SLC26A5
-
Official Full Name
solute carrier family 26, member 5 (prestin) -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the SLC26A/SulP transporter family. The protein functions as a molecular motor in motile outer hair cells (OHCs) of the cochlea, inducing changes in cell length that act to amplify sound levels. The transmembrane protein is an incomplete anion transporter, and does not allow anions to cross the cell membrane but instead undergoes a conformational change in response to changes in intracellular Cl- levels that results in a change in cell length. The protein functions at microsecond rates, which is several orders of magnitude faster than conventional molecular motor proteins. Mutations in this gene are potential candidates for causing neurosensory deafness. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
SLC26A5;solute carrier family 26, member 5 (prestin);PRES, prestin (motor protein);prestin;deafness;neurosensory;autosomal recessive;61;DFNB61;Deafness neurosensory autosomal recessive 61;DFNB 61;MGC118886;MGC118887;MGC118888;MGC118889;PRES;Prestin (motor protein);S26A5_HUMAN;Solute carrier family 26 member 5 (prestin);Solute carrier family 26 member 5;OTTHUMP00000195085;OTTHUMP00000195086;OTTHUMP00000195087;OTTHUMP00000195088;OTTHUMP00000195089;OTTHUMP00000195090;OTTHUMP00000195091;OTTHUMP00000195092;OTTHUMP00000211775;OTTHUMP00000211776
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rat
- Pig
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cell
- E.coli
- Yeast
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- His&Fc&Avi
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLC26A5-112H | Recombinant Human SLC26A5, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| SLC26A5-11519Z | Recombinant Zebrafish SLC26A5 | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| SLC26A5-15343M | Recombinant Mouse SLC26A5 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
|
|
| SLC26A5-3517C | Recombinant Chicken SLC26A5 | Mammalian Cell | Chicken | His |
|
|
| SLC26A5-5486R | Recombinant Rat SLC26A5 Protein | Mammalian Cell | Rat | His |
|
|
| SLC26A5-1190P | Recombinant Pig SLC26A5 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Pig | His | Ala524-Ser712 |
|
