CTBP1
-
Official Full Name
C-terminal binding protein 1 -
Overview
CtBP1 (C-terminal binding protein 1) was first recognized as a cellular factor that interacts with the C-terminal portion of adenovirus E1A, a protein involved in the transcriptional regulation of key cellular genes (1). CtBP1 is able to regulate gene act -
Synonyms
CTBP1;C-terminal binding protein 1;C-terminal-binding protein 1;BARS;brefeldin A ribosylated substrate;brefeldin A-ribosylated substrate;MGC104684
Recombinant Proteins
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Human
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is CTBP1 Protein?
CTBP1, or C-terminal binding protein 1, is like a multitasking protein in the cell. It plays several roles, mainly acting as a corepressor in the nucleus where it influences gene expression. By binding to specific transcription factors, CTBP1 can turn down the expression of certain genes, impacting processes like cell growth, development, and cell death. Its ability to regulate these processes makes it significant in normal cellular functions and also in diseases. In cancer, for example, CTBP1 might help tumor cells survive by repressing genes that would normally induce cell death. This dual role in promoting or inhibiting gene expression makes CTBP1 an interesting target for research, especially for therapies that could alter its activity to treat diseases.What is the Function of CTBP1 Protein?
CTBP1 is like a switchboard operator inside cells. It primarily works as a transcriptional corepressor, meaning it helps turn down or silence genes when needed. By hooking up with various transcription factors, CTBP1 can adjust gene expression, affecting crucial cellular processes like growth, division, and survival. It’s pretty essential in normal development and helps maintain balance in cells. In some cases, though, it can contribute to diseases. For example, in cancer, CTBP1 can interfere with normal cell death, letting tumor cells keep growing. Its role in balancing gene activity makes it a key focus for researchers looking at ways to treat conditions where gene regulation goes off track.CTBP1 Related Signaling Pathway
CTBP1 is involved in several signaling pathways that control cell behavior. Think of it as a master regulator that partners up with other proteins to manage how genes are expressed. One key pathway it’s tied to is the Wnt signaling pathway, which is crucial during embryonic development and for cell growth. In this pathway, CTBP1 helps regulate the balance between cell proliferation and death. It acts by repressing or activating genes based on the context, influencing how cells react to signals. In some cancers, this ability to modulate gene expression can go awry, leading CTBP1 to assist in tumor growth by shutting down genes that would normally suppress tumors. Understanding CTBP1’s role in these pathways is vital for grasping how it might contribute to diseases and how it can be targeted for therapies.CTBP1 Related Diseases
