ZGLP1
-
Official Full Name
zinc finger, GATA-like protein 1 -
Overview
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) formerly called insulinotropin, is a metabolic hormone derived from the transcription product of the proglucagon gene. GLP-1 is a physiologic mediator of satiety and regulates energy absorption and disposal. GLP-1 stimulate secretion of insulin in the presence of elevated blood glucose concentrations, but not during periods of low blood glucose concentrations (hypoglycemia). GLP-1 is a potent stimulator of insulin release in pancreas and has the ability to render pancreatic beta-cells glucose-competent. It has been used in the therapy of type 2 diabetes. -
Synonyms
GLP1;GLP-1
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZGLP1-167H | Recombinant Human Zinc Finger, GATA-Like Protein 1 | Human Cell | Human | Non |
|
|
| ZGLP1-19171M | Recombinant Mouse ZGLP1 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
|
|
| ZGLP1-4394Z | Recombinant Zebrafish ZGLP1 | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| ZGLP1-941H | Recombinant Human Zinc Finger, GATA-like Protein 1 | E.coli | Human | Non |
|
|
| ZGLP1-10375M | Recombinant Mouse ZGLP1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| ZGLP1-10375M-B | Recombinant Mouse ZGLP1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is ZGLP1 protein?
ZGLP1 gene (zinc finger GATA like protein 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19p13. ZGLP1 encodes an evolutionary conserved transcriptional regulator with GATA-like zinc fingers. In females, it is expressed in embryonic germ cells and is essential for oogenic fate determination. It acts downstream of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and is involved in the regulation of genes involved in RNA processing, transcription and chromatin modification, retrotransposon regulation, meiotic cell cycle, and oocyte development. In males it is not required for the germ cell sex determination but is required by the spermatogonia for efficiently completing the meiotic prophase. The ZGLP1 protein is consisted of 271 amino acids and ZGLP1 molecular weight is approximately 29.6 kDa.
What is the function of ZGLP1 protein?
It plays a crucial role in the development of female germ cells, specifically in determining the oogenic fate in mice. ZGLP1 acts downstream of bone morphogenetic protein signaling and is essential for initiating the oogenic program and promoting entry into meiosis. Overexpression of ZGLP1 can induce the differentiation of primordial germ cell-like cells into fetal oocytes by activating oogenic programs that are repressed by Polycomb activities. This function of ZGLP1 is vital for sexual reproduction and contributes to our understanding of the mechanisms underlying the sex determination of germ cells. The findings related to ZGLP1 also have implications for advancing the field of in vitro gametogenesis and reproductive medicine by providing insights into the regulation of germ cell development.

Fig1. Model for oogenic fate determination in mice. (So I Nagaoka, 2020)
ZGLP1 Related Signaling Pathway
As a downstream effector of BMP signaling pathway, ZGLP1 is involved in regulating oocyte development and meiosis initiation. Although ZGLP1 is not directly involved in the RA signaling pathway, RA signaling contributes to the maturation of oocyte programs and inhibition of primordial germ cell (PGC) programs. In studies of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), ZGLP1 may promote fatty acid oxidation and improve glycolipid metabolism by activating these signaling pathways. ZGLP1 may play a role in the treatment of NAFLD by up-regulating the expression of GLP-1 receptor in liver tissue and activating the cAMP-PKA signaling pathway.
ZGLP1 Related Diseases
The ZGLP1 protein is closely related to germ cell development, especially in mice, where ZGLP1 is a key factor in determining the fate of the egg source. Although there is no direct evidence linking ZGLP1 to specific human diseases, abnormal function of ZGLP1 may affect the normal development of germ cells and the formation of gonads, which is associated with certain diseases of the reproductive system. For example, if the function of ZGLP1 is interfered with, it may lead to abnormal differentiation of germ cells, affecting the formation of eggs or sperm, which in turn is associated with problems such as infertility.
Bioapplications of ZGLP1
Functional studies of ZGLP1 have led to the development of in vitro gametophytic techniques, providing new strategies for treating certain types of infertility, especially in cases where the production of functional gametophytes needs to be induced from stem cells or primortal-like cells. A deeper understanding of the function of ZGLP1 may help develop new fertility control strategies to achieve contraception or promote fertility by regulating the development process of germ cells. As a transcriptional regulator, the regulation of the activity of ZGLP1 may have a guiding role in the development of drugs that affect germ cell development, especially in the treatment of diseases of the reproductive system and related cancers.
Case Study
Case Study 1: So I Nagaoka, 2020
Sex determination of germ cells is vital to creating the sexual dichotomy of germ cell development, thereby ensuring sexual reproduction. However, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Here, researchers show that ZGLP1, a conserved transcriptional regulator with GATA-like zinc fingers, determines the oogenic fate in mice. ZGLP1 acts downstream of bone morphogenetic protein, but not retinoic acid (RA), and is essential for the oogenic program and meiotic entry. ZGLP1 overexpression induces differentiation of in vitro primordial germ cell-like cells (PGCLCs) into fetal oocytes by activating the oogenic programs repressed by Polycomb activities, whereas RA signaling contributes to oogenic program maturation and PGC program repression.

Fig1. Percentages of ZGLP1+ cells among DDX4+ cells per ovarian section.
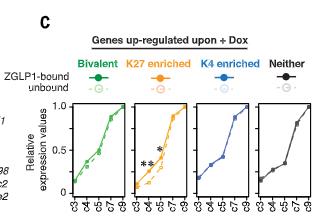
Fig2. Expression dynamics of ZGLP1-bound and ZGLP1-unbound genes.
Involved Pathway
ZGLP1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ZGLP1 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ZGLP1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
ZGLP1 has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding,RNA polymerase II transcription factor binding,chromatin binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ZGLP1 itself. We selected most functions ZGLP1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ZGLP1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| RNA polymerase II transcription factor binding | SPI1,MIXL1,KLF4,ZFPM2,GSC,GATA4,ZFPM1,CHST13,TOX2,SFPI1 |
| RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | CREB3,GATA2B,LMO2,ZFP39,RXRA,ZBTB16A,RORA,PHF21B,FOXK1,DBP |
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific binding | MAFB,GABPA,NR1I2,ALX1,RAD21,TP53,MSGN1,GRHL3,BARX1,ATF5 |
| zinc ion binding | RNF180,TRIM8,AGTPBP1,SLC30A7,MMP15,PRICKLE1A,MSRB3,SOD3A,MT1B,ADAM8A |
| chromatin binding | MEN1,NFIA,NONO,ATAD2B,TGIF1,TP73,PCGF2,UBTF,ARID3A,POLD1 |
Interacting Protein
ZGLP1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ZGLP1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ZGLP1.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


