LBR
-
Official Full Name
lamin B receptor -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the ERG4/ERG24 family. It localized in the nuclear envelope inner membrane and anchors the lamina and the heterochromatin to the membrane. It may mediate interaction between chromatin and lamin B. Mutations of this gene has been associated with autosomal recessive HEM/Greenberg skeletal dysplasia. Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
LBR;lamin B receptor;PHA;LMN2R;TDRD18;DHCR14B;lamin-B receptor;tudor domain containing 18;integral nuclear envelope inner membrane protein
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is LBR Protein?
LBR, which stands for Lamin B Receptor, plays a big role in the inner nuclear membrane. Think of it as a helpful anchor that keeps everything in place by attaching chromatin to the nuclear envelope. But LBR does more than just hold things together; it’s involved in organizing chromatin and controlling genes, which are crucial during cell division. When LBR doesn't work right, it can cause issues like Pelger-Huët anomaly, messing with the shape and function of blood cells. Scientists are really keen on studying LBR because it’s so important for how the nucleus is organized and its links to genetic disorders.What is the Function of LBR Protein?
LBR, or Lamin B Receptor, is crucial for keeping the nuclear envelope intact by anchoring chromatin to the inner nuclear membrane. It helps organize chromatin and regulates genes, which supports normal cell division and growth. LBR’s function is vital for maintaining nuclear structure and plays a role in cell cycle regulation. Disruptions in LBR can cause issues like Pelger-Huët anomaly, affecting blood cells. Its importance in nuclear architecture and genetic influence makes it a significant focus for research, especially concerning genetic disorders and nuclear integrity.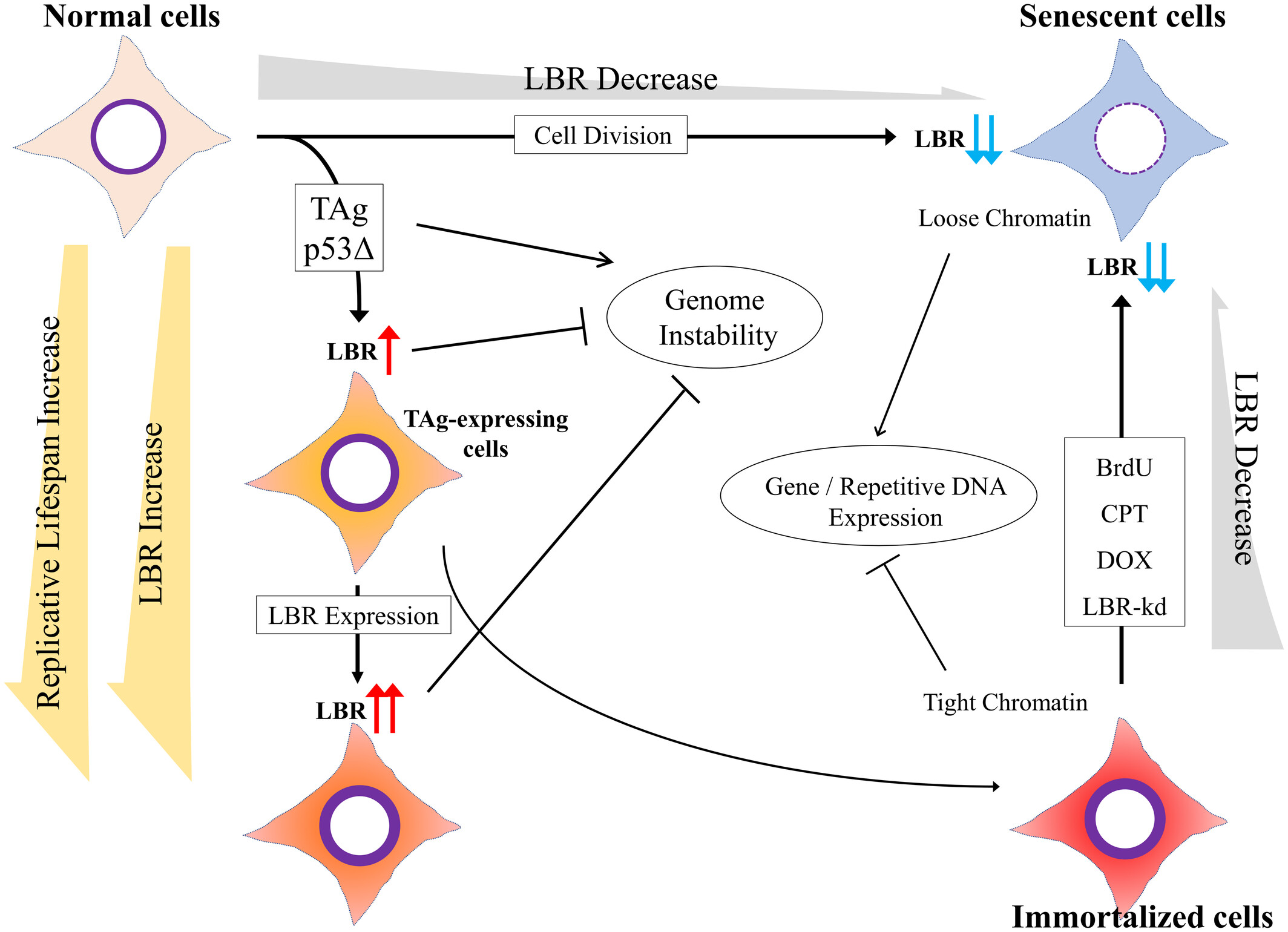
Fig1. Hypothetical model for the role of LBR in cellular immortalization. (Atsuki En, 2024)
LBR Related Signaling Pathway
The Lamin B receptor (LBR) is a crucial piece in the intricate puzzle of cellular structure, specifically within the nuclear membrane in human cells. It acts as an anchor for both the nuclear lamina and heterochromatin, providing essential stability to the nucleus. Mutations in the LBR gene can lead to various genetic conditions, including Greenberg skeletal dysplasia and Pelger-Huet anomaly. Beyond its structural duties, LBR interacts with numerous proteins and chromatin elements, playing a