ALDH1A3
-
Official Full Name
aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member A3 -
Overview
Aldehyde dehydrogenase isozymes are thought to play a major role in the detoxification of aldehydes generated by alcohol metabolism and lipid peroxidation. The enzyme encoded by this gene uses retinal as a substrate, either in a free or cellular retinol-binding protein form. -
Synonyms
ALDH1A3;aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member A3;ALDH6;aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member A3;RALDH3;retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 3;RALDH-3;aldehyde dehydrogenase 6;acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 6;ALDH1A6
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- Chicken
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Yeast
- His
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
Background
What is ALDH1A3 Protein?
ALDH1A3, or aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member A3, is one of the 19 types of ALDH enzymes buzzing around in our bodies. This enzyme is pretty vital since it helps churn out retinoic acid (RA), kind of like a hormone. You’ll mostly find it hanging out in places like the salivary glands, stomach, and kidneys, where it plays a big part in how embryos grow and how cells do their thing, like multiplying and changing into different types. ALDH1A3 can turn all-trans-retinal into retinoic acid, which is a big deal when it comes to tweaking the way a bunch of genes work and affecting many cell activities. Plus, this enzyme isn’t just sticking to the basics—it shows up a lot in cancerous tissues. It’s linked to markers for cancer stem cells and gets involved in how tumors start, grow, and even resist chemotherapy. So ALDH1A3 isn’t just important when everything’s running smoothly; it also plays a part in cancer and other diseases, making it a pretty versatile enzyme.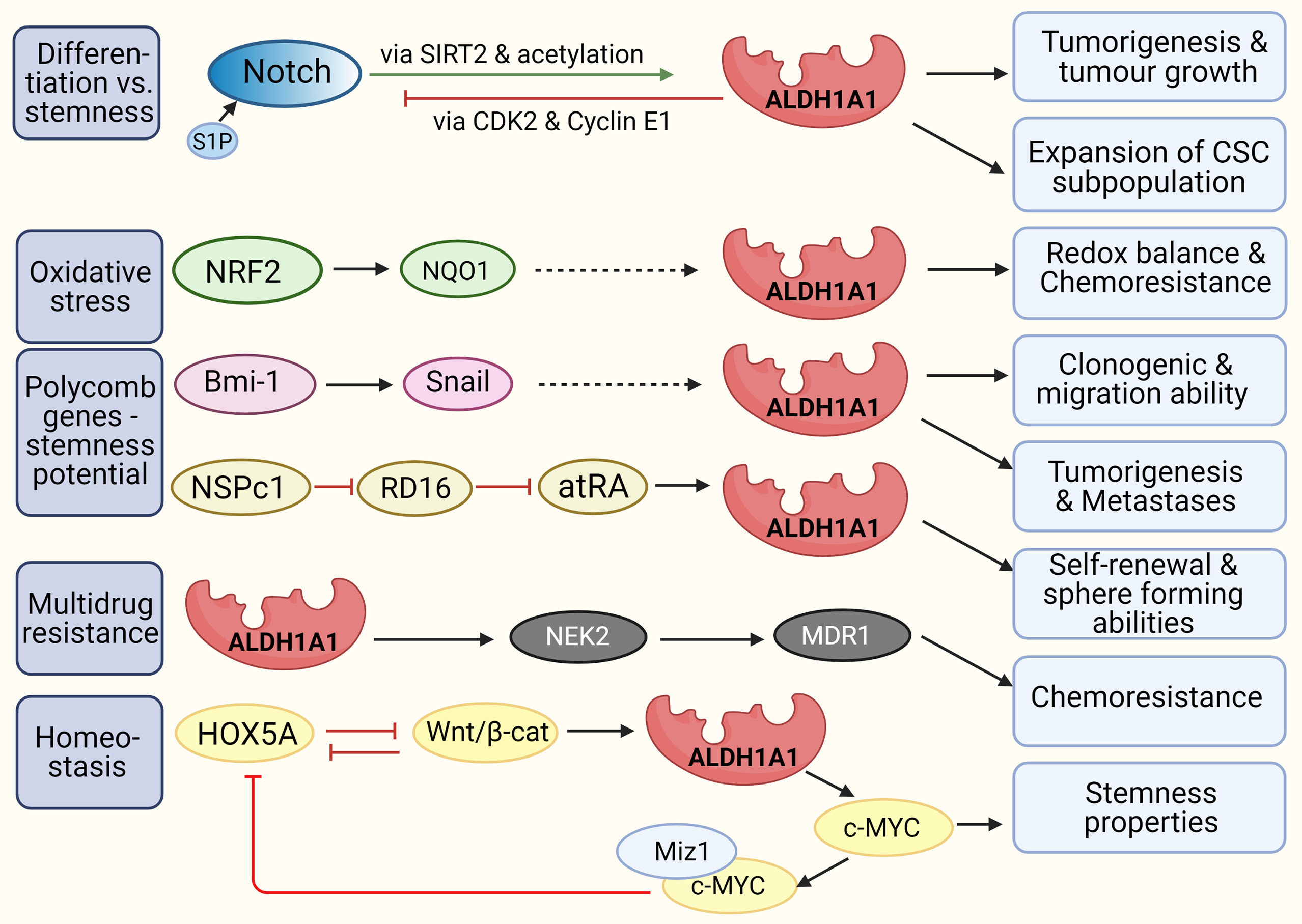
Fig1. Interactions of ALDH1A1 with other molecules. (M. Poturnajova, 2021)
What is the Function of ALDH1A3 Protein?
