SYNJ1
-
Official Full Name
synaptojanin 1 -
Overview
has inositol 5-phosphatase activity; interacts with dynamin to play a role in synaptic vesicle recycling [RGD, Feb 2006] -
Synonyms
SYNJ1;synaptojanin 1;synaptojanin-1;synaptic inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase 1;synaptic inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- Mouse
- Human
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SYNJ1-1617Z | Recombinant Zebrafish SYNJ1 | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| SYNJ1-5868R | Recombinant Rat SYNJ1 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Rat | His |
|
|
| Synj1-247M | Recombinant Mouse Synj1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | DDK&Myc |
|
|
| SYNJ1-3073H | Recombinant Human SYNJ1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Human | DDK&Myc |
|
|
| SYNJ1-3074H | Active Recombinant Human SYNJ1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Human | DDK&Myc |
|
|
| SYNJ1-5527R | Recombinant Rat SYNJ1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| SYNJ1-5527R-B | Recombinant Rat SYNJ1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
Background

Fig1. The domain structures and identified mutations of Synj1 isoforms. (Hassaam Choudhry, 2021)
What is SYNJ1 protein?
SYNJ1 (synaptojanin 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 21 at locus 21q22. The SYNJ1 protein is a phosphoinositide phosphatase enzyme that plays a crucial role in various cellular processes. It is involved in the regulation of membrane phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate levels, which in turn affects synaptic transmission and membrane trafficking. The protein is expressed in several tissues with enhanced expression in the brain and retina. SYNJ1 is also implicated in clathrin-mediated endocytosis and the rearrangement of actin filaments. It interacts with five other proteins and is classified under various categories such as disease-related genes, enzymes, metabolic proteins, potential drug targets, and human disease-related genes. The SYNJ1 protein is consisted of 1573 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 173.1 kDa.
What is the function of SYNJ1 protein?
SYNJ1 participates in clathrin-mediated endocytosis, a process critical for the internalization of membrane proteins and lipids. Furthermore, it has been implicated in the rearrangement of actin filaments through its interaction with actin regulatory proteins. SYNJ1's function is also associated with the metabolism of phosphoinositides, which are important signaling molecules in the cell. It interacts with five other proteins and is classified under various categories such as disease-related genes, enzymes, metabolic proteins, potential drug targets, and human disease-related genes.
SYNJ1 Related Signaling Pathway
In addition to its role in synaptic vesicle recycling, SYNJ1 is also implicated in endosomal and autophagic trafficking. It interacts with various proteins involved in endocytosis, such as endophilin and amphiphysin, through its proline-rich domain (PRD). Furthermore, SYNJ1's enzymatic activity on lipids is essential for the formation of membrane curvature and the completion of endocytosis. Recent research has advanced our knowledge of SYNJ1's structure and function, broadening our perspective on how it regulates synaptic and endosomal trafficking in different organisms and cell types. Despite significant progress, the precise mechanisms connecting SYNJ1 to trafficking, signaling, and pathogenesis are not fully understood and require further investigation.
SYNJ1 Related Diseases
Mutations in the SYNJ1 gene have been linked to neurological disorders such as Parkinson's disease (PD) and intellectual disabilities. The connection between SYNJ1 dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases is thought to involve impaired membrane trafficking, which can affect synaptic function and contribute to disease pathogenesis. For example, SYNJ1 mutations can lead to inefficient synaptic vesicle recycling, which may impair neurotransmission.
Bioapplications of SYNJ1
SYNJ1 is a gene linked to familial forms of parkinsonism. Missense mutations in SYNJ1 have been associated with complex forms of familial parkinsonism, and studying these mutations can help in understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the disease. Given its role in neuroprotection and cellular processes relevant to PD, SYNJ1 is considered a potential therapeutic target for the development of treatments for PD and possibly other neurological disorders.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Xinyu Zhu, 2023
The accumulation of α-synuclein (α-syn)-enriched protein aggregates is thought to arise from dysfunction in degradation systems within the brain. Recently, missense mutations of SYNJ1 encoding the SAC1 and 5'-phosphatase domains have been found in families with hereditary early-onset Parkinsonism. Previous studies showed that Synj1 haploinsufficiency (Synj1+/-) leads to accumulation of the autophagy substrate p62 and pathologic α-syn proteins in the midbrain (MB) and striatum of aged mice. This study aims to investigate the neuronal degradation pathway using the Synj1+/- MB culture from mouse pups of mixed sex as a model. The data show that GFP-LC3 puncta formation and cumulative mKeima puncta formation are unaltered at baseline in Synj1+/- MB neurons. However, GFP-LAMP1 puncta is reduced with a similar decrease in endogenous proteins, including lysosomal-associated membrane protein (LAMP)1, LAMP2, and LAMP2A. The LAMP1 vesicles are hyperacidified with enhanced enzymatic activity in Synj1+/- MB neurons. Consistently, expressing the SYNJ1 R258Q mutant in N2a cells reduces the lysosome number. Interestingly, the endolysosomal defects in Synj1+/- neurons does not impact the clearance of exogenously expressed wild-type (WT) α-syn; however, the clearance of α-syn A53T was impaired in the axons of Synj1+/- MB neurons.
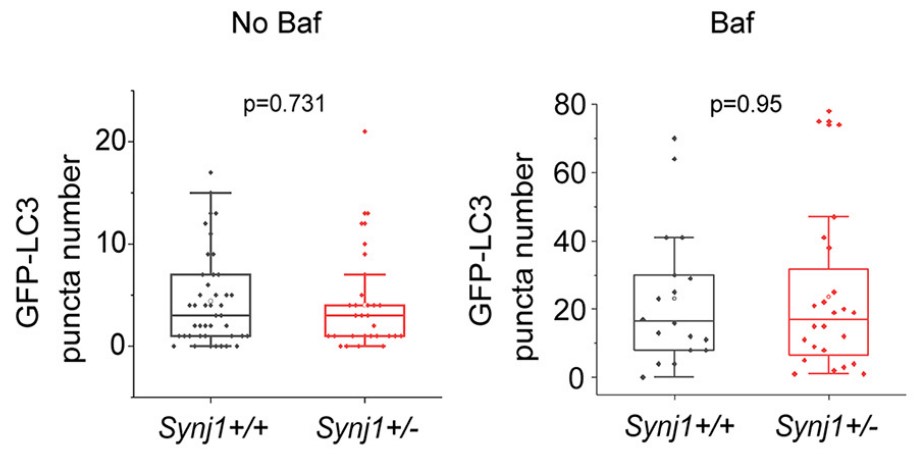
Fig1. GFP-LC3-labeled autophagosome in the soma of Synj1+/+ and Synj1+/− MB neurons.
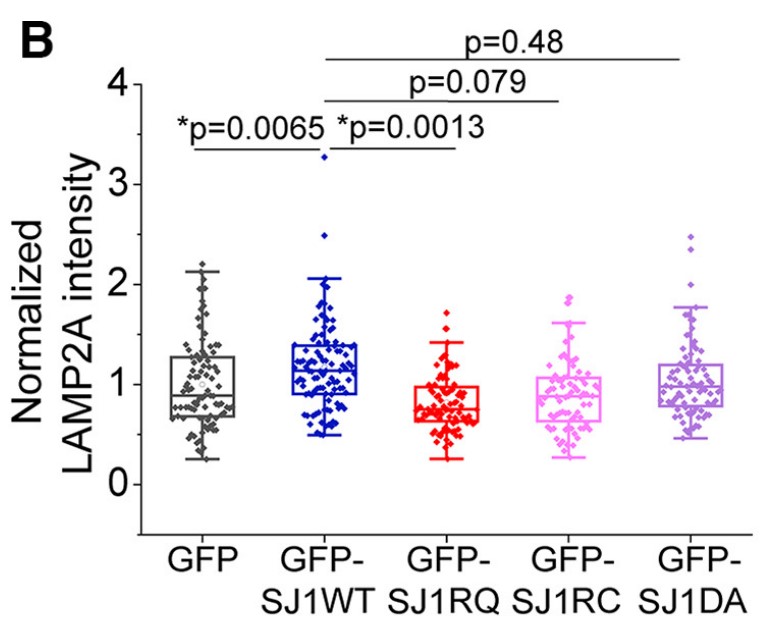
Fig2. Immunofluorescence analysis of LAMP2A in N2a cells.
Case Study 2: Yueqin Tian, 2023
This study aimed to explore the role of SYNJ1 in Parkinson's disease (PD) and its potential as a neuroprotective factor. The researchers found that SYNJ1 was decreased in the SN and striatum of hSNCA-A53T-Tg and MPTP-induced mice compared to normal mice, associated with motor dysfunction, increased α-synuclein and decreased tyrosine hydroxylase. To investigate its neuroprotective effects, SYNJ1 expression was upregulated in the striatum of mice through injection of the rAdV-Synj1 virus into the striatum, which resulted in the rescue of behavioral deficiencies and amelioration of pathological changes. Subsequently, transcriptomic sequencing, bioinformatics analysis and qPCR were conducted in SH-SY5Y cells following SYNJ1 gene knockdown to identify its downstream pathways, which revealed decreased expression of TSP-1 involving extracellular matrix pathways. The virtual protein-protein docking further suggested a potential interaction between the SYNJ1 and TSP-1 proteins. This was followed by the identification of a SYNJ1-dependent TSP-1 expression model in two PD models.

