RAB13
-
Official Full Name
RAB13, member RAS oncogene family -
Overview
Could participate in polarized transport, in the assembly and/or the activity of tight junctions. -
Synonyms
RAB13;RAB13, member RAS oncogene family;ras-related protein Rab-13;RAS-associated protein RAB13;growth-inhibiting gene 4 protein;cell growth-inhibiting gene 4 protein;GIG4
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- HEK293T
- GST
- His
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
- Myc&DDK
Background
What is RAB13 protein?
RAB13 gene (RAB13, member RAS oncogene family) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q21. This gene is a member of the Rab family of small G proteins and plays a role in regulating membrane trafficking between trans-Golgi network (TGN) and recycling endosomes (RE). The encoded protein is involved in the assembly of tight junctions, which are components of the apical junctional complex (AJC) of epithelial cells. The AJC plays a role in forming a barrier between luminal contents and the underlying tissue. Additional functions associated with the protein include endocytic recycling of occludin, regulation of epithelial cell scattering, neuronal regeneration and regulation of neurite outgrowth. The RAB13 protein is consisted of 203 amino acids and RAB13 molecular weight is approximately 22.8 kDa.
What is the function of RAB13 protein?
RAB13 is involved in endocytic recycling and plays a role in regulating the transport of transmembrane proteins, such as the tight junction protein occludin, to the plasma membrane. This regulation affects the assembly and activity of tight junctions, which are essential for maintaining cell polarity and the barrier function of epithelial cells. Furthermore, RAB13 may also regulate tight junction assembly by activating the PKA signaling pathway and by reorganizing the actin cytoskeleton through the activation of downstream effectors like PRKACA and MICALL2, respectively. Through its role in tight junction assembly, RAB13 may contribute to the establishment of the Sertoli cell barrier and is also implicated in angiogenesis, neurite outgrowth, and glucose homeostasis through its involvement in insulin-induced transport of the glucose transporter GLUT4.
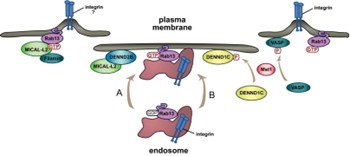
Fig1. Rab13 activation drives cell migration. (Maria S Ioannou, 2016)
RAB13 Related Signaling Pathway
RAB13 plays a crucial role in the endocytic recycling pathway, regulating the transport of transmembrane proteins like occludin to the plasma membrane, which affects the assembly and activity of tight junctions. RAB13 is involved in angiogenesis by regulating endothelial cell chemotaxis, which is essential for the formation of new blood vessels. In liver cancer, RAB13 is suggested to be involved in the MTORC1 signaling pathway, which is associated with cell growth and proliferation. RAB13 is identified as a regulator in breast cancer stem cells, supporting tumor-stroma crosstalk by controlling the transport of specific receptors and activating AKT and STAT3 signaling pathways, which in turn modulate the expression of GM-CSF and IL-8.
RAB13 Related Diseases
RAB13 is associated with various diseases, particularly in the context of cancer and neurological disorders. In cancer, RAB13's role in endocytic recycling and its influence on the tumor microenvironment suggest its involvement in tumor growth and metastasis. Furthermore, RAB13 has been implicated in the regulation of cancer stem cells, which are critical for cancer initiation, maintenance, and therapy resistance. In the realm of neurological disorders, RAB13's function in vesicle trafficking and its dysregulation in diseases such as Parkinson's disease (PD) highlight its potential as a therapeutic target and biomarker.
Bioapplications of RAB13
RAB13, a member of the Ras-related protein family, has emerged as a protein with significant bioapplication potential in various fields, particularly in cancer research and therapeutic development. RAB13 has been implicated in the regulation of cancer stem cells, which are critical for cancer initiation, maintenance, and therapy resistance. Furthermore, RAB13's involvement in the tumor microenvironment and its association with immune responses suggest its potential as a therapeutic target for modulating the sensitivity of cancers to immunotherapy. High-resolution structural studies and bioinformatics analysis have provided insights into the mechanisms of action of RAB13 and its interaction with other proteins, which can inform the design of more effective targeted therapies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Scott A Hinger, 2020
Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs), 50-150 nm in diameter, have been proposed to mediate cell-cell communication with important implications in tumor microenvironment interactions, tumor growth, and metastasis. Researchers previously showed that mutant KRAS colorectal cancer (CRC) cells release sEVs containing Rab13 protein and mRNA. Previous work had shown that disruption of intracellular Rab13 trafficking inhibits epithelial cell proliferation and invasiveness. Here, Rab13 additionally regulates the secretion of sEVs corresponding to both traditional exosomes and a novel subset of vesicles containing both β1-integrin and Rab13. Researchers find that exposure of recipient cells to sEVs from KRAS mutant donor cells increases proliferation and tumorigenesis and that knockdown of Rab13 blocks these effects.

Fig1. Rab13 knockdowns.

Fig2. β1-integrin+/Rab13+ EVs are distinct from CD63+ exosomes.
Case Study 2: Maria S Ioannou, 2016
Rab GTPases are critical regulators of membrane trafficking. The canonical view is that Rabs are soluble in their inactive GDP-bound form, and only upon activation and conversion to their GTP-bound state are they anchored to membranes through membrane insertion of a C-terminal prenyl group. Here, by performing Western blot of subcellular fractionation extracts and live cell imaging, researchers demonstrate that C-terminal prenylation is not required for Rab13 to associate with and traffic on vesicles. Instead, inactive Rab13 appears to associate with vesicles via protein-protein interactions. Only following activation does Rab13 associate with the plasma membrane, presumably with insertion of the C-terminal prenyl group into the membrane.
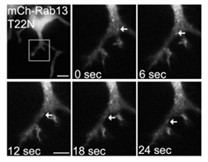
Fig3. PC12 cells differentiated for NGF and expressing mCh-Rab13 T22N were imaged live.

Fig4. Rab13 associates with membranes via protein-protein interactions in cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (RAB13-2038HFL)
Involved Pathway
RAB13 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RAB13 participated on our site, such as Tight junction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RAB13 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Tight junction | ACTN4,MYH1C,MYLPFA,EPB41L1,AKT2,CLDN18,GNAI1,MYH7,ACTN1,MYL7 |
Protein Function
RAB13 has several biochemical functions, for example, GTP binding,GTPase activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RAB13 itself. We selected most functions RAB13 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RAB13. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | HSPA5,GNL3L,UBQLN4,GINS2,MVP,MAX,RAB7L1,DCP1A,ZFP2,MRM1 |
| GTP binding | RHOGA,RAB11A,RAB11BA,RABL6,LRRK1,TUBD1,DNM2B,RAB44,ARL9,GIMAP4 |
| GTPase activity | RAB27A,GNA12A,LSG1,NOA1,RAB3DA,REM2,LRRK2,RAB11BB,TUBA8L2,RAB31 |
Interacting Protein
RAB13 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RAB13 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RAB13.
Micall2;Leprotl1;PDE6D;gtp;PRKACA;OCRL;PRKACA
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