ALDH1A3 is an enzyme that you’ll find hanging out in our bodies, mainly in places like the salivary glands, stomach, and kidneys. It’s part of the bigger ALDH family, which is known for turning aldehydes into less harmful carboxylic acids during metabolism. This process helps clear out toxic aldehydes that can come from things like lipid damage and amino acid breakdown. ALDH1A3 is quite special because it converts a vitamin A form, all-trans-retinal, into all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA), which is crucial for sending signals to cells. Its role is vital, especially during embryo development, because if it’s missing, even eye formation can go off track in humans and mice. Interestingly, ALDH1A3 pops up in certain cancer stem cells too, with higher levels often pointing to poor outcomes in various cancers. This enzyme doesn’t just help with normal body functions but also plays a part in cancer progression and treatment responses.ALDH1A3 Related Signaling Pathway
ALDH1A3 is a protein that plays quite a role in various signaling pathways, especially when it comes to the production of retinoic acid (RA) and the unique traits of cancer stem cells. If we dive into its functions, ALDH1A3 is part of a larger family known as the ALDH superfamily. Its main job is converting all-trans-retinal into retinoic acid (ATRA or RA), which is super important for cell signaling. It’s like the molecular buddy of nuclear hormone receptors, helping control the expression of tons of genes. When RA teams up with these receptors, it steers cell activities like growth, differentiation, and even cell death. Going a step further, ALDH1A3 is also linked to how cells resist various drugs. By kicking off the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and other downstream targets like PPARγ, it boosts the expression of enzymes like hexokinase 2 (HK2). This move ramps up glycolysis in cancer cells, which can help those cells spread and become resistant to treatment.ALDH1A3 Related Diseases
ALDH1A3 is a protein that’s quite involved in a range of health issues, especially cancer. Researchers have spotted it in several cancer types, such as breast, lung, pancreatic, glioblastoma, and certain skin cancers. When ALDH1A3 levels are up, it usually means the cancer might be more aggressive. This protein’s got a role in cancer stem cells too, influencing how tumors grow, how they withstand chemotherapy, and the characteristics of cancer cells themselves. Beyond cancer, ALDH1A3 also seems to have a hand in blood vessel muscle cell growth and movement, which might tie into atherosclerosis. In cases of pulmonary hypertension, this protein seems to interact with metabolism and gene regulation, potentially driving the disease forward. There are even links between ALDH1A3 mutations and eye conditions like microphthalmia or isolated anophthalmia. All of this makes ALDH1A3 a significant factor in various diseases, marking it as both a key biomarker and a promising target for treatment strategies.Bioapplications of ALDH1A3