significant role in processes like cholesterol and lipid metabolism. These interactions highlight its versatile nature within cellular functions. Exploring LBR-related pathways not only offers insights into its contribution to maintaining nuclear integrity but also its potential link to genetic disorders, making it a focal point for ongoing scientific inquiry.LBR Related Diseases
Lamin B receptor (LBR) is tied to some interesting genetic conditions, mainly Greenberg skeletal dysplasia and Pelger-Huet anomaly. So, what's the story here? Greenberg skeletal dysplasia is pretty rare and tends to take a toll on bone formation, which you can actually pick up on even before birth. Then there's Pelger-Huet anomaly, where your white blood cells look a bit funky under the microscope—a simple blood test can reveal this odd nuclear shape. Both these conditions are due to glitches in the LBR gene, impacting how things work inside the cell nucleus. Scientists are keen on digging deeper into these LBR-related pathways to truly get what’s going on with these genetic quirks and maybe find some answers or treatments down the line.Bioapplications of LBR
The Lamin B receptor (LBR) is stirring up quite a buzz in biology circles! Beyond its day job of keeping the nucleus well-organized, LBR is being explored in some exciting ways. Take genetic research—LBR helps scientists figure out how our genes get switched on or off, a handy thing for tackling genetic conditions. Then there’s its link with cholesterol, which could mean fresh ideas for dealing with cholesterol issues. And don’t forget stem cells! Researchers are curious about how LBR might play a part in regenerating tissues or aiding cell therapy. So, LBR might just be opening a whole new world of possibilities in biomedical research.Case Study
Case Study 1: Patil S. et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2023
Lamin B Receptor (LBR) is crucial for nuclear structure, but reducing LBR leads to mitotic issues and chromosomal losses. LBR depletion causes nuclear blebs and micronuclei, with frequent chromosomal loss, and larger tumor growth in mice. This highlights LBR's role as a tumor suppressor. It interacts with telomere factors, and its loss boosts TRF1 levels. Knocking down TRF1 alongside LBR depletion helps keep chromosome stability, suggesting LBR and TRF1 together maintain stability in colorectal cancer cells.-
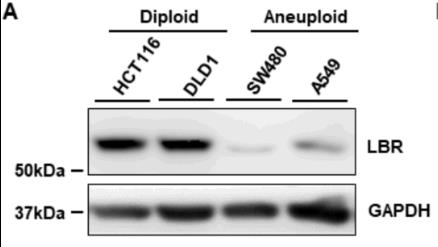 Fig1. Representative western blots to assess the expression levels of LBR across cancer cell lines.