| SLC26A5-1520H | Recombinant Human SLC26A5 Protein, His-tagged | Yeast | Human | His |
|
|
| SLC26A5-5145R | Recombinant Rat SLC26A5 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| SLC26A5-5145R-B | Recombinant Rat SLC26A5 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| SLC26A5-8302M | Recombinant Mouse SLC26A5 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| SLC26A5-8302M-B | Recombinant Mouse SLC26A5 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is SLC26A5 Protein?
SLC26A5, better known as Prestin, is a key protein found abundantly in the side membrane of outer hair cells (OHCs) in the cochlea. This protein is pivotal for the strong electromechanical movements of the cells, linked to what’s called a voltage-dependent nonlinear capacitance (NLC), reflecting its shape changes. By altering cell length, SLC26A5 enhances sound levels, providing the vertebrate auditory system with its acute sensitivity and precise frequency selection. Unlike traditional motor proteins, Prestin operates at lightning-fast microsecond speeds. Alterations in this gene could lead to sensorineural hearing loss. Beyond the ear, SLC26A5 is also expressed in various tissues, including the adrenal glands and kidneys.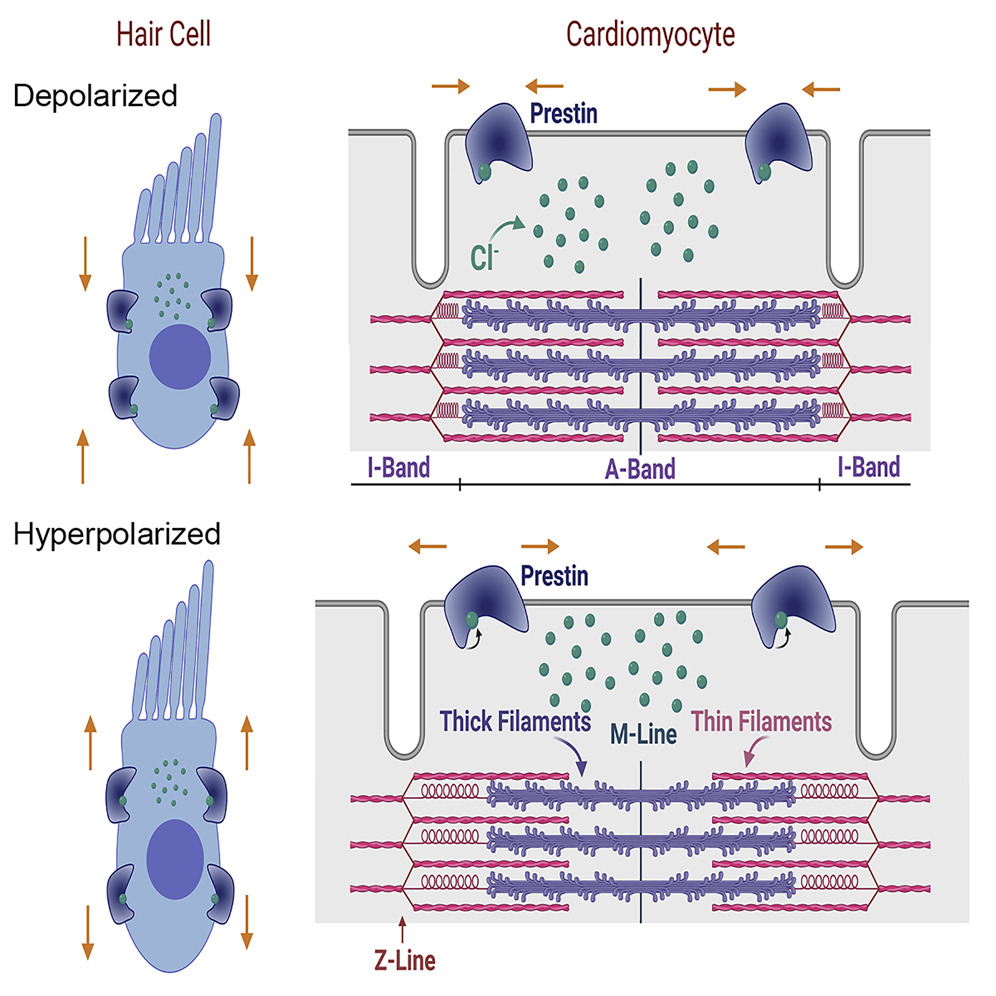
Fig1. Prestin serves a broader cellular motor function. (Xiao-Dong Zhang, 2021)
What is the Function of SLC26A5 Protein?
The SLC26A5 protein, known as Prestin, acts as a molecular motor in the cochlea’s outer hair cells, crucial for amplifying sound by altering cell length. Although it’s a partial anion transporter, it doesn’t directly let anions pass through the cell membrane. Instead, it changes shape in response to shifts in chloride ion levels inside the cell, causing these length changes essential for normal hearing. Prestin operates much faster than typical motor proteins, and mutations in its gene can potentially cause sensorineural hearing loss. Besides its auditory function, Prestin might also contribute to heart mechanics by serving as an elastic component, boosting actin-driven muscle contractions.SLC26A5 Related Signaling Pathway