CTBP1 is linked to a variety of diseases because of its role in gene regulation. One notable disease area is cancer. In many types of cancer, CTBP1 can help tumor cells survive and grow by turning off genes that would typically control cell death or limit growth. This makes it easier for the cancer to progress. It’s not just cancer, though; CTBP1 is also associated with developmental disorders. Since it’s involved in crucial developmental pathways, any imbalance in its function can potentially lead to issues in how the body and brain develop. Researchers are exploring CTBP1 as a target for new treatments, looking at ways to tweak its activity to restore normal cell function and potentially halt disease progression. Understanding its impact across different diseases could open doors to novel therapeutic strategies.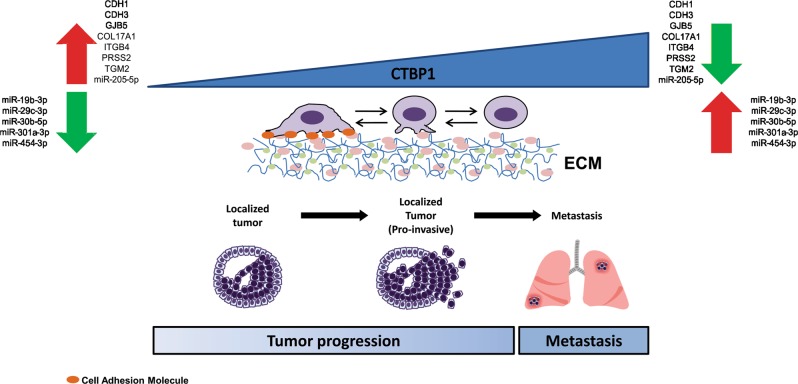
Fig1. As PCa progresses CTBP1 expression will increase and, in the case of MeS, its activity will also be enhanced. (Guillermo Nicolás Dalton, 2019)
Bioapplications of CTBP1
CTBP1 is a key player in both developmental biology and disease processes. It's instrumental in regulating genes during embryonic development and is also implicated in cancer, sometimes aiding tumor growth, making it a target for cancer research. Additionally, CTBP1 is linked to neurological disorders like Alzheimer's and Parkinson’s, as scientists explore its role in gene regulation within the brain. So, CTBP1 is crucial across various fields, holding potential insights into development, cancer treatment, and neurological health.Case Study
Case Study 1: Liang Y. et al. Clin Transl Med. 2021
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a tough cancer, often diagnosed late or spread to lymph nodes. Circular RNA, circIMMP2L, is found in higher levels in tumors and blood of advanced ESCC patients, linked to worse survival rates. It's a marker for lymph node metastasis, even in early stages. Reducing circIMMP2L can slow down ESCC progression. It works by interacting with CtBP1 in the cell's nucleus, affecting genes like E-cadherin and p21, which are involved in cell growth and metastasis.-
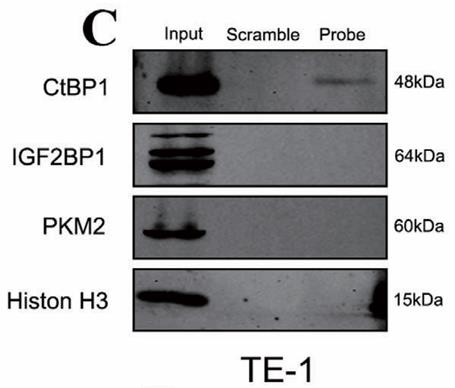 Fig1. Western blot analysis of CtBP1, IGF2BP1, and PKM2 after pull-down assay showing CtBP1 specifically interacting with circIMMP2L.
Fig1. Western blot analysis of CtBP1, IGF2BP1, and PKM2 after pull-down assay showing CtBP1 specifically interacting with circIMMP2L. -
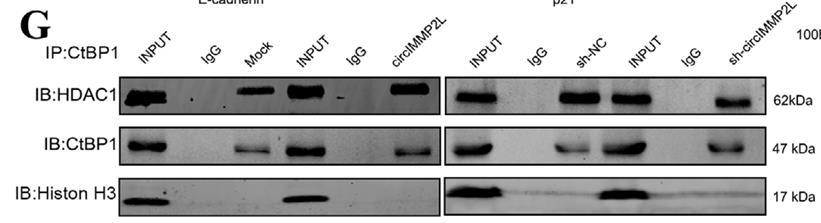 Fig2. Co-IP and western blot assays showing differential interaction levels between CtBP1 and HDAC1.
Fig2. Co-IP and western blot assays showing differential interaction levels between CtBP1 and HDAC1.
Case Study 2: Ding B. et al. Cell Death Dis. 2020
CtBP2 is high in aggressive ovarian cancer, like HGSOC. It's unclear if HGSOC relies on CtBP2 or its partner CtBP1. These proteins block cell death by silencing death receptors DR4/5. Removing CtBP1/2 boosts DR4/5 levels, activating apoptosis with caspase 8, varying by cell type. This also makes HGSOC cells more sensitive to TRAIL, which induces cell death. CtBP1/2 act as repressors, binding to DR4/5 promoters to shut them down, needing both to work.-
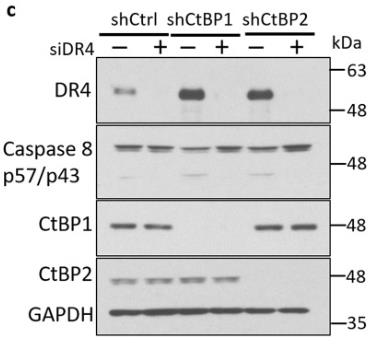 Fig3. KURAMOCHI cells were treated with indicated siRNAs along with shRNAs.
Fig3. KURAMOCHI cells were treated with indicated siRNAs along with shRNAs. -
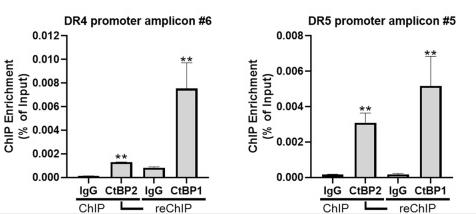 Fig4. ChIP-reChIP assay showing CtBP1/2 occupancy at the indicated regions of the DR4/5 promotors.
