Lysostaphin
-
Official Full Name
-
Overview
Lysostaphin is a Staphylococcus simulans metalloendopeptidase. It can function as an antimicrobial against Staphylococcus aureus. Lysostaphin is a 27 KDa glycylglycine endopeptidase, an antibacterial enzyme which is capable of cleaving the crosslinking pentaglycin bridges in the cell wall of Staphylococci. Lysotaphin was first isolated from a culture of Staphylococcus simulans by Schindler and Schuhardt in 1964. S. aureus cell walls contain high proportions of pentaglycin, making lysostaphin a highly effective agent against both actively growing and quiescent bacteria. Staphylococcal infections of both Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis continue to be a major issue in clinical settings, particularly those with implantable devices. Staphylococci cause a significant percentage of device infections, and like many other pathogens, rather than living as free planktonic cells within the host they have the ability to form a multilayered community of sessile bacteria cells known as a biofilm on implantable devices. Once a "Staphylococcal" biofilm has formed on an implanted medical device, it is difficult to disrupt due to its antibiotic resistance and protection against bacterial action. -
Synonyms
Lysostaphin;Staphylococcus simulans metalloendopeptidase;27 KDa;glycylglycine endopeptidase;antibacterial enzyme;Glycyl-glycine endopeptidase;Iss
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lysostaphin-90 | Recombinant Lysostaphin | E.coli | Non | |||
| Lysostaphin-91S |
Active Native Staphylococcus staphylolyticus Lysostaphin
|
Staphylococcus Staphylolyticus | Staphylococcus staphylolyticus | Non |
|
Background
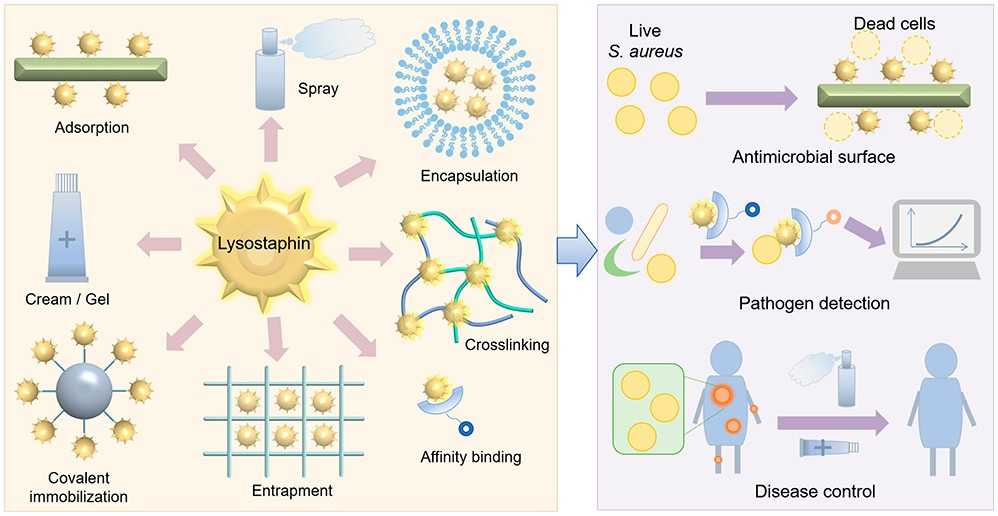
Fig1. Engineering and potentiation toward better applications of lysostaphin. (Jian Zha, 2022)
What is LYSOSTAPHIN protein?
Lysotaphin was first isolated from a culture of Staphylococcus simulans by Schindler and Schuhardt in 1964. Lysostaphin is a Staphylococcus simulans metalloendopeptidase. It can function as an antimicrobial against Staphylococcus aureus. Lysostaphin is a 27 KDa glycylglycine endopeptidase, an antibacterial enzyme which is capable of cleaving the crosslinking pentaglycin bridges in the cell wall of Staphylococci. Lysostaphin consists of an n-terminal catalytic domain and a C-terminal peptidoglycan-binding domain. It exerts its bactericidal effect by hydrolyzing peptidoglycan bonds in the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus.
What is the function of LYSOSTAPHIN protein?
LYSOSTAPHIN rapidly triggers the cleavage of bacteria, including planktic cells and biofilm cells, by hydrolyzing the pentaglycine cross-linked structure in the S. aureus cell wall peptidoglycan. It has potential applications in agriculture, the food industry and the pharmaceutical industry, especially in the fight against antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection has shown enhanced activity. LYSOSTAPHIN acts as a protein antibiotic that shows activity against several antibiotic-resistant strains of S. aureus, including MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) and VRSA (Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). In addition, LYSOSTAPHIN has been engineered to increase its potency, reduce immunogenicity, extend action time, and improve its stability and durability through formulation and immobilization, as well as for low-cost industrial production and field biological control through recombinant expression.