Prestin, or SLC26A5, plays a crucial role in hearing by boosting auditory sensitivity and frequency tuning through outer hair cells in the cochlea. While it’s part of the SLC26 anion transporter family, Prestin’s main job isn’t moving ions directly across membranes. Instead, it undergoes shape changes when internal chloride levels shift, altering cell length and enhancing sound amplification. Beyond hearing, SLC26A5 is linked to other pathways, such as inflammation. It might intersect with inflammation and immune response signaling, especially when triggered by TLR pathways that activate MAP kinase, NF-κB, and IRF. Thus, Prestin is integral not only to hearing but also potentially to inflammatory responses.SLC26A5 Related Diseases
The SLC26A5 protein is linked to various hearing-related conditions. SLC26A5 is mainly linked to a type of hearing loss called Autosomal Recessive 61, and Pendred syndrome, a genetic disorder often causing thyroid problems and hearing impairment. Additionally, it has an important role in how the inner ear works and is associated with non-syndromic neurosensory deafness. Mutations in the SLC26A5 gene might also contribute to sensorineural hearing loss. These connections highlight the critical role of SLC26A5 in maintaining proper auditory functions, and disruptions in its operation can lead to hearing impairments.Bioapplications of SLC26A5
The recombinant SLC26A5 protein plays a significant role in scientific research, industrial production, and medical studies. In basic science, it’s used to explore the structure and function of SLC26A5, shedding light on its role in outer hair cells of the cochlea and the mechanisms of sound amplification. Medically, this protein helps us understand SLC26A5-related conditions like deafness and paves the way for potential treatments. Beyond these uses, recombinant SLC26A5 protein is crucial for developing diagnostic tools, such as ELISA kits, which detect disease markers. These applications not only deepen our grasp of SLC26A5’s functions but also offer fresh avenues for diagnosing and treating related diseases.Case Study
Case Study 1: Zhongying Wang, 2021