Fig1. Representative western blots to assess the expression levels of LBR across cancer cell lines. -
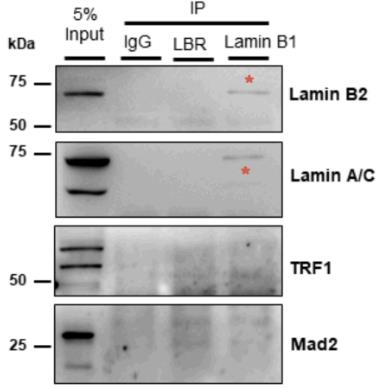 Fig2. Representative co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) using anti-LBR and anti-Lamin B1 antibodies.
Fig2. Representative co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) using anti-LBR and anti-Lamin B1 antibodies.
Case Study 2: En A. et al. FEBS Open Bio. 2020
Cellular senescence involves halted cell growth and is linked to protein accumulation due to decreased proteasome activity. MG132, a proteasome inhibitor, induces senescence by misplacing and reducing Lamin B Receptor (LBR), crucial for organizing chromatin. Overexpressing LBR counteracts this effect. These findings indicate that disrupted LBR function, triggered by proteasome inhibition, induces senescence through chromatin misregulation.-
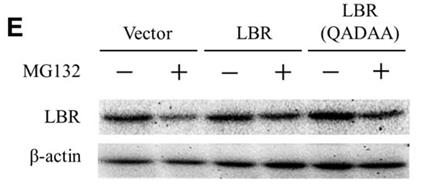 Fig3. HeLa cells were transfected with an empty vector, pCMV-LBR or pCMV-LBR(QADAA), and treated with MG132 for 4 days.
Fig3. HeLa cells were transfected with an empty vector, pCMV-LBR or pCMV-LBR(QADAA), and treated with MG132 for 4 days. -
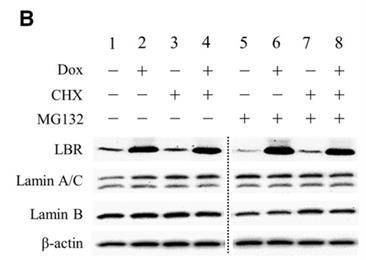 Fig4. Protein lysates were prepared from HeLaT-LBR cells.
Fig4. Protein lysates were prepared from HeLaT-LBR cells.
