WDR77
-
Official Full Name
WD repeat domain 77 -
Overview
WDR77 is a component of the 20S PRMT5 (MIM 604045)-containing methyltransferase complex, which modifies specific arginines to dimethylarginines in several spliceosomal Sm proteins (see MIM 601061). This modification targets Sm proteins to the survival of motor neurons (SMN) complex (see MIM 600354) for assembly into small nuclear ribonucleoprotein core particles (Friesen et al., 2002 [PubMed 11756452]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008] -
Synonyms
WDR77;WD repeat domain 77;p44;MEP50;MEP-50;HKMT1069;Nbla10071;p44/Mep50;methylosome protein 50;androgen receptor cofactor p44;WD repeat-containing protein 77
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Insect Cell
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His&SUMO
- His
- GST
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
Background
What is WDR77 Protein?
The WDR77 protein, also known as p44 or MEP50, is an important player in the androgen receptor (AR) pathway, which is crucial for prostate cell growth and differentiation. It acts as a coactivator with AR, enhancing its activity in the prostate gland and cancerous cells. WDR77 forms a complex with protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5), impacting the modification of certain proteins involved in RNA processing. This protein shifts between the nucleus and cytoplasm depending on the cell's state, influencing whether prostate cells proliferate or differentiate. Interestingly, in prostate cancer cells, WDR77 tends to stay in the cytoplasm, which supports cell growth. Plus, WDR77 interacts with other proteins like PKG, which helps regulate its function and localization, further affecting prostate cancer progression.What is the Function of WDR77 Protein?
WDR77, also known as MEP50 or p44, serves quite a functional role in the cell. It's primarily an androgen receptor coactivator, which means it boosts the activity of the androgen receptor, especially in prostate cells. This protein partners up with PRMT5 to alter several spliceosomal Sm proteins by converting specific arginines into dimethylarginines. Its location within the cell is key; WDR77 is usually found in the nucleus of normal prostate cells but shifts to the cytoplasm in cancerous ones, suggesting a possible link to cell proliferation and cancer progression. This shift might impact how prostate cells grow and differentiate. Beyond prostate interactions, WDR77 is involved in various cellular processes, including RNA processing and modification, making it a vital cog in the wheel of cell function and growth.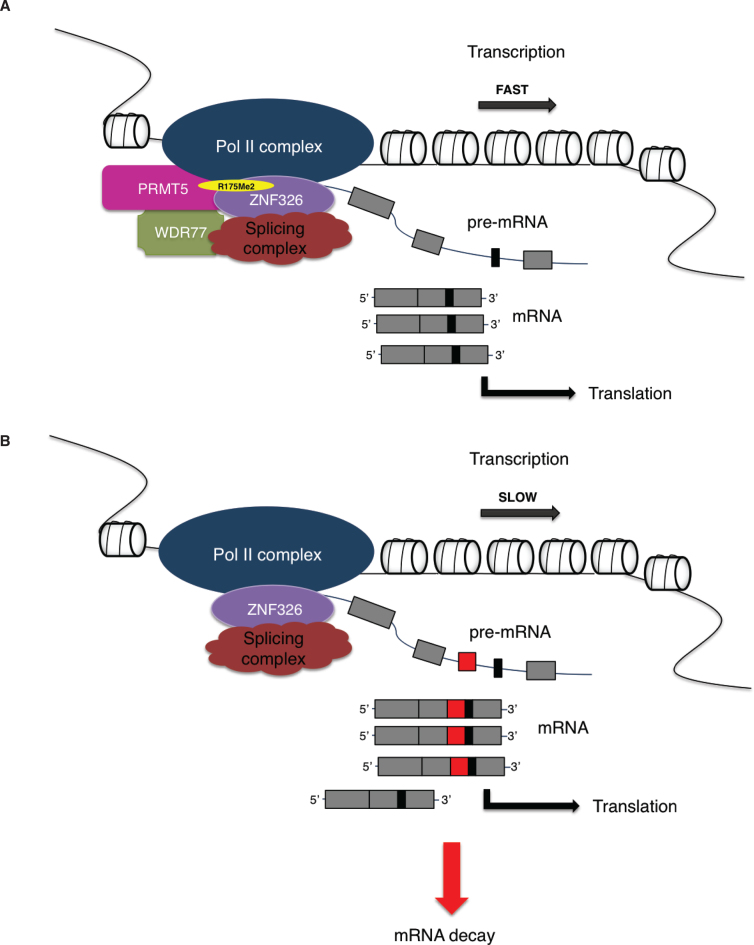
Fig1. The PRMT5/WDR77 complex shapes the transcriptome of MDA-MB-231 cells through methylation of ZNF326. (Madhumitha Rengasamy, 2017)
WDR77 Related Signaling Pathway