Fig4. ChIP-reChIP assay showing CtBP1/2 occupancy at the indicated regions of the DR4/5 promotors.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CTBP1-2053H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CTBP1-2053H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CTBP1-3399H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CTBP1-3399H)
Involved Pathway
CTBP1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CTBP1 participated on our site, such as Chronic myeloid leukemia,Deactivation of the beta-catenin transactivating complex,Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CTBP1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Deactivation of the beta-catenin transactivating complex | RBBP5,SOX4B,BCL9L,PYGO1,TLE4,BCL9,SOX6,SOX32,TLE1,CBY1 |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | TGFBR2,KRAS,GRB2,BCL2L1,HRAS,CRKL,TGFB1,CBLB,AKT1,GAB2 |
| Diseases of signal transduction | HEY2,MIB1,CTBP2,KREMEN2,DERL2,OPN1SW,LRRFIP1,TNKS2,CUX1,RLBP1 |
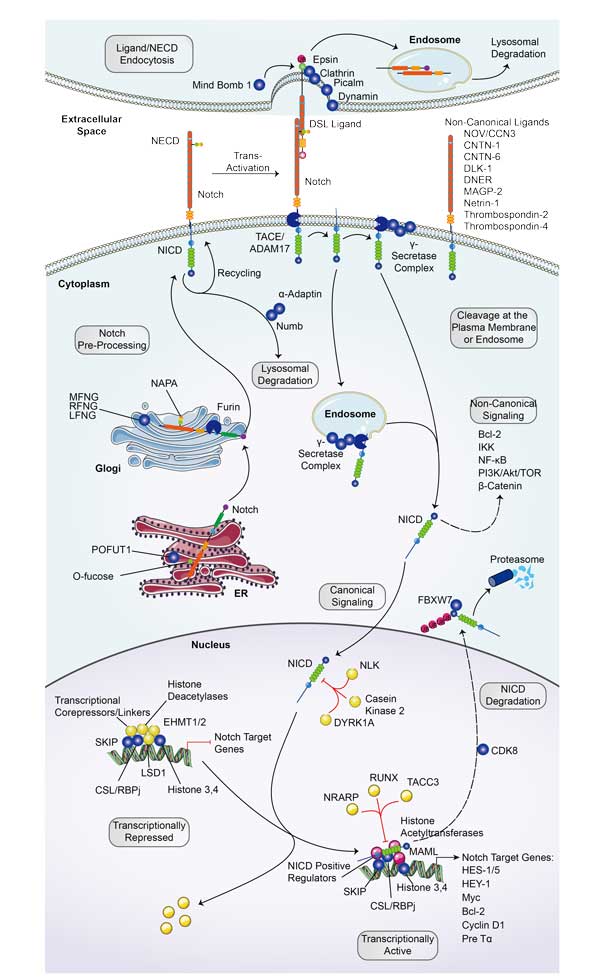
| Notch signaling pathway | DNER,MFNG,HDAC2,APH1B,DTX4,NCSTN,YY1,TLE3A,PSEN2,PTCRA |
| Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex | FAM123B,TLE1,TLE3B,TLE4,AES,TLE2,CTBP2,TLE3 |
| Notch-mediated HES/HEY network | HEY1,YY1,RCAN1,TLE1,HES6,BGLAP,MYOD1,MYB,GATA1,ASCL1 |
| Disease | ANTXR2,SUPT5H,gag,PDCD6IP,KERA,CCDC167,PSIP1,RLBP1,CUX1,RDBP |
-
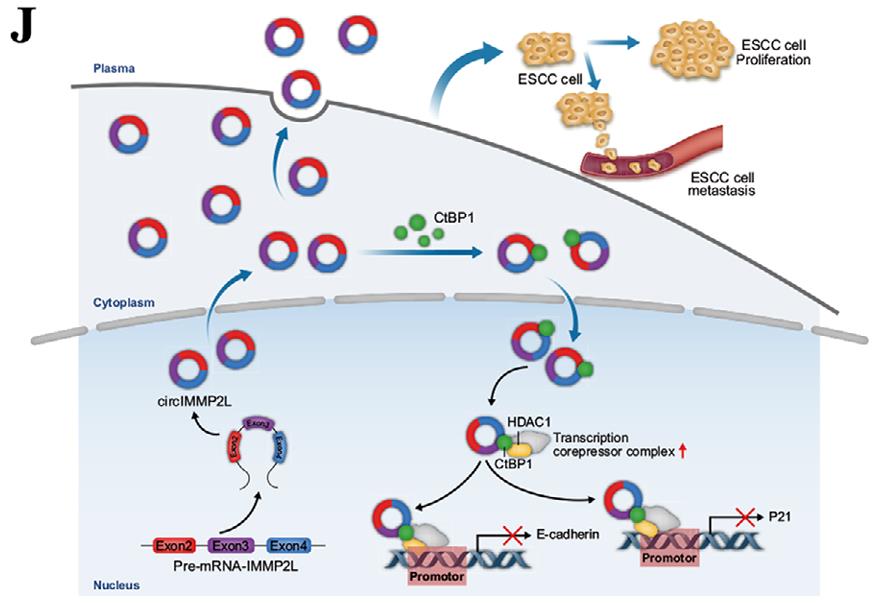 Fig1. CircIMMP2L regulates the E-cadherin and p21 transcription in ESCC through an epigenetic manner. (Yingkuan Liang, 2021)
Fig1. CircIMMP2L regulates the E-cadherin and p21 transcription in ESCC through an epigenetic manner. (Yingkuan Liang, 2021) -