Prestin (SLC26A5) plays a key role in how vertebrates hear, enabling acute sensitivity and specific frequency detection. Our knowledge largely comes from techniques like site-directed mutagenesis, comparing prestin’s sequence to similar proteins. In amphibians, research on prestin has been limited, with the American bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana, having its SLC26A5 gene recently sequenced, mapped, and cloned using RNA-Seq. We examined prestin’s nonlinear capacitance (NLC) in both the bullfrog’s ear cells and HEK293T cells engineered to express this gene. The engineered cells mirrored the bullfrog’s ear cell characteristics. When compared, chick and zebrafish prestin lacked NLC, and a primitive frog species showed functional differences from Rana.-
 Fig1. Non-linear capacitance obtained from the rana prestin transfected cells.
Fig1. Non-linear capacitance obtained from the rana prestin transfected cells. -
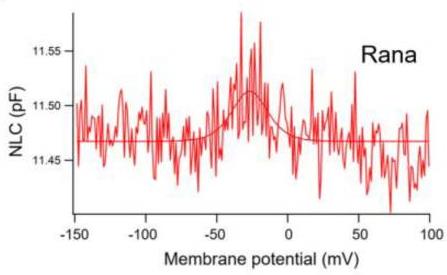 Fig2. Non-linear capacitance obtained from the HEK293T cells expressing rana prestin.
Fig2. Non-linear capacitance obtained from the HEK293T cells expressing rana prestin.
Case Study 2: Satoe Takahashi, 2024
Mammalian SLC26 proteins are membrane-based anion transporters linked to hereditary diseases. Structural studies show that many SLC26 members share a similar homodimeric structure, prompting the question of how they perform varied functions. This study focused on SLC26A4, SLC26A5, and SLC26A9, revealing that a basic residue at the anion binding site is key for SLC26A4’s anion antiport and SLC26A5’s motor function. Changes to a nonpolar residue are essential for SLC26A9’s fast uncoupled anion transport. Polar residues found in the cytosolic areas are important for SLC26A4’s function, but not for SLC26A5 and SLC26A9. Also, the hydrophobic interactions between the last transmembrane helices play an essential role in SLC26A4 and SLC26A5.-
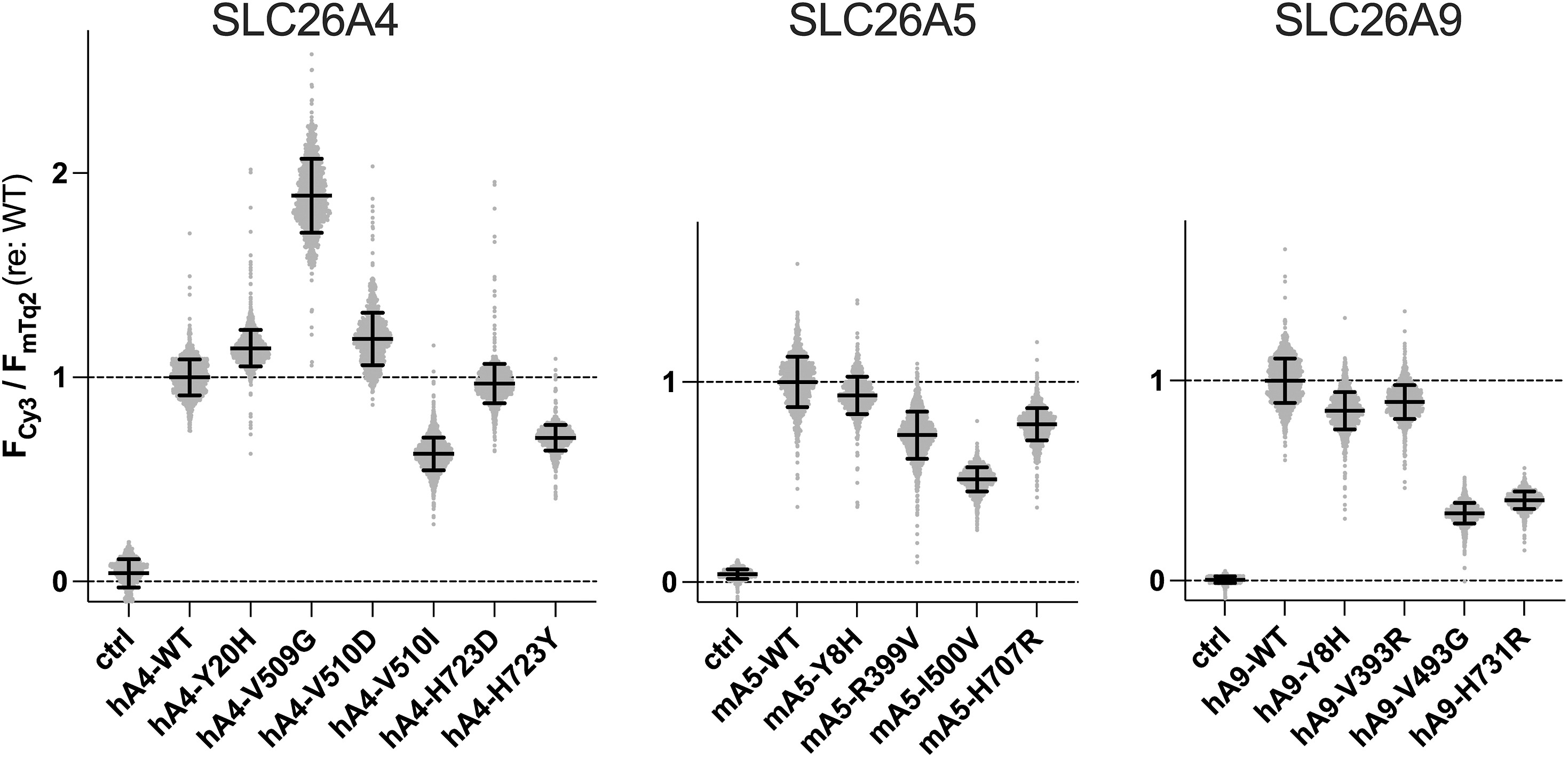 Fig3. The membrane targeting efficiencies of the SLC26 constructs.
Fig3. The membrane targeting efficiencies of the SLC26 constructs. -
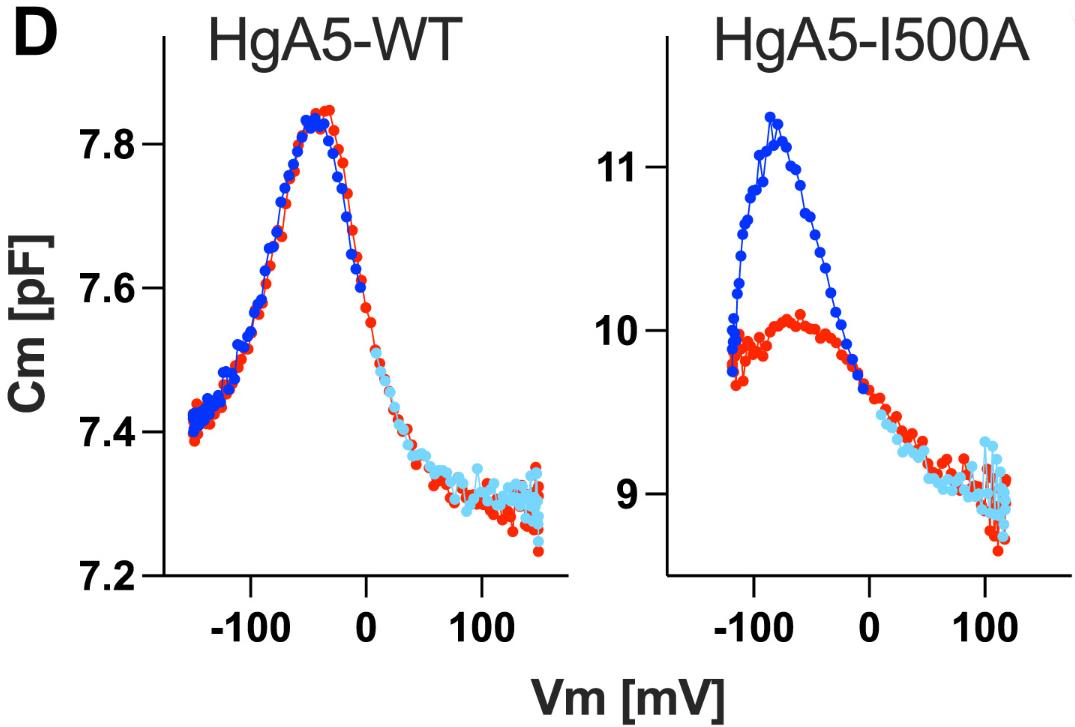 Fig4. NLC recorded in HEK293T cells expressing naked mole-rat SLC26A5.
Fig4. NLC recorded in HEK293T cells expressing naked mole-rat SLC26A5.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SLC26A5-1520H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SLC26A5-1520H)
-