WDR77, or p44, is involved in a few key signaling pathways. In the prostate, it's part of how androgen receptors (AR) work. Basically, WDR77 teams up with AR to boost its activity, which is crucial for prostate cell function and growth. Another part of the puzzle is its interaction with the enzyme PRMT5, forming a complex that affects RNA splicing and modification. This interaction highlights WDR77's role in the AR pathway, where it regulates protein expression and modifies certain proteins, impacting cell cycle progression and potentially cancer development. WDR77's cellular location also matters—it often shifts between the nucleus, where it aids in gene expression, and the cytoplasm, where it's linked to cell proliferation. By understanding these pathways, researchers get insights into how prostate and possibly other cancers could be targeted through WDR77's actions.WDR77 Related Diseases
WDR77, known for its interaction with androgen receptors in the prostate, has been implicated in several diseases, especially cancers. Its role becomes more evident in prostate cancer, where it helps regulate growth by modifying gene expression. In normal cells, WDR77 is typically found in the nucleus, but in cancer cells, it's mostly in the cytoplasm, which can lead to increased cell proliferation. This shift contributes to tumor progression and is a marker in both prostate and lung cancers. The protein's involvement with PRMT5, another important molecular player, suggests it might also interact with pathways that could be targeted in cancer therapies. While mainly studied in relation to cancer, WDR77’s interaction with other proteins and influence on gene expression might point to broader implications in other disease processes.Bioapplications of WDR77
WDR77, also known as p44, plays an intriguing role in various bioapplications owing to its interaction with androgen receptors and involvement in cell growth and differentiation pathways. In medical research, it's particularly significant in cancer studies, especially prostate and lung cancer. The protein assists in modifying the expression of genes linked to tumor growth, making it an interesting target for cancer therapies. Its ability to shift between cellular locations—moving from the nucleus to the cytoplasm—impacts cellular functions and can promote or inhibit cancer cell proliferation. This behavior provides clues for developing drugs that can influence WDR77's localization and activity, potentially controlling cancer advancement. Additionally, WDR77 is involved in RNA processing, impacting how cells respond to stress and repair damage, thus broadening its relevance in biotechnological applications and disease treatment strategies.Case Study
Case Study 1: Gao S. et al. PLoS One. 2012
Scientists aren't quite sure yet how prostate cells grow and change. They’ve found this 44-kDa protein, called p44/wdr77, that hooks up with an androgen receptor, playing a big role in managing genes linked to prostate cells and cancer. Here's what they've noticed: when prostate cells are just getting started, p44 hangs out in the cell's cytoplasm, which seems to help the cells proliferate. But when it moves into the nucleus of these cells in adults, it helps them mature and start secreting specific proteins. This shift in location, from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, is key to whether prostate cells grow or differentiate.-
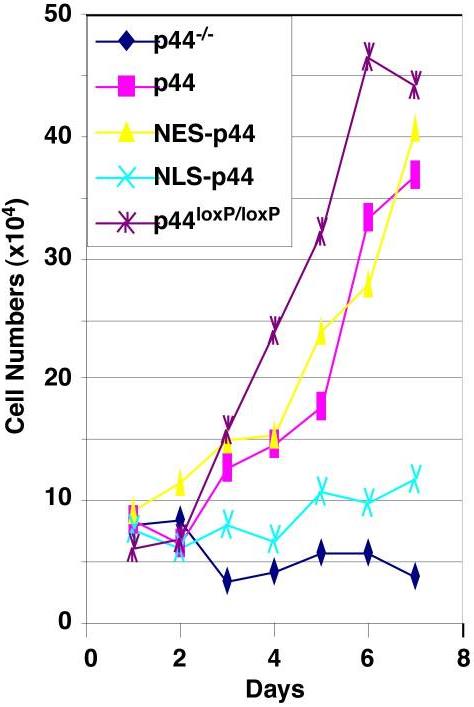 Fig1. Cytoplasmic p44 fully restored growth arrest of prostate epithelial cells induced by loss of p44.