The recombinant ALDH1A3 protein finds its way into various applications across scientific research, industrial production, and medical studies. In the research world, ALDH1A3 is a hot topic due to its crucial role in producing retinoic acid, which is vital for early embryo development, cancer stem cell traits, and tumor spread. On the industrial front, techniques to produce recombinant ALDH1A3 protein help in developing new bioproducts and medicines, particularly in cancer diagnosis and treatment. Medically, this protein is associated with several diseases like pancreatic, breast, and non-small cell lung cancers. When ALDH1A3 is highly expressed, it often ties in with a not-so-great outlook, influencing how tumors grow, how they resist chemotherapy, and some stem cell traits. Its part in marking cancer stem cells makes ALDH1A3 a promising target for tackling cancer. Hence, the recombinant ALDH1A3 protein is crucial in figuring out disease processes, checking out drug targets, and crafting new treatments.Case Study
Case Study 1: Fernando W. et al. Oncogene. 2024
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) have a natural flexibility that helps balance critical processes like EMT/MET and glycolysis/oxidative phosphorylation during breast cancer progression. ALDH1A3 plays a key role in managing these processes and the levels of breast CSC populations. It boosts ALDH+ cells while lowering CD24−CD44+ cells through retinoic acid signaling. This change leads to less cell migration but more invasion and an intermediate EMT state. ALDH1A3 also enhances oxidative phosphorylation and reduces glycolysis and ROS. The glycolysis inhibitor 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2DG) counteracts ALDH1A3 reduction, cutting down the CD24−CD44+ population and ROS in cell cultures and tumor models. Targeting ALDH1A3 and glycolysis together shows promise in reducing breast tumor growth and CSCs, offering a potential treatment strategy.-
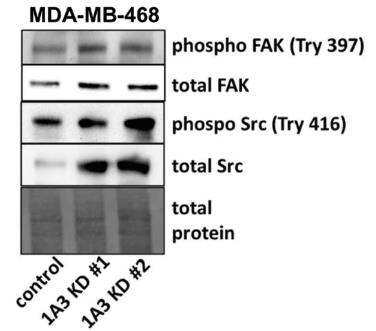 Fig1. The effect of ALDH1A3 knockdown or overexpression on the protein levels quantified by western blotting.
Fig1. The effect of ALDH1A3 knockdown or overexpression on the protein levels quantified by western blotting. -
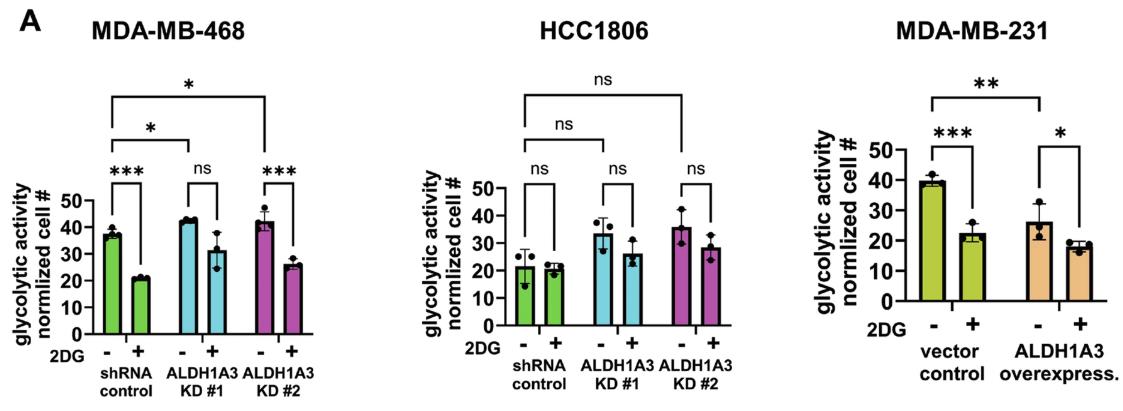 Fig2. The glycolytic activity of MDA-MB-468 and HCC1806 cells is determined by a fluorescent Glycolysis Assay.
Fig2. The glycolytic activity of MDA-MB-468 and HCC1806 cells is determined by a fluorescent Glycolysis Assay.
Case Study 2: Li G. et al. Cell Death Dis. 2018
As studies have highlighted, aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) serves as a key stem cell marker linked to cancer progression. ALDH1A3, in particular, might play a significant role in the aggressive behavior of gliomas, though more clarity is needed. Our research aimed to decode the mechanisms of ALDH1A3 in gliomas to lay groundwork for clinical applications. Using various lab techniques, including Aldefluor assays and transwell tests, we examined ALDH1A3’s role in maintaining ALDH activity and its functions in glioblastoma (GBM). Statistical analyses like LASSO-COX and survival analyses were conducted to predict GBM outcomes. Our findings revealed that ALDH1A3 is crucial for mesenchymal differentiation in GBM across diverse populations and supports ALDH activity. It also acts as an activator for mesenchymal changes in GBM, with its markers predicting survival rates over several years. Overall, ALDH1A3 is pivotal for ALDH function and mesenchymal transition in GBM, aiding in prognosis and treatment planning for patients.-
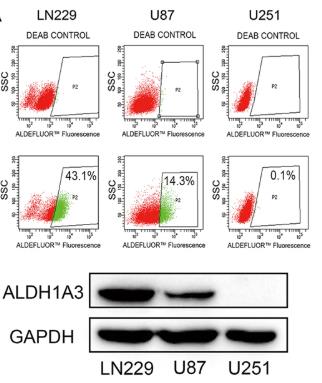 Fig3. Flow cytometry revealed that the protein expression of ALDH1A3 was positively correlated with the enzyme activity of ALDH.