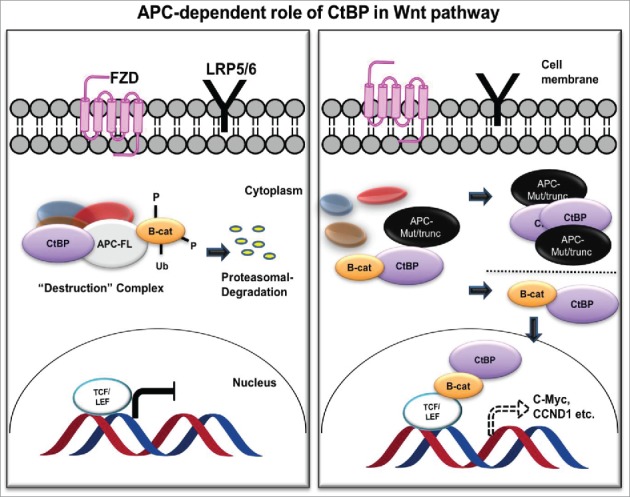 Fig2. APC-dependent role of CtBP in the Wnt/ β-catenin pathway. (M Michael Dcona, 2017)
Fig2. APC-dependent role of CtBP in the Wnt/ β-catenin pathway. (M Michael Dcona, 2017)
Protein Function
CTBP1 has several biochemical functions, for example, NAD binding,NADH binding,RNA polymerase II transcription corepressor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CTBP1 itself. We selected most functions CTBP1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CTBP1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| repressing transcription factor binding | RUNX2,SKI,CBX5,HDAC1,MAGEA2B,DDX20,HDAC4,EIF4E,GMNN,PRDM5 |
| NADH binding | CTBP2,QDPR,CTBP2A |
| NAD binding | CTBP2L,GPD1C,ADH4,GPD1A,HSD3B5,HSD17B10,ADH1,IDH3B,HIBADHB,CTBP2A |
| protein binding | HP,SEC22A,FAS,RBM5,BAIAP2L1,GFER,RELB,EIF1AD,ZNF239,ABLIM3 |
| protein domain specific binding | HAND2,YWHAE,ACSL3,VPS11,TWIST1,ANGEL1,CALM1,ZBTB16,HIST1H4N,RARA |
| oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor | AKR1B15,UEVLD,LDHBB,MDH1AA,CTBP2,HSD3B6,GRHPRA,SDR42E1,HSD3B5,GPD1C |
| transcription factor binding | PDX1,KAT6B,EPN1,PARP1,SNF8,BCL3,FOXO1,GATA2,POU1F1,MAPK1 |
| RNA polymerase II transcription corepressor activity | TCERG1,UXT,BEND6,SIN3A,SOX3,URI1,HDGF,ELANE,TXLNB,CITED2 |
| protein homodimerization activity | MBL1,TBX18,PLOD1,CHMP4C,PKD2,TBC1D22A,GLA,TWIST1,FAP,DDX1 |
Interacting Protein
CTBP1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CTBP1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CTBP1.
HIC1;ZNF366;e1a_ade05;RBBP8;CTBP2;EBNA6;KLF4
CTBP1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References