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SLC26A5-1190P)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SLC26A5-1190P)
Involved Pathway
SLC26A5 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SLC26A5 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SLC26A5 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
SLC26A5 has several biochemical functions, for example, anion:anion antiporter activity,bicarbonate transmembrane transporter activity,chloride channel activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SLC26A5 itself. We selected most functions SLC26A5 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SLC26A5. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| oxalate transmembrane transporter activity | SLC26A7,SLC26A3.2,SLC26A1,SLC26A3.1,SLC26A9,SLC26A11,SLC26A2,SLC26A3,SLC26A4,SLC26A6L |
| spectrin binding | ADD1,EPB41,KIF3A,GNB1,GBP1,DCTN2,UNC13A,CAMSAP1L1,MYO7A,CAMSAP1 |
| transcription factor binding | CAMTA2,NIF3L1,ETS1,UBE2I,TMEM173,LMO4,NR0B2,KCNA3,SP1,HEYL |
| anion:anion antiporter activity | SLC26A2,SLC26A4,SLC26A11,SLC26A3.1,Slc4a2,SLC26A3.2,SLC4A2B,SLC26A7,SLC4A8,SLC26A9 |
| bicarbonate transmembrane transporter activity | SLC4A1,SLC26A11,CFTR,SLC26A2,SLC26A9,SLC4A11,SLC26A3.2,SLC26A1,SLC26A4,SLC26A6 |
| secondary active sulfate transmembrane transporter activity | SLC26A3,SLC26A1,SLC26A4,SLC26A9,SLC26A11,SLC26A7,SLC26A6L,SLC26A6,SLC26A2,SLC26A3.1 |
| sulfate transmembrane transporter activity | SLC26A3.1,SLC26A3.2,SLC26A4,SLC26A3,SLC26A1,SLC26A6,SLC26A6L,SLC26A11,SLC26A2,SLC26A7 |
| chloride channel activity | GABRG2,GABRA6,SLC1A4,GABRD,ANO2,CLIC3,SLC26A3,GRAP2,BEST1,GABRR3 |
| protein homodimerization activity | ACTN3,PRPS1,XDH,RPL7,GDF6,TMEM192,GALE,CD247,GSTM2,TRIM37 |
Interacting Protein
SLC26A5 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SLC26A5 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SLC26A5.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Song, L; Santos-Sacchi, J; et al. An Electrical Inspection of the Subsurface Cisternae of the Outer Hair Cell. BIOPHYSICAL JOURNAL 108:568-577(2015).
- Liu, HZ; Pecka, JL; et al. Characterization of Transcriptomes of Cochlear Inner and Outer Hair Cells. JOURNAL OF NEUROSCIENCE 34:11085-11095(2014).