Fig1. Cytoplasmic p44 fully restored growth arrest of prostate epithelial cells induced by loss of p44. -
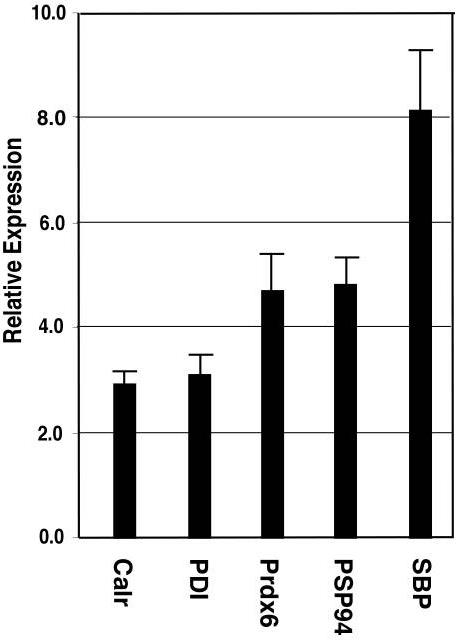 Fig2. Nuclear p44 enhanced expression of prostate-secreted proteins.
Fig2. Nuclear p44 enhanced expression of prostate-secreted proteins.
Case Study 2: Zhou L. et al. PLoS One. 2013
The androgen receptor (AR) pathway is key in how prostate cells grow and differentiate. Here a new AR cofactor called p44/WDR77 that boosts AR activity in the prostate. To dig deeper, researchers used yeast two-hybrid screening and discovered that PKG, a protein kinase, interacts with p44/WDR77. Tests showed that PKG-Iβ connects with and phosphorylates both p44 and AR, amping up AR activity along with p44 when androgens and cGMP are present. Also, PKG1β helps move p44 into the nucleus and slows prostate cancer cell growth by stopping the cell cycle at G1 phase. These findings introduce PKG as a new player in AR-mediated transcription, enhancing p44/WDR77’s role and offering fresh insight into controlling prostate cancer cell growth via androgen signaling.-
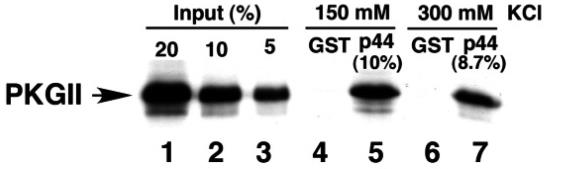 Fig3. The PKG-II KD interacts directly with p44.
Fig3. The PKG-II KD interacts directly with p44. -
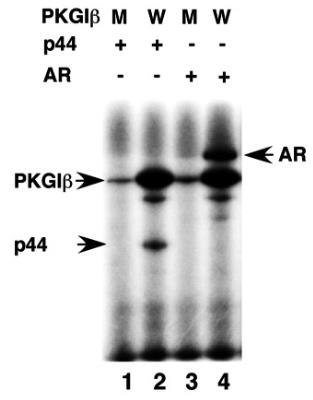 Fig4. PKG-Iβ phosphorylates AR and p44.