Fig3. Flow cytometry revealed that the protein expression of ALDH1A3 was positively correlated with the enzyme activity of ALDH. -
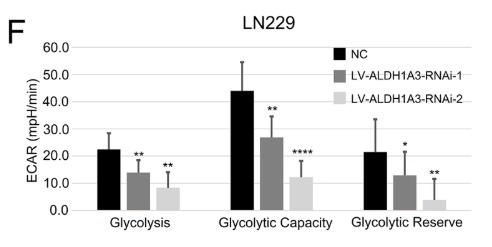 Fig4. ALDH1A3 silence markedly inhibited glycolysis, glycolytic capacity and glycolytic reserve of GSCs.
Fig4. ALDH1A3 silence markedly inhibited glycolysis, glycolytic capacity and glycolytic reserve of GSCs.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ALDH1A3-2118H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ALDH1A3-2118H)
-
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ALDH1A3-0561H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ALDH1A3-0561H)
Involved Pathway
ALDH1A3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ALDH1A3 participated on our site, such as Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis,Histidine metabolism,Tyrosine metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ALDH1A3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P | UGT1A4,UGT2A1,MGST1.1,HSD11B1,UGT1AB,UGT1A6,EPHX1,GSTT2B,DHDHL,UGT2B7 |
| Drug metabolism - cytochrome P | GSTA5,UGT1A4,GSTM1,UGT1A6A,GSTAL,FMO4,MAOA,FMO6P,MAOB,GSTA1 |