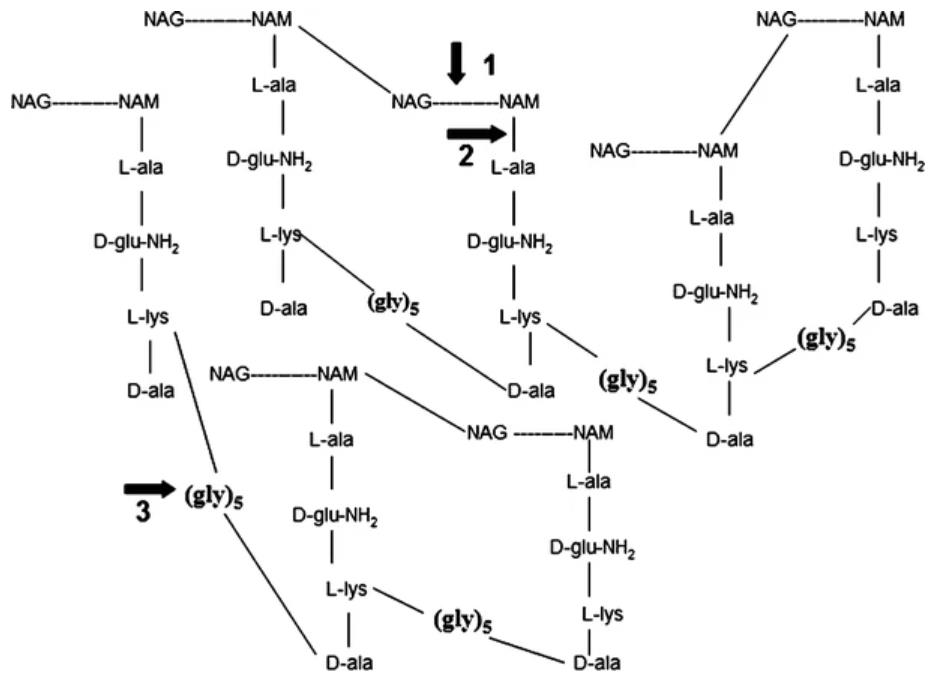
Fig2. Enzymatic activities of lysostaphin. (Jaspal K Kumar, 2008)
LYSOSTAPHIN Related Diseases
Lysostaphin is an enzyme with antimicrobial properties that is primarily used against a variety of infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant strains, i.e., MRSA), including skin infections such as eczema, cellulitis, impetigo, and pyoderma; Endocarditis, an infection of the heart valves; Osteomyelitis, an infection of the bones; And medical device-associated infections caused by biofilms. In addition, Lysostaphin has also shown potential in reducing S. aureus nasopharyngeal colonization and in treating mastitis in cows and S. aureus infections in newborns.
Bioapplications of LYSOSTAPHIN
Lysostaphin has shown therapeutic potential due to its activity against several antibiotic-resistant strains of S. aureus, including methicillin-resistant strains (MRSA). It can effectively eliminate floating cells and stationary bacteria, as well as inhibit S. aureus growth in biofilms, which is an important property in many antibiotics that require active cell metabolism to be effective. In different animal models, Lysostaphin has shown therapeutic potential for a variety of infections caused by resistant S. aureus, including wound infections, intraocular infections, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, and bovine mastitis.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Kuan-Jung Chen, 2022
Fusing cellulose binding domain (CBD) to mLst significantly reduced the insoluble expression of mLst in E. coli. Employing mLst-cleavable peptides as fusion linkers leaded to an effective self-cleavage expression that CBD and mLst could be completely cleaved off from the fusions during the expression process. The presence of residue linker fragment at N-terminus of the cleaved-off mLst strongly inhibited the cell lytic activity of the recovered recombinant mLst, and only ~ 50% of the wild-type mLst activity could be retained. Intact CBD-Lst fusions were obtained when uncleavable peptide linkers were employed. With CBD at N-terminus of mLst, the intact fusion completely lost its cell lytic activity but the dipeptidase activity still remained. In contrast, approximately 10% cell lytic activity of mLst still could be maintained for the fusion with CBD at C-terminus of mLst.