Fig4. PKG-Iβ phosphorylates AR and p44.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (WDR77-318H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (WDR77-318H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (WDR77-1049H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (WDR77-1049H)
Involved Pathway
WDR77 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways WDR77 participated on our site, such as Chromatin modifying enzymes,Chromatin organization,Gene Expression, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with WDR77 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Gene Expression | TSEN15,SETB,ZNF571,ZNF302,TDRD1,NT5C3B,ZNF684,GTF3A,BRF2,RARG |
| Chromatin organization | RUVBL2,SMYD3,KDM3A,SUZ12A,KDM5D,ING5A,MTA2,SMYD2,SMARCD3,MTA1 |
| RMTs methylate histone arginines | SMARCA4,PRMT7,SMARCB1,PBRM1,SMARCC1,SMARCA2,PBRM1L,SMARCD1,SMARCD3B,SMARCD3 |
| Chromatin modifying enzymes | ATXN7L3,KANSL2,KDM5A,SUZ12B,MORF4L2,CAPNS2,TADA3,CHD4,BRPF1,SUZ12 |
| Signaling events mediated by HDAC Class I | GATA1,SIRT7,SIRT4,MXD1,SIRT5,SIRT2,NR2C1,GATA2,FKBP3,TFCP2 |
| Metabolism of non-coding RNA | PRMT5,SNUPN,DDX20,PEAK1,CLNS1A |
| snRNP Assembly | DDX20,CLNS1A,PEAK1,SNUPN |
-
 Fig1. PRMT5 is targeted to multiple histone and nuclear targets by cofactors. (Nicole Stopa, 2015)
Fig1. PRMT5 is targeted to multiple histone and nuclear targets by cofactors. (Nicole Stopa, 2015) -
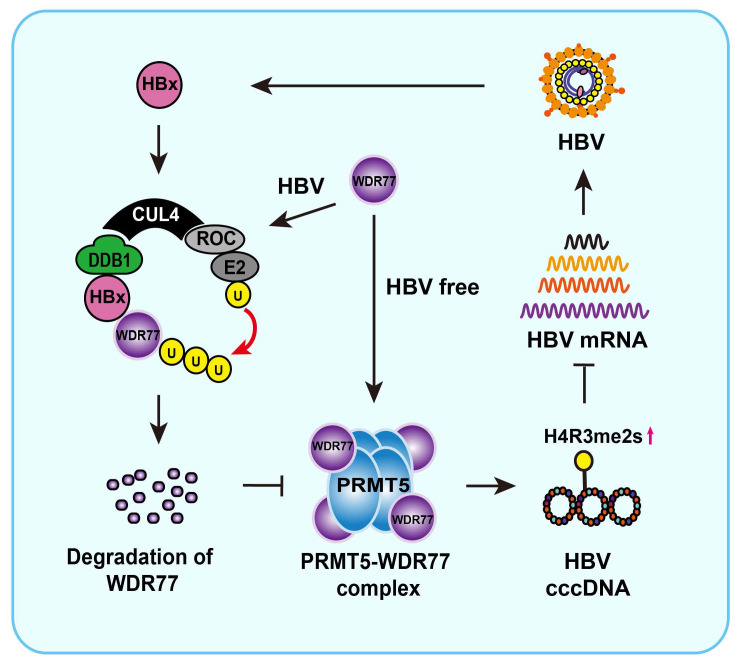 Fig2. A model of HBx degrading WDR77 to enhance HBV replication by DDB1-mediated WDR77 degradation in the liver. (Hongfeng Yuan, 2021)
Fig2. A model of HBx degrading WDR77 to enhance HBV replication by DDB1-mediated WDR77 degradation in the liver. (Hongfeng Yuan, 2021)
Protein Function
WDR77 has several biochemical functions, for example, ligand-dependent nuclear receptor transcription coactivator activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by WDR77 itself. We selected most functions WDR77 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with WDR77. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ligand-dependent nuclear receptor transcription coactivator activity | THRAP3,ZCCHC12,PPRC1,HELZ2,HMGA1-RS1,SS18,PPARG,MED24,ACTN1,DCAF6 |
| protein binding | VAV2,TRAF7,ITPRIPL1,HIST1H3C,CYC1,XPO1,CTCF,TAOK1,SSX1,ITCH |
Interacting Protein
WDR77 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with WDR77 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of WDR77.
PRMT5;Cct3;Hnrnph1;Ccnd1;YWHAQ;YWHAB;YWHAZ;CTDP1;ZNF207;AQR;PQBP1;BAG2;SNRPC;HNRNPM
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