| Tyrosine metabolism | AOX4,TAT,MAOB,TYRP1B,IL4I1,DBH,GOT1,COMTA,GOT2B,ALDH3B2 |
| Chemical carcinogenesis | UGT2B7,GSTM4,SULT1A2,CYP3A7,UGT1A6B,GSTM2,MGST1,ARNT,GSTO2,CYP2C9 |
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | G6PC3,PGAM1A,ADH1C,PGK2,ADH2-1,ADH2-2,ACSS1,TPI1,ENO3,AKR1A1 |
| Metabolic pathways | CYP3A7-CYP3AP1,PKM,DAD1,PIGA,TK2,POLR3D,IPMK,PKMA,P4HA1B,SCLY |
| Phenylalanine metabolism | GM4952,MAOB,MAOA,GOT2A,HPDB,HPDA,AOC3,IL4I1,GOT1,KEG1 |
| beta-Alanine metabolism | ALDH9A1A.1,ACADM,ALDH6A1,SRM,ALDH9A1,SMOX,ALDH3B1,ALDH3A1,HADHA,ALDH2.1 |
| Histidine metabolism | HAL,ALDH2,HDC,ALDH9A1B,FTCD,CNDP1,ALDH7A1,ALDH3A2A,AMDHD1,ALDH1B1 |
-
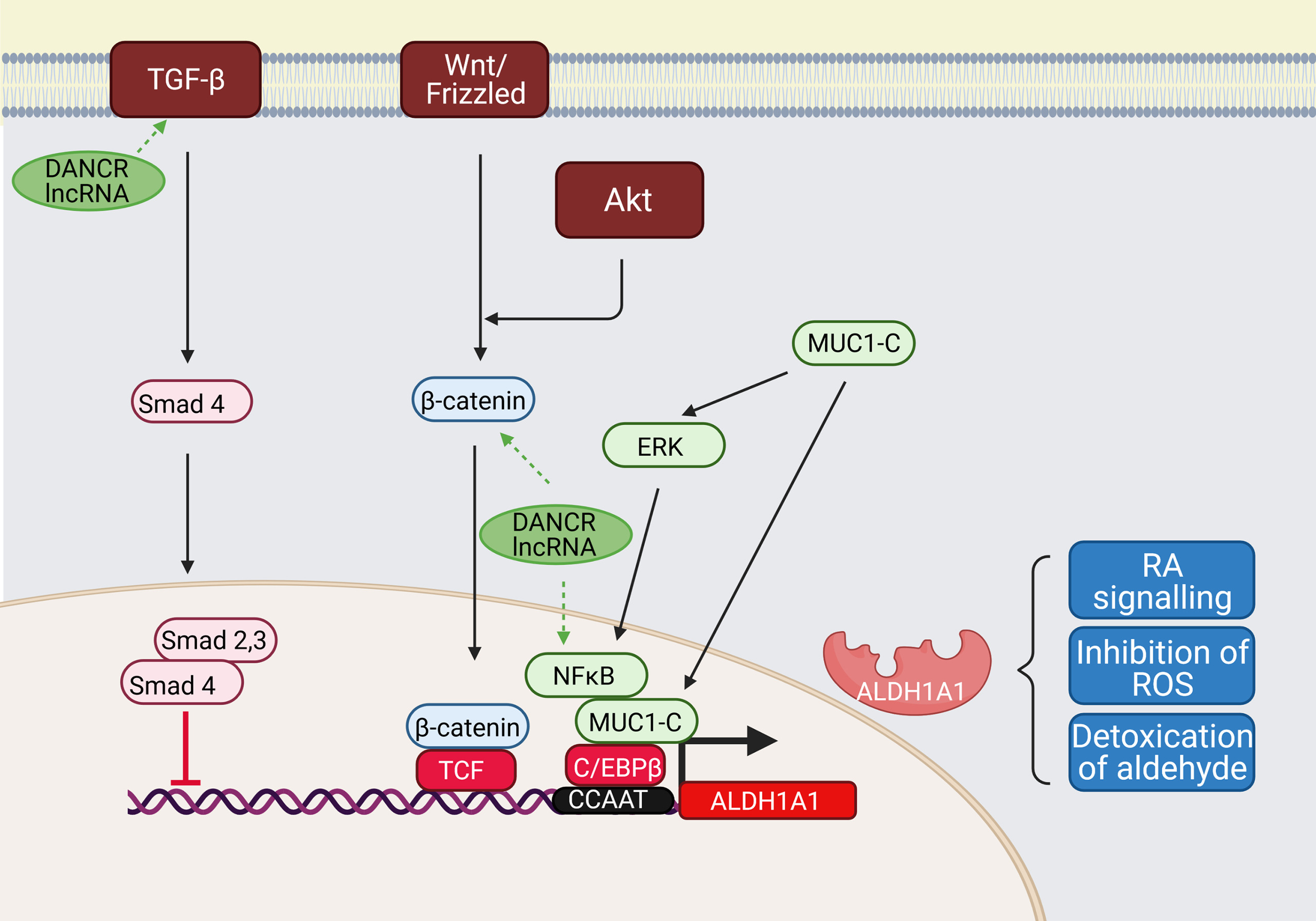 Fig1. Transcriptional regulation of ALDH1A1. (M. Poturnajova, 2021)
Fig1. Transcriptional regulation of ALDH1A1. (M. Poturnajova, 2021) -
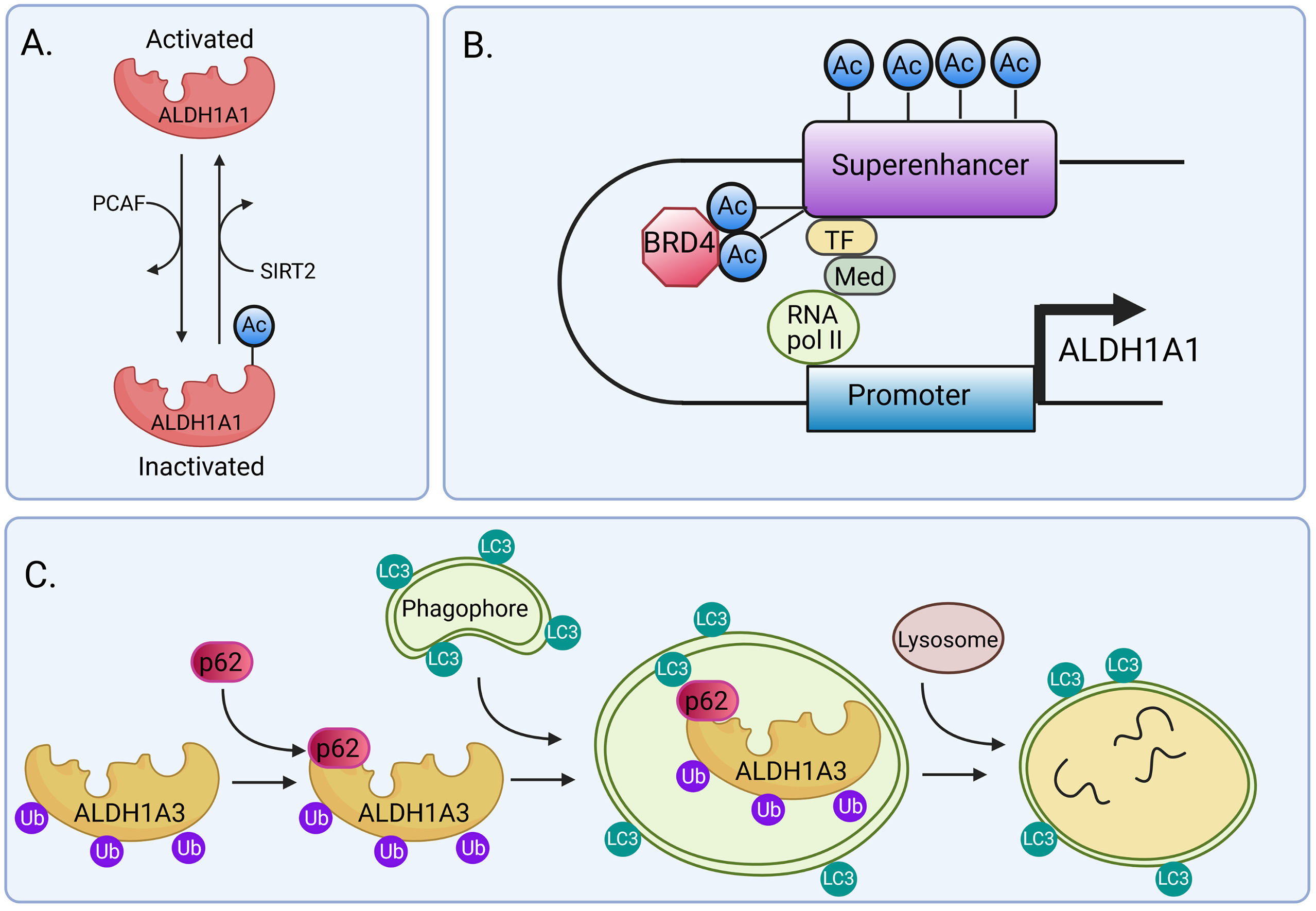 Fig2. Epigenetic and post-transcriptional regulation of ALDH1A1 and ALDH1A3. (M. Poturnajova, 2021)
Fig2. Epigenetic and post-transcriptional regulation of ALDH1A1 and ALDH1A3. (M. Poturnajova, 2021)
Protein Function