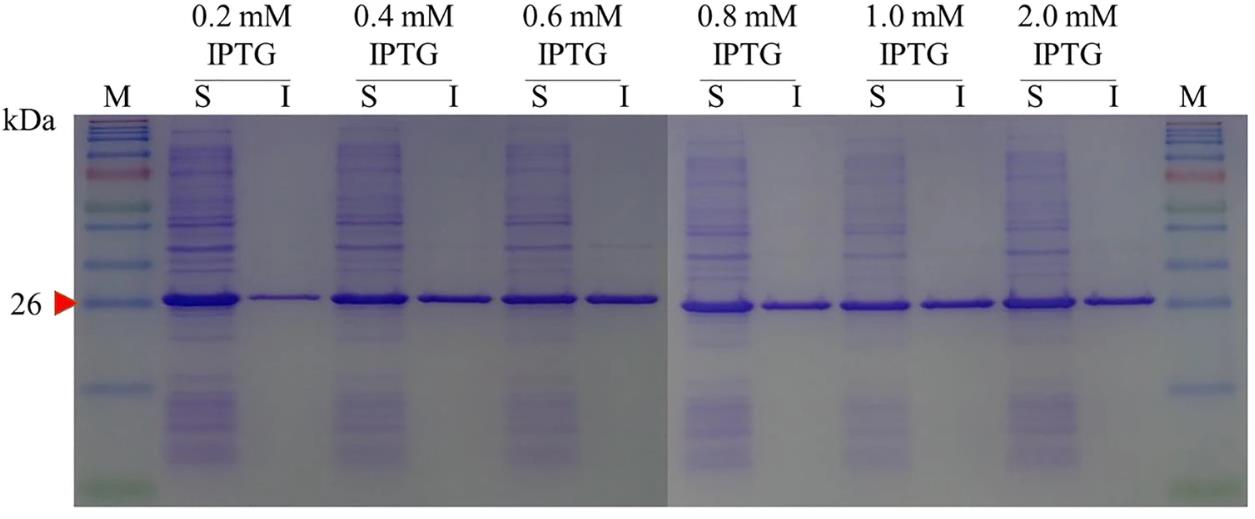
Fig1. SDS-PAGE analysis of expressed mLst with respect to IPTG induction concentration.
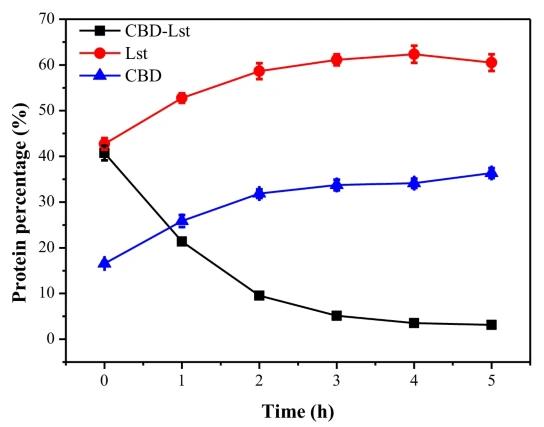
Fig2. The fraction of component proteins during in vitro self-cleavage of CBD-Lst.
Case Study 2: Somayeh Sadeghi, 2019
Staphylococcus aureus is the most common persistent pathogen in humans, so development of new formulations to combat pathogen invasion is quite necessary. In the current study, for the first time, the synergistic activity of recombinant lysostaphin and LL-37 peptide was studied against S. aureus. Moreover, different niosomal formulations of the peptide and protein were prepared and analyzed in terms of size, shape, zeta potential, and entrapment efficiency. Also, a long-term antibacterial activity of the best niosomal formulation and free forms was measured against S. aureus in vitro. The results showed that the optimal niosomal formulation was obtained by mixing the surfactants, cholesterol, and dicetylphosphate at a ratio of 47:47:6, respectively. They showed uniform spherical shapes with the size of 565 and 325 nm for lysostaphin and LL-37, respectively. The lysostaphin/LL-37 niosomal formulation synergistically inhibited growth of S. aureus for up to 72 hours. Cytotoxicity assay specified that lysostaphin/LL-37 niosomal combination had no deleterious effect on normal fibroblast cells at effective antimicrobial concentrations.
