RBKS
-
Official Full Name
ribokinase -
Overview
The ribokinase encoded by this gene belongs to the pfkB family of carbohydrate kinases. It phosphorylates ribose to form ribose-5-phosphate in the presence of ATP and magnesium as a first step in ribose metabolism. -
Synonyms
RBKS;ribokinase;DKFZp686G13268;RBSK;5230400M11Rik
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mammalian Cell
- E.coli
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- His
- Non
- His&SUMO
- Myc&DDK
- His&Fc&Avi
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBKS-13985M | Recombinant Mouse RBKS Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
|
|
| RBKS-28123TH | Recombinant Human RBKS, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 322 amino acids |
|
| RBKS-3382H | Recombinant Full Length Human Ribokinase / RBKS Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Full L. 1-322 a.a. |
|
| RBKS-345Z | Recombinant Zebrafish RBKS | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| RBKS-380H | Recombinant Full Length Human RBKS, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Full L. Met1-Phe322 |
|
| RBKS-2485HCL | Recombinant Human RBKS 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| RBKS-3412H | Recombinant Human RBKS protein, His-SUMO-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&SUMO | 2-322aa |
|
| Rbks-5408M | Recombinant Mouse Rbks Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | HEK293T | Mouse | Myc&DDK |
|
|
| RBKS-7464M | Recombinant Mouse RBKS Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| RBKS-7464M-B | Recombinant Mouse RBKS Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
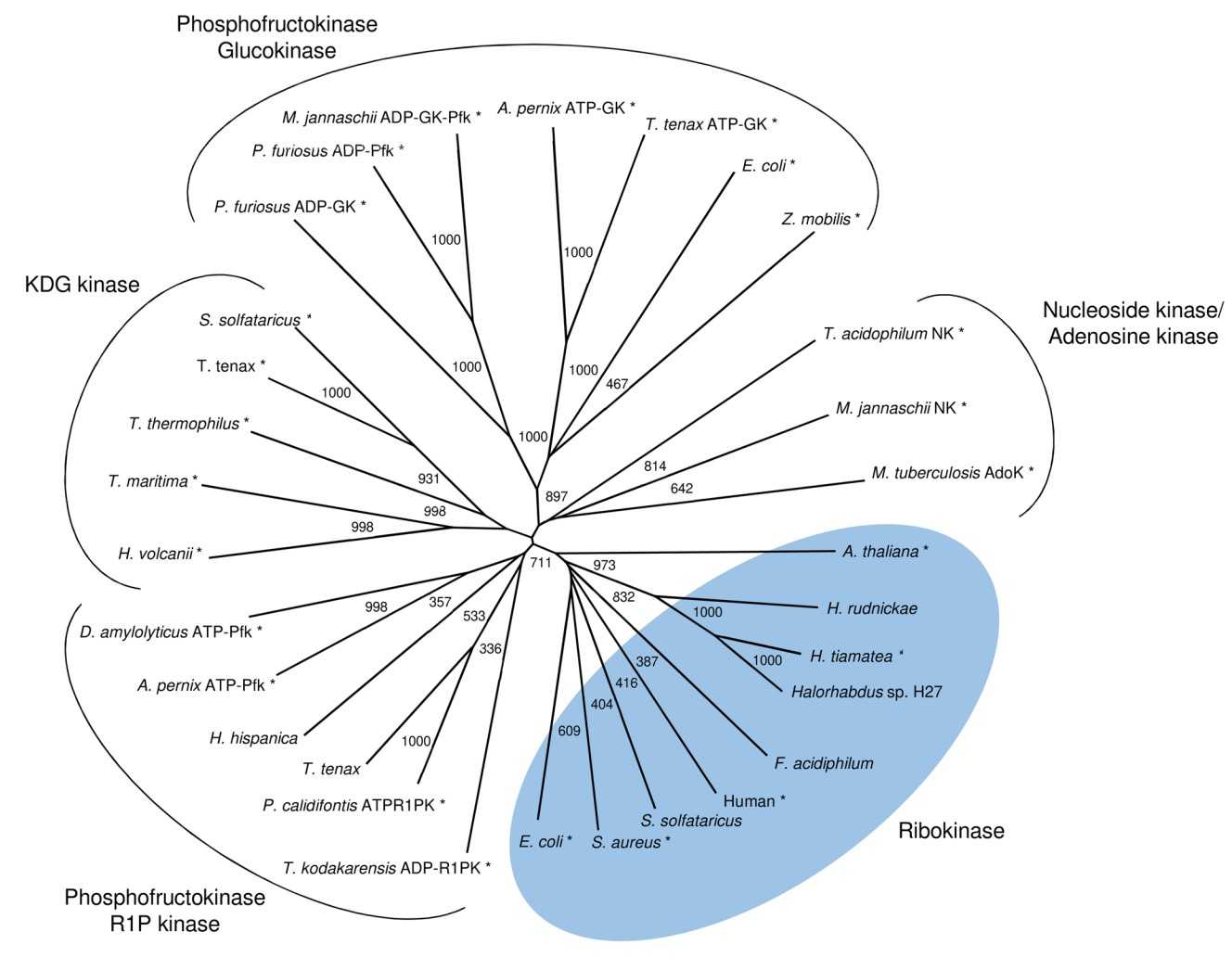
Fig1. Phylogenetic relationship of ribokinase from H. tiamatea with ribokinases from bacteria, eukarya and archaea and related members of the ribokinase superfamily. (Jan-Moritz Sutter, 2020)
What is RBKS protein?