Fig3. Western blot analysis of SYNJ1.

Fig4. The docking model revealing a stable binding interaction between the secondary structures of SYNJ1.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SYNJ1-3074H)
Involved Pathway
SYNJ1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SYNJ1 participated on our site, such as Inositol phosphate metabolism,Metabolic pathways,Phosphatidylinositol signaling system, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SYNJ1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Inositol phosphate metabolism | PIK3C2A,PLD4,PLCB1,PLCZ1,PIK3CA,PIP4K2AA,TPI1A,MTMR14,MIOX,ITPKC |
| Metabolic pathways | PIGL,NDUFV3,ST6GALNAC5,GLUD2,PDHB,POLR3GL,SMS,FUT4,NDUFA12,GGT1 |
| Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | IPMK,CALM2A,PTENA,PIP4K2AA,INPP5D,PIP4K2B,PPIP5K2,CALM2B,PRKCBA,PIK3R3B |
Protein Function
SYNJ1 has several biochemical functions, for example, hydrolase activity,nucleic acid binding,nucleotide binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SYNJ1 itself. We selected most functions SYNJ1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SYNJ1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| phosphoric ester hydrolase activity | SACM1LB,INPP5F,REXO4,GDPD4,FBP1A,ENDOU2,TMPPE,ZRANB3,RNASEKB,RNASEKA |
| nucleotide binding | ENOX1,NCBP2,CPEB4,TRNAU1AP,SFRS3B,ABCA1B,GUCY2E,GLULB,RBMX2,G3BP2 |
| nucleic acid binding | ZFP746,RAVER2,PRDM12B,ZNF728,ZNF740,KLF11A,ENPP1,CPSF1,N6AMT2,TRNAU1APA |
| phosphatidylinositol phosphate 5-phosphatase activity | INPP5K |
| hydrolase activity | BAT1,RAG1,CTSSA,NUDT3B,TMPRSS4A,ABHD13,CHD8,MMP1A,IMMP2L,PNPLA5 |
Interacting Protein
SYNJ1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SYNJ1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SYNJ1.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