Involved Pathway
LBR involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways LBR participated on our site, such as Cholesterol biosynthesis,Gastric cancer network 2,Metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with LBR were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Metabolism of lipids and lipoproteins | SLC25A1,CYP2U1,FAAH2B,HSD17B11,APOA4A,AKR1C2,CERS4A,MED31,NFYAL,ACOT9.1 |
| Gastric cancer network 2 | BRIX1,PLAC8,TOP2A,CHTF18,SNURF,MTDH,S100A6,SNRPN,DSCC1,CEBPZ |
| Metabolism | LYPLA1,PTPMT1,B3GNT1,MED26,APOA4B.1,DSEL,CYP2D6,YAP1,SLC4A1A,DPEP1 |
| cholesterol biosynthesis II (via 24,25-dihydrolanosterol) | EBP,DHCR24 |
| cholesterol biosynthesis I | EBP,DHCR24,DHCR7 |
| Cholesterol biosynthesis | ARV1,CYP51A1,DHCR7,SREBF2,EBP,PMVK,DHCR24 |
| cholesterol biosynthesis III (via desmosterol) | EBP |
-
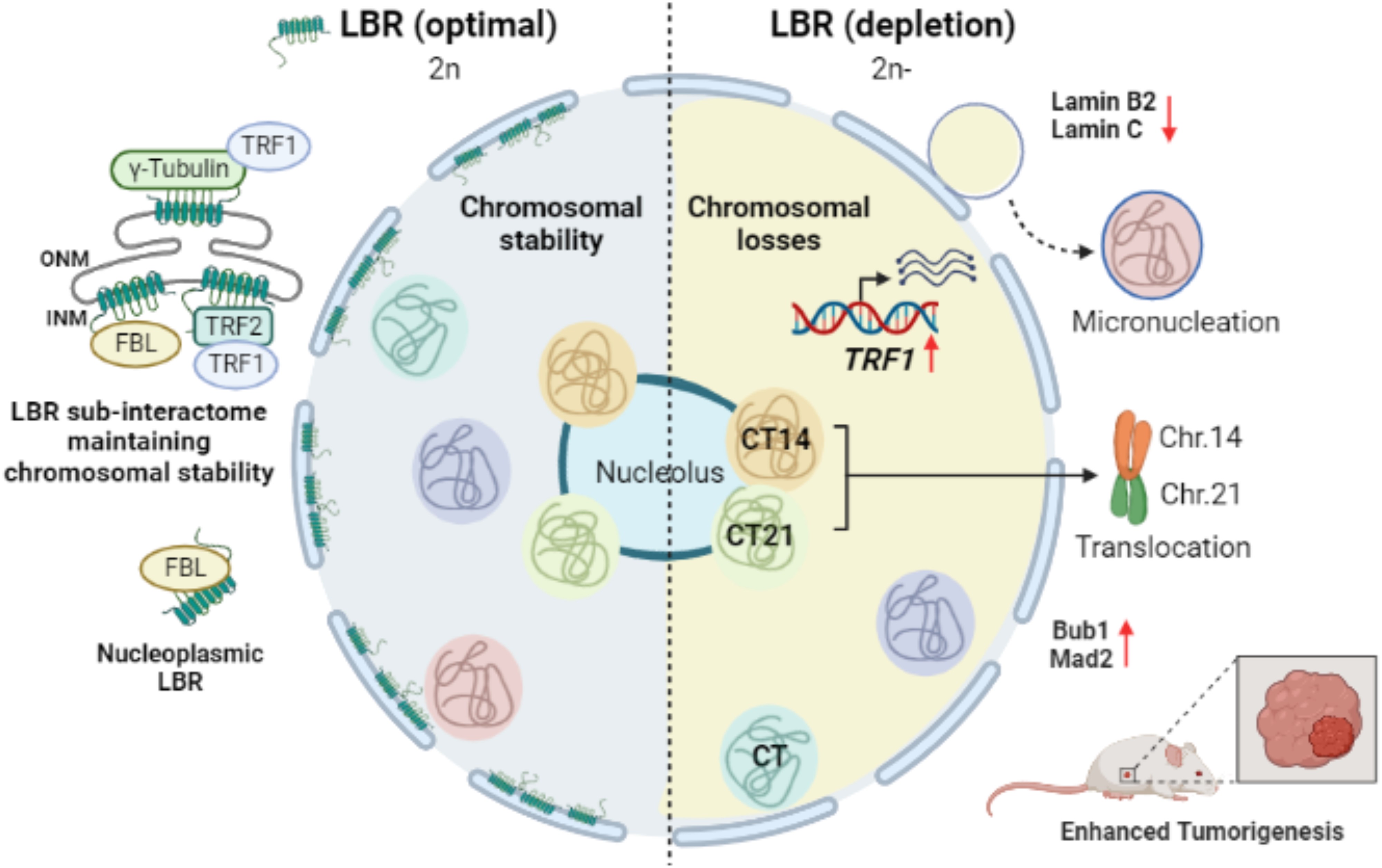 Fig1. LBR protects the genome from chromosomal aberrations and tumorigenesis. (Shalaka Patil, 2023)
Fig1. LBR protects the genome from chromosomal aberrations and tumorigenesis. (Shalaka Patil, 2023) -
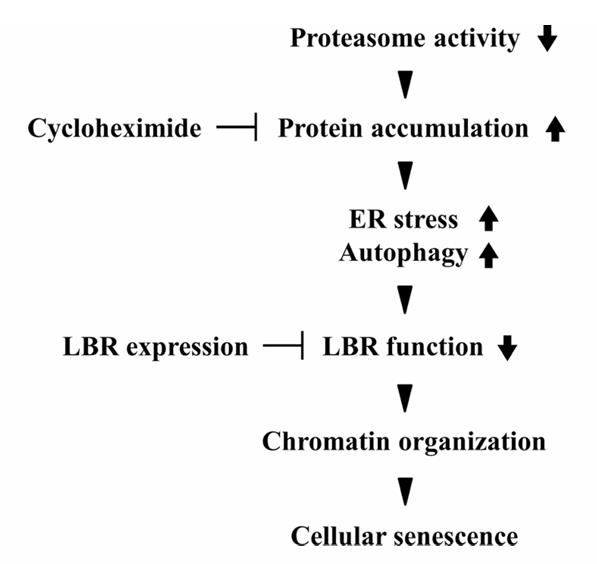 Fig2. Schematic illustration of the model for cellular senescence induced by proteasome inhibition. (Atsuki En, 2020)
Fig2. Schematic illustration of the model for cellular senescence induced by proteasome inhibition. (Atsuki En, 2020)
Protein Function