RBKS (ribokinase) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2p23. RBKS protein is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in cellular metabolism. It catalyzes the phosphorylation of ribose at the O-5 position, a reaction that requires ATP and magnesium. This enzymatic activity leads to the formation of D-ribose-5-phosphate, which is a versatile precursor used in various biosynthetic pathways. The RBKS protein is consisted of 322 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 34.1 kDa.
What is the function of RBKS protein?
The primary function of RBKS protein is to convert ribose into D-ribose-5-phosphate, which is an essential step in the metabolism of ribose and serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of nucleotides, including purines and pyrimidines, as well as histidine and tryptophan. D-ribose-5-phosphate is also a component of the pentose phosphate pathway, which is important for the generation of NADPH and ribonucleotides. RBKS protein is a member of the carbohydrate kinase PfkB family and has been shown to interact with other proteins, indicating its role in metabolic pathways. Alternative splicing of the RBKS gene results in multiple transcript variants, which may have different functions or regulatory properties.
RBKS Related Signaling Pathway
RBKS catalyzes the phosphorylation of ribose to form ribose-5-phosphate, which is the first and rate-limiting step in the metabolism of ribose. The product of RBKS enzymatic activity, D-ribose-5-phosphate, is a key intermediate in the pentose phosphate pathway. This pathway is crucial for the generation of NADPH, which provides reducing power for various biosynthetic reactions, and ribonucleotides that are precursors for nucleic acid synthesis. RBKS contributes to the synthesis of certain amino acids, such as histidine and tryptophan, through its role in generating ribose-5-phosphate, which is a precursor in their biosynthetic pathways. RBKS is a member of the carbohydrate kinase PfkB family, indicating its role in the broader context of carbohydrate metabolism. The pentose phosphate pathway, in which RBKS plays a role, is also involved in the cellular response to stress, such as oxidative stress, by providing NADPH for the regeneration of glutathione.
RBKS Related Diseases
Given that RBKS is involved in the phosphorylation of ribose to form ribose-5-phosphate, any disruption in this process could potentially lead to metabolic disorders. The pentose phosphate pathway, in which RBKS plays a role, is often upregulated in cancer cells to support rapid cell proliferation and nucleotide synthesis. Therefore, alterations in RBKS activity could theoretically impact cancer development or progression. As RBKS is involved in the synthesis of nucleotides and energy metabolism, it may have implications in neurodegenerative diseases where energy metabolism and nucleotide homeostasis are disrupted. There is research indicating that RBKS may play a role in inducing the expression of PD-L1 in macrophages related to small cell lung cancer by activating glycolysis. RBKS is suggested to be a drug target or biomarker for various diseases, including immune diseases.
Bioapplications of RBKS
RBKS may be used as complementary factors in cell culture for primary cell expansion, differentiation or stem cell reprogramming. In the field of diagnostics, RBKS recombinant proteins may be used to develop and standardize immunoassay methods such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), Western Blot, and immunohistochemistry (IHC). In 3D cell culture and organoid generation, RBKS recombinant proteins may be useful for disease modeling and drug discovery research.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Santhosh Gatreddi, 2018
Leishmania is an auxotrophic protozoan parasite which acquires D-ribose by transporting it from the host cell and also by the hydrolysis of nucleosides. The enzyme ribokinase (RK) catalyzes the first step of ribose metabolism by phosphorylating D-ribose using ATP to produce D-ribose-5-phosphate. To understand its structure and function, the gene encoding RK from L. donovani was cloned, expressed and purified using affinity and size-exclusion chromatography. Circular-dichroism spectroscopy of the purified protein showed comparatively more α-helix in the secondary-structure content, and thermal unfolding revealed the Tm to be 317.2 K. Kinetic parameters were obtained by functional characterization of L. donovani RK, and the Km values for ribose and ATP were found to be 296 ± 36 and 116 ± 9.0 μM, respectively. Crystals obtained by the hanging-drop vapour-diffusion method diffracted to 1.95 Å resolution and belonged to the hexagonal space group P61. Analysis of the crystal content indicated the presence of two protomers in the asymmetric unit, with a Matthews coefficient (VM) of 2.45 Å3 Da-1 and 49.8% solvent content.

