driven processes, and also jumps into the JNK pathway, which is key for stuff like wound healing and cell growth. MED1 teams up with follistatin to affect the TGF-β superfamily signaling, influencing major pathways like Smad and MAPK, pivotal in cell differentiation and development. On top of that, MED1 is involved in immune responses and inflammation through autophagic lysosomal and innate immune signaling pathways. And then there's cancer—MED1 tends to go overboard in some types, especially hormone-related ones like breast and prostate cancer, fueling their growth. In short, MED1 acts like a master switch, orchestrating a web of signals in our cells that plays a role in everything from healing wounds to cancer cell progression.
MED1 Related Diseases
MED1 is a major player in various diseases, especially cancer and heart issues. In cancer, it's tied to how breast and prostate tumors grow and spread, and it's part of the DNA repair system—problems here can lead to things like hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome. For the heart, MED1 helps keep everything running smoothly, and without it, issues like dilated cardiomyopathy can crop up. On the neurological side, it's linked to cognitive changes post-stroke and is involved in genetic and neurodegenerative conditions. All in all, MED1's role in these various health problems makes it an important focus for research and potential treatments.
Bioapplications of MED1
Recombinant MED1 protein is a versatile tool in both research and potential therapy development. In scientific studies, MED1 helps unravel how gene transcription works, particularly its role in the Mediator complex that regulates RNA polymerase II-dependent genes, influencing cell differentiation and development. On the therapeutic side, MED1's potential as a target is explored, especially in breast cancer where its overexpression can lead to treatment resistance, like with tamoxifen. Understanding MED1 more could pave the way for tackling such resistance. Although not explicitly detailed, in the biotech industry, recombinant proteins like MED1 are often used to develop new drugs or advanced drug delivery systems and diagnostic tools due to their intricate interactions and functions. All in all, MED1 is a key protein in molecular biology and medicine, bridging research, therapy, and potential industrial applications.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Chen Wang, 2022
It turns out that BMP and TGF-β pathway issues are pretty important in both human and rodent pulmonary hypertension (PH). MED1 and KLF4 are big names in controlling how genes work in endothelial cells, but the way they mess with these pathways and end up causing pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is still a bit of a mystery. We looked into how MED1 and KLF4 mess with the genes BMPR2, ERG, and TGFBR2, which are key players in PH. Using high-throughput sequencing and computational techniques, alongside lab tests on endothelial cells and patient lung tissues, we discovered that MED1 and KLF4 work together to enhance these genes' expression by altering chromatin structure. MED1 levels were low in PAH patients and animal models, but boosting MED1 helped reduce PH symptoms, while its absence made mice more PH-prone.

Fig1. MED1 protein levels were measured by Western blot.

Fig2. Western blot analysis of MED1 and α-tubulin in lung endothelial cells (ECs) from EC-MED1−/− and their EC-MED1+/+ littermates.
Case Study 2: Harunori Honjoh, 2022
Homologous recombination (HR) is one of the main ways our cells fix broken DNA and has ties to how cancer can develop, with HR deficiency being a target for treatment. This study focused on a new HR factor, MED1, and its interaction with BRCA1. Using various lab techniques, we found that MED1 binds with BRCA1's BRCT domain and enhances its transcription by twofold. Without MED1, important HR genes like RPA and γH2AX struggled to reach DNA damage sites, and HR activity dropped. Additionally, cells lacking MED1 showed increased R-loop accumulations and related DNA damage.
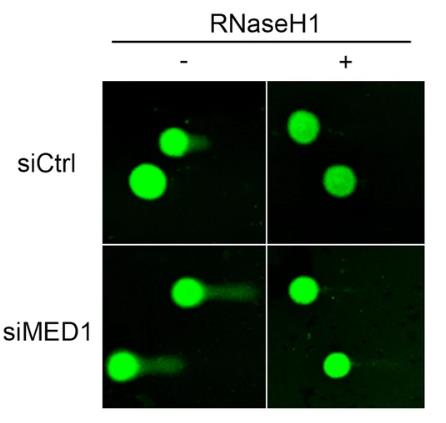
Fig3. Comet assay. Effects of MED1 on R-loop processing.

Fig4. Comet assay with U2OS cells. U2OS cells were seeded onto 6-well plates and transfected with siRNA for 24 h.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MED1-436H)
Involved Pathway
MED1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MED1 participated on our site, such as Thyroid hormone signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MED1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | NOTCH3,MED12,PLCB4,SRC,NOTCH4,ITGAV,ESR1,PIK3R3,MAP2K2,MED13 |
Protein Function
MED1 has several biochemical functions, for example, LBD domain binding,RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding,RNA polymerase II transcription cofactor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MED1 itself. We selected most functions MED1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MED1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| chromatin DNA binding | BCL6,ZIC2,HIST1H1B,SMAD3,MYOG,INSM1B,GRHL3,H2AFZ,FOXC2,EZH2 |
| peroxisome proliferator activated receptor binding | ASXL1,EP300,HMGA1,ASXL2,NR0B2,CREBBP,PRMT2,IKBKG,HMGA1-RS1,NFATC4 |
| chromatin binding | CREB3L1,ASH1L,SNAI2,DNMT3B,WDHD1,BRD4,COQ7,NR5A1,SP100,FOXC1A |
| receptor activity | TLR4,TLR1,IL18RAP,RNF139,EDA2R,CMKLR1,KLRB1B,CSF3R,VMN1R40,KIR2DL3 |
| vitamin D receptor binding | MED16,THRAP3,MED24,TAF11,MED30,SNW1,MED4,RUNX2B,MED14,RXRA |
| mediator complex binding | SMC3,NIPBL,SMC1A |
| transcription coactivator activity | TAF6L,ENY2,PMF1,SOX17,GRIP1,NRIP1,NFKBIB,ESRRB,COPS5,EDF1 |
| thyroid hormone receptor binding | TAF7,THRAP3,GTF2B,NR0B2,MED17,GAS2L1,OASL,NCOR1,PRMT2,NUP62 |
| retinoic acid receptor binding | ASXL1,CTBP2,RXRA,AASS,HMGA1-RS1,PRAMEF1,MED25,PRAMEF2,CNOT1,PRAMEF10 |
Interacting Protein
MED1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MED1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MED1.
MED10;CDK8;MED19;THRA
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