LBR has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,chromo shadow domain binding,lamin binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by LBR itself. We selected most functions LBR had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with LBR. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| lamin binding | PLCB1,TMEM201,PPP4C,BNIP3L,IFI27,NARF,SUN1,TOR1AIP1,TMPO,SUN2 |
| DNA binding | POLD2,ZFAND5A,POLE4,MBD3B,ZBTB44,NR6A1,ZNF48,RBPJ,UNCX,ZFP292 |
| oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor | TM7SF2,SRD5A3,BDH2,DHCR24 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | CCBL2,FKBP4,ALG13,HNRPLL,ASS1,SRFBP1,SAMD4,RPL14,NOL11,ELAVL1 |
| oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors | GCDHB,SRD5A2B,TECRL,TECRL2B,ACOXL,SRD5A3,TM7SF2,TECR,TECRB,GCDHA |
| chromo shadow domain binding | TRIM28,NIPBL,SP100,ATRX,CHAF1A |
| protein binding | EPHB4,CCT6A,GPR37L1,SIPA1L2,IRF7,LRRC47,CBFA2T2,WAPAL,TOMM22,CALCOCO1 |
Interacting Protein
LBR has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with LBR here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of LBR.
CBX3;CBX5;YWHAG;SRPK1;7242199;MYC;YWHAB;PHLDA3;E2F3;ARRB2;CLK3;LRRK2
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Goans, RE; Iddins, CJ; et al. APPEARANCE OF PSEUDO-PELGER HUET ANOMALY AFTER ACCIDENTAL EXPOSURE TO IONIZING RADIATION IN VIVO. HEALTH PHYSICS 108:303-307(2015).
- Cicinelli, E; Matteo, M; et al. Prevalence of chronic endometritis in repeated unexplained implantation failure and the IVF success rate after antibiotic therapy. HUMAN REPRODUCTION 30:323-330(2015).


