GNS
-
Official Full Name
glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase -
Overview
The product of this gene is a lysosomal enzyme found in all cells. It is involved in the catabolism of heparin, heparan;sulphate, and keratan sulphate. Deficiency of this enzyme results in the accumulation of undegraded substrate and the;lysosomal storage disorder mucopolysaccharidosis type IIID (Sanfilippo D syndrome). Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIID is;the least common of the four subtypes of Sanfilippo syndrome. -
Synonyms
GNS;glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase;N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase;N acetylglucosamine 6 sulfatase;Sanfilippo disease IIID;N28088;2610016K11Rik;AU042285;C87209;G6S;Glucosamine (N-acetyl) 6 sulfatase;Glucosamine 6 sulfatase;Glucosamine-6-sulfatase;GNS_HUMAN;MGC21274;N acetylglucosamine 6 sulfatase [Precursor]
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Mouse
- CHO
- Human Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
Background
What is GNS Protein?
GNS, or glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase, is no protein star but it does work on our bodies to degrade complex sugars. It functions to preserve and recycle so-called glycosaminoglycans — the constituent of connective tissues. People might be told about GNS when there are some genetic disorders where that enzyme isn't working properly and those sugars accumulate. GNS is important enough for some diseases to be a real talking point – although not always around the dinner table.
What is the Function of GNS Protein?
Glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase, or GNS, is a body enzyme essential for degrading highly complex sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans in connective tissue and joints. You can think of GNS as a natural ally to make sure these sugar chains don't accumulate too much and lead to disorder. Without a functioning GNS, the body accumulates chemicals that could be a source of disease, such as Sanfilippo syndrome type D, a rare genetic disorder. GNS is fundamentally concerned with the maintenance of normal cell behaviour and tissue wellbeing.
GNS Related Signaling Pathway
GNS (glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase) is a protein in a class of molecules that breakdown complicated molecules. It is part of the body's recycling machine, which dissolves and repurposes materials in our cells. If something snafus this protein, there can be a pooling of junk in the body (as occurs with some genetic conditions). For those of us in the lysosomal storage disorder camp, GNS is what lets us see how we might address these accumulation problems.
GNS Related Diseases
GNS protein is associated with a handful of conditions, mainly a syndrome known as Sanfilippo syndrome type D, a category of diseases known as lysosomal storage disorders. This is when the body doesn't have an enzyme that breaks down certain sugar molecules, and therefore they build up, especially in the brain and nervous system. Symptoms generally manifest as early as childhood. Typically they involve development delay, behaviour issues and eventually, skill loss. Unfortunately, over time, this can even interfere with walking and other aspects of our bodies and become extremely problematic. For now, treatment is generally symptomatic and goal-directed to enhance patients' quality of life.GNS protein is associated with a handful of conditions, mainly a syndrome known as Sanfilippo syndrome type D, a category of diseases known as lysosomal storage disorders. This is when the body doesn't have an enzyme that breaks down certain sugar molecules, and therefore they build up, especially in the brain and nervous system. Symptoms generally manifest as early as childhood. Typically they involve development delay, behaviour issues and eventually, skill loss. Unfortunately, over time, this can even interfere with walking and other aspects of our bodies and become extremely problematic. For now, treatment is generally symptomatic and goal-directed to enhance patients' quality of life.
Bioapplications of GNS
Recombinant GNS (Glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatases) proteins have tremendous potential in several different areas. These proteins have been commonly studied in biology and disease – particularly in lysosomal storage disorders such as Sanfilippo Syndrome, where GNS deficiency is a central concern. Recombinant proteins could be useful for therapeutic enzymes, or as a platform for drug production and biochemical research at the industrial scale, because they represent a more cost-effective and predictable method to synthesize complex proteins in large quantities. Such tools are used to develop medical treatments and make more accurate predictions about biological processes.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Kai-Wen Cheng, 2021
ERT is one effective treatment for lysosomal storage disorders. Enzymes for ERT are normally produced from cell cultures of mammals, but lysosomal enzymes in good enough quality are hard to obtain (low-secretion). To induce more Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell production, they ran a number of synthetic signal peptides against two synthetic human lysosomal enzymes. Adjusting signal peptides could regulate secretion, they discovered, and some, such as murine Ig or human chymotrypsinogen B1, were particularly good for modulating secretion of these enzymes.

Fig1. The intracellular and extracellular expression of rhNAGLU and rhGNS expression in cells.

Fig2. rhGNS secretion was normalized respect to transfection efficiency.
Case Study 2: Feng Wang, 2021
We can't cure Mucopolysaccharidosis IIID (MPS IIID, or Sanfilippo syndrome type D): an absence of the enzyme -N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase (GNS). Symptoms mainly impact the brain, so any treatments will have to penetrate the blood-brain barrier to act. Step forward: they tried enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) by implanting recombinant human GNS (rhGNS) into newborn mice's brains using MPS IIID. They could manufacture this enzyme in laboratory cells and it remained stable in brain-like fluids. When given, rhGNS restored enzyme function to the brain tissues, and appeared to reduce harmful substances that usually accumulate in affected cells.

Fig3. SDS-PAGE of purified rhGNS.
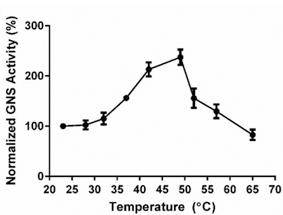
Fig4. Purified rhGNS activity was assessed at different temperatures to assess its thermal stability.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GNS-5101H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GNS-4204H)
Involved Pathway
GNS involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GNS participated on our site, such as Glycosaminoglycan degradation,Metabolic pathways,Lysosome, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GNS were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Lysosome | CTSA,ATP6V0A2,ASAH1A,GUSB,M6PR,PSAPL1,SMPD1,ASAH1B,ASAH1,LITAF |
| Glycosaminoglycan degradation | IDS,SPAM1,GUSB,HPSE2,GLB1,HYAL2,GNSB,GNSA,HYAL4,ARSB |
| Metabolic pathways | ackA,GOT2,POLR3A,ALOX5A,POLR2G,aLA,MBOAT2B,QPRT,AADAT,CMASA |
Protein Function
GNS has several biochemical functions, for example, N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase activity,metal ion binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GNS itself. We selected most functions GNS had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GNS. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | TACSTD2,USP42,CCDC55,NAMPT,KCNQ5,RBM12B,PIPOX,PPP1CB,ELANE,NRBF2 |
| N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase activity | GNSB,SULF1,GNSA,SULF2 |
| sulfuric ester hydrolase activity | SULF2B,ARSA,GNSA,SULF2A,STS,GNSB,SGSH,GALNS |
| metal ion binding | ZNF615,ANTXR1,RPP21,ZHX1,WDFY3,ZBTB42,NEURL1B,ZNF776,EYA3,ZFP553 |
Interacting Protein
GNS has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GNS here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GNS.
ABL1;FYN;SRC;NCK1;GRB2;q8clp4_yerpe;Cep152;KIF2A;FGFR1OP;cona_canen;Msn;Prkaa1;PARD6B
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Couser, WG; Johnson, RJ; et al. The etiology of glomerulonephritis: roles of infection and autoimmunity. KIDNEY INTERNATIONAL 86:905-914(2014).
- Danovi, D; Folarin, A; et al. A High-Content Small Molecule Screen Identifies Sensitivity of Glioblastoma Stem Cells to Inhibition of Polo-Like Kinase 1. PLOS ONE 8:-(2013).


