STMN2
-
Official Full Name
stathmin-like 2 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the stathmin family of phosphoproteins. Stathmin proteins function in microtubule dynamics and signal transduction. The encoded protein plays a regulatory role in neuronal growth and is also thought to be involved in osteogenesis. Reductions in the expression of this gene have been associated with Downs syndrome and Alzheimers disease. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed for this gene. A pseudogene of this gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 6. -
Synonyms
STMN2;stathmin-like 2;SCGN10;stathmin-2;SCG10;Neuronal growth associated protein;Protein SCG10;SCG 10;SCG10 protein;SCGN 10;SGC 10;SGC10;Stathmin 2;Stathmin like 2;STMN 2;STMN2_HUMAN;Superior cervical ganglia neural specific 10;Superior cervical ganglion 10 protein;Superior cervical ganglion-10 protein;Superiorcervical ganglia neural specific 10;OTTHUMP00000226983;OTTHUMP00000226984;OTTHUMP00000227682;neuron-specific growth-associated protein;superior cervical ganglia, neural specific 10;neuronal growth-associated protein (silencer element)
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- Mammalian Cell
- E.coli
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- His
- Non
- His&SUMO
- Myc&DDK
- His&Fc&Avi
Background
What is STMN2 protein
Stathmin or oncoprotein 18-like protein 2 (STMN2) is a microtubule-destabilizing protein that plays a crucial role in neurons' formation, network connectivity, synaptic plasticity, and injury response. The STMN2 protein emerged from a series of meticulously directed studies over the years. Scientists identified them in the early 2000s when sourcing for neuronal-specific markers. Through extensive histopathological examination, scientists ascertained that the STMN2 protein is highly concentrated in the mature cells of the nervous system. The protein is encoded by the STMN2 gene that is prevalently expressed in various species, including humans, mice, and rats - suggesting its established role in higher organisms' nervous systems.
The human STMN2 gene is located on chromosome 8 (8q21.13). This gene encodes a protein of 172 amino acids and spans a genomic region of approximately 16kbp. The protein's molecular weight is approximately 20 kDa.
The STMN2 protein exhibits a highly conserved structural makeup with its stathmin family counterparts. It features a tubulin-binding stathmin-like domain, particularly necessary for its function in microtubule dynamics. This protein harbors four phosphorylation sites, which play a critical role in regulating its microtubule-destabilizing function.
Functions of STMN2 Protein
Primarily, the STMN2 protein operates via microtubule dynamics, crucial in neuron morphology, neurite growth, regeneration, and plasticity. Given its efficient binding with β-tubulin subunits, STMN2 sequesters them, preventing their polymerization and leading to microtubule disassembly. Moreover, when phosphorylated, STMN2 protein loses its microtubule-destabilizing capability, thus facilitating microtubule assembly and stability.
Adding to this, the STMN2 protein plays a significant role in synaptogenesis and neural plasticity. Notably, it participates in axon guidance and synaptic vesicle transport - critical for proper synaptic functioning. Additionally, STMN2 modulates regeneration after nerve injury by promoting axonal sprouting and re-growth.
STMN2 protein related signal pathway
The STMN2 protein's effect on the cellular signal pathway illuminates its importance in neuroplasticity and neuroprotection. At the microtubule level, STMN2 plays a pivotal role, serving as a preferred substrate for several kinases, including Protein Kinase A (PKA), Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK5), Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase (CAMK2), and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK2). These kinases phosphorylate STMN2, thereby altering its affinity for tubulin and modulating microtubule dynamics.
STMN2 protein related diseases
Altered STMN2 expression is prevalent in several neurological disorders, making it a critical biomarker. These include Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), wherein decreased STMN2 mRNA levels are identified. Furthermore, decreased STMN2 protein levels are seen in post-mortem brain samples from Alzheimer's disease patients, further highlighting STMN2's crucial role in neurodegeneration. Additional studies have also linked STMN2 with mental disabilities, ischemic stroke, glioblastoma, and certain psychiatric disorders like schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
- Ciliopathies: Mutations cause disorders like Joubert syndrome by disrupting cilia assembly/function.
- Neurodevelopmental disorders: Abnormal expression implicated in autism, intellectual disability of genetic or unknown origins.
- Epilepsy: Potential role in seizure susceptibility through effects on neuronal microtubules and migration.
- Neurodegeneration: May contribute to pathogenesis of conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.
- Cancer therapy: Targeting elevated STMN2 may treat certain cancers with metastatic potential.
- Neurodevelopment/regeneration: Understanding its roles can inform neural stem cell differentiation/axonal regeneration.
- Cilia research: STMN2 modulation/knockout models aid basic studies of ciliogenesis, ciliary signaling in health/disease.
- Fertility treatment: Correction of STMN2 deficiency may benefit male infertility associated with asthenozoospermia.
Due to its association with various neurodegenerative disorders, the STMN2 protein serves as a promising diagnostic tool. In disease states like ALS, STMN2-derived peptides in the cerebrospinal fluid can serve as informative biomarkers. Furthermore, therapeutic modulation of STMN2 pathway might hold the key to interventions designed to promote nerve repair and regeneration.
Beyond being a diagnostics tool, STMN2 might also present as a therapeutic target. For instance, in diseases, where STMN2 expression is low, strategies aimed at enhancing STMN2 levels might help preserve neuronal integrity and function.
- Cancer therapy: Targeting elevated STMN2 may treat certain cancers with metastatic potential.
- Neurodevelopment/regeneration: Understanding its roles can inform neural stem cell differentiation/axonal regeneration.
- Cilia research: STMN2 modulation/knockout models aid basic studies of ciliogenesis, ciliary signaling in health/disease.
- Fertility treatment: Correction of STMN2 deficiency may benefit male infertility associated with asthenozoospermia.
Case Study
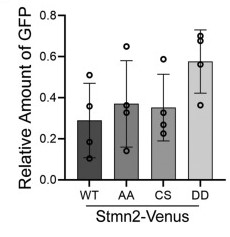
(Emma J.C. Thornburg-Suresh, 2023)
Fig3. Differences in Stmn2 variant protein levels were not statistically significant.
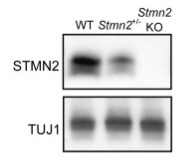
(Kelsey L. Krus, 2022)
Fig4.STMN2 protein in brain lysates from 3-month-old mice heterozygous and homozygous for Stmn2 deletion allele.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (Cat. No.: STMN2-3251H)
Involved Pathway
STMN2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways STMN2 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with STMN2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
STMN2 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium-dependent protein binding,protein binding,tubulin binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by STMN2 itself. We selected most functions STMN2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with STMN2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | DCP1B,HSPA8,APOBEC2A,SLC35A2,PROX1,SH3RF1,PPIL1,TMEM66,PIN1,IL1RL1 |
| calcium-dependent protein binding | ANXA7,CALM3,ANXA6,MASP2,A2M,KOP,CD209A,PLSCR3,S100B,RAC3 |
| tubulin binding | TTLL6,STMN4,RPS3,MTAP7D3,TBCC,TPR,ALDOA,GPAA1,MTAP4,VBP1 |
Interacting Protein
STMN2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with STMN2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of STMN2.
TEX11;TXLNA;TFCP2;NGFR;EEF1A1;GCNT1;CEP70;VOPP1;GPRASP2;CCDC85A
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