Fig1. Far-UV circular dichroism spectrum of LdRK.

Fig2. Crystallization of LdRK.
Case Study 2: Jae Park, 2007
The gene responsible for ribokinase (RK) in human/eukaryotic cells has not yet been identified/characterized. Blast searches with E. coli RK have identified a human protein showing significant similarity to the bacterial RK. The cDNA for this protein was expressed in E. coli and the recombinant protein efficiently phosphorylated ribose to ribose-5-phosphate using ATP, confirming its identity as RK. In contrast to ribose, the enzyme exhibited very little to no phosphorylation of D-arabinose, D-xylose, D-fructose and D-galactose. The catalytic activity of human RK was dependent upon the presence of inorganic phosphate, as observed previously for E. coli RK and mammalian adenosine kinases (AK). A number of activators and inhibitors of human AK, produced very similar effects on the human and E. coli RKs, indicating that the catalytic mechanism of RK is very similar to that of the AKs.
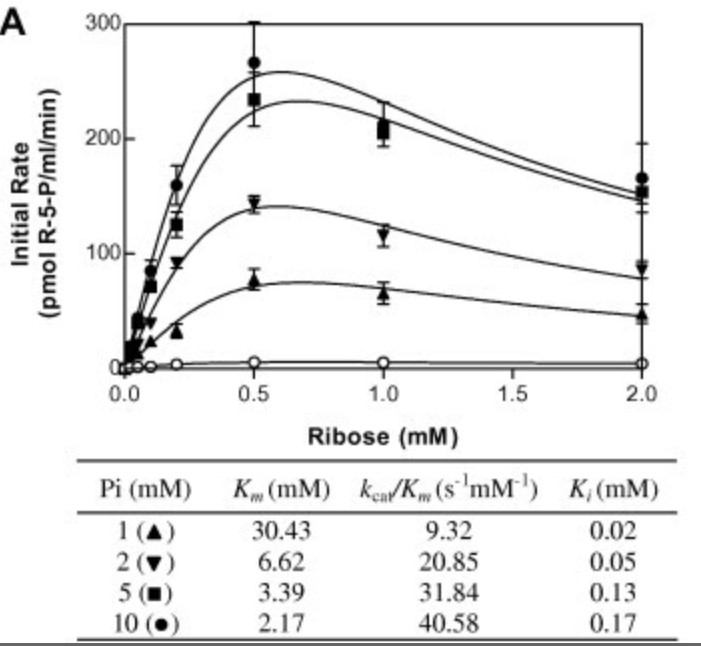
Fig3. Effect of inorganic phosphate on the initial velocity of human RK at varying ribose concentrations.

Fig4. Effects of various AK activators on the activity of human ribokinase.
Involved Pathway
RBKS involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RBKS participated on our site, such as Pentose phosphate pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RBKS were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Pentose phosphate pathway | TKTL1,PRPS1B,PGLS,FBP1,PFKMA,GPI,ALDOAB,ALDOB,G6PD,TKTL2 |
Protein Function
RBKS has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,protein binding,ribokinase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RBKS itself. We selected most functions RBKS had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RBKS. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | GNE,TNK2B,PRKCI,UPF1,DDX58,NSFB,PRKAA1,ZAK,GTF2F2B,CAMK1D |
| protein binding | TFAM,VPS37A,FAM120B,LARS,BCL2L10,BMX,TGFB2,UBE4A,IL36RN,Rhox5 |
Interacting Protein
RBKS has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RBKS here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RBKS.
ACD;POT1;Hax1;Magoh;ATL3;Kctd5
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Petrovova, M; Tkadlec, J; et al. NAD(P)H-Hydrate Dehydratase- A Metabolic Repair Enzyme and Its Role in Bacillus subtilis Stress Adaptation. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).
- Paul, R; Patra, MD; et al. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of a ribokinase from Vibrio cholerae O395. ACTA CRYSTALLOGRAPHICA SECTION F-STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY COMMUNICATIONS 70:1098-1102(2014).