ALDH1A3 has several biochemical functions, for example, NAD+ binding,aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD) activity,aldehyde dehydrogenase [NAD(P)+] activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ALDH1A3 itself. We selected most functions ALDH1A3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ALDH1A3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| thyroid hormone binding | CRYM,CTSH,THRB,THRA |
| NAD+ binding | SIRT3,HADH,SIRT2,SIRT5,SIRT7,UXS1,GLUD1,SIRT1,SIRT4,SIRT6 |
| retinal dehydrogenase activity | ALDH8A1,AKR1C3,AKR1B10,Aldh1a7,ALDH1A1,AKR1C4,AKR1B8,AKR1C6 |
| protein homodimerization activity | SQSTM1,CEACAM5,MAP3K5,PEX11A,DMRTB1,MTERFD3,UGT1A6A,GNPTG,SMAD1,SRGAP2A |
| aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD) activity | ALDH3A2,ALDH3B2,ALDH9A1B,ALDH1A1,ALDH16A1,ALDH3A1,ALDH9A1,ALDH1L1,ALDH6A1,ALDH8A1 |
| aldehyde dehydrogenase [NAD(P)+] activity | ALDH3A1,ALDH2,ALDH3A2A,ALDH3A2B,ALDH3B2,ALDH3B1,ALDH3A2 |
Interacting Protein
ALDH1A3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ALDH1A3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ALDH1A3.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