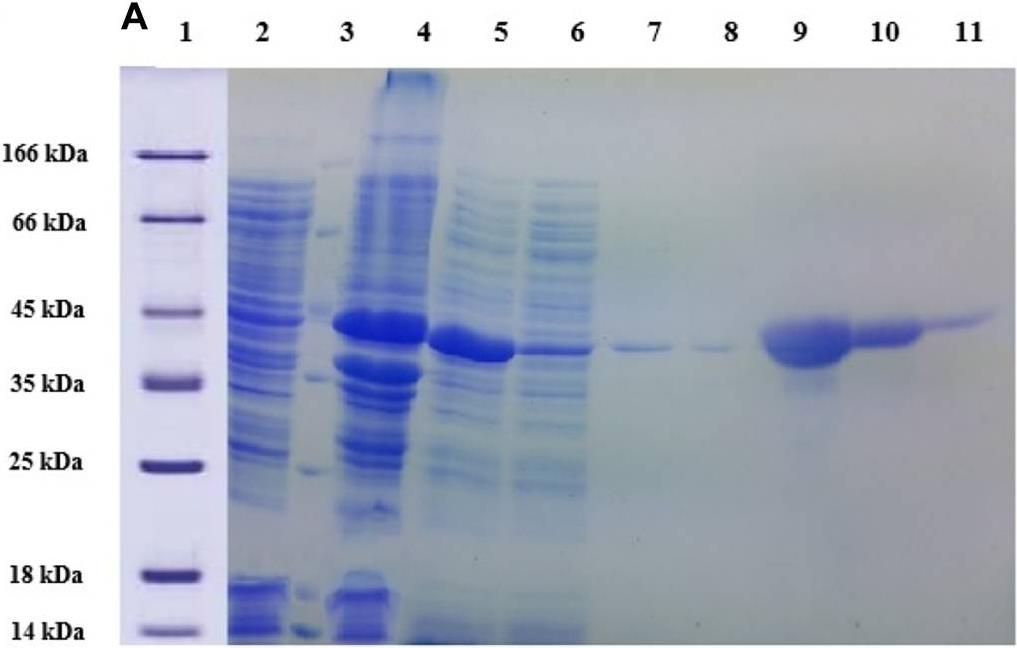
Fig3. SDS PAGE (12%) gel showing expression and purification of lysostaphin.
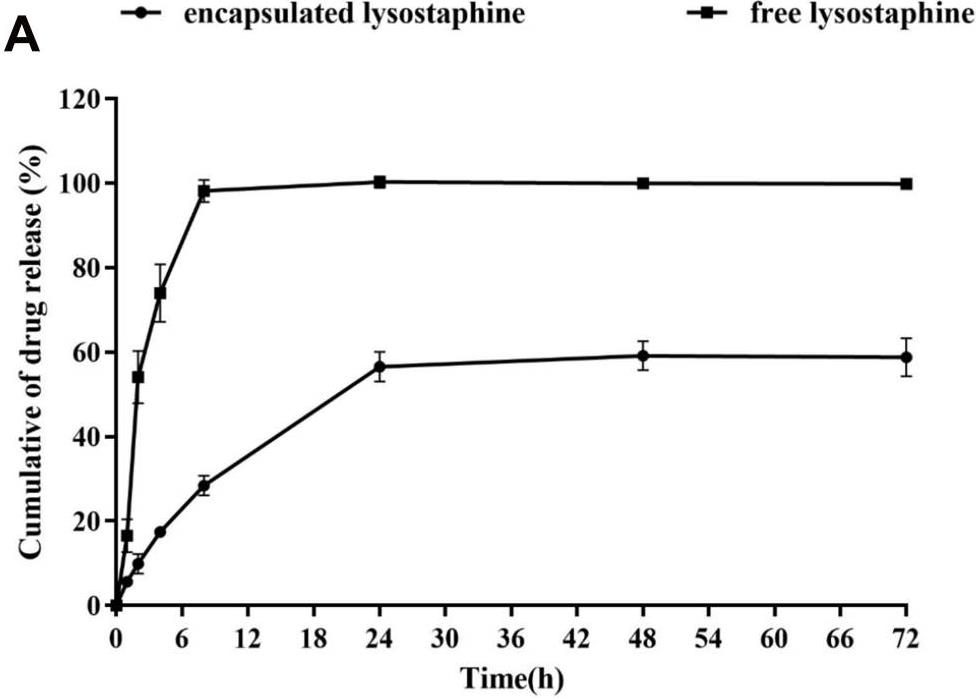
Fig4. In vitro release profile of lysostaphin from niosomal formulation containing surfactants.
Involved Pathway
Lysostaphin involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Lysostaphin participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Lysostaphin were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
Lysostaphin has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Lysostaphin itself. We selected most functions Lysostaphin had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Lysostaphin. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
Lysostaphin has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Lysostaphin here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Lysostaphin.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


