PRKDC
-
Official Full Name
protein kinase, DNA-activated, catalytic polypeptide -
Overview
This gene encodes the catalytic subunit of the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK). It functions with the Ku70/Ku80 heterodimer protein in DNA double strand break repair and recombination. The protein encoded is a member of the PI3/PI4-kinase family.[provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010] -
Synonyms
PRKDC;protein kinase, DNA-activated, catalytic polypeptide;HYRC;p350;DNAPK;DNPK1;HYRC1;XRCC7;DNA-PKcs;DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit;p460;DNA-PK catalytic subunit;hyper-radiosensitivity of murine scid mutation, complementing 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- E.coli
- HeLa
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cell
- HEK293
- His
- Non
- His&T7
- His&Fc&Avi
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRKDC-3252H | Recombinant Human PRKDC protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 3979-4128 aa | |
| PRKDC-860H |
Recombinant Human PRKDC Protein

|
HeLa | Human | Non |
|
|
| PRKDC-13375M | Recombinant Mouse PRKDC Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
|
|
| PRKDC-28357TH | Recombinant Human PRKDC | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 110 amino acids |
|
| PRKDC-6226C | Recombinant Chicken PRKDC | Mammalian Cell | Chicken | His |
|
|
| PRKDC-859H | Recombinant Human PRKDC Protein | Insect Cell | Human | Non |
|
|
| Prkdc-1774M | Recombinant Mouse Prkdc protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His&T7 | Ala3899~Met4128 |
|
| Prkdc-3370M | Recombinant Mouse Prkdc protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His | 3747-4015aa |
|
| PRKDC-7100M | Recombinant Mouse PRKDC Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| PRKDC-7100M-B | Recombinant Mouse PRKDC Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is PRKDC protein?
PRKDC gene (protein kinase, DNA-activated, catalytic subunit) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 8 at locus 8q11. This gene encodes the catalytic subunit of the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK). It functions with the Ku70/Ku80 heterodimer protein in DNA double strand break repair and recombination. The protein encoded is a member of the PI3/PI4-kinase family. The PRKDC protein is consisted of 4128 amino acids and PRKDC molecular weight is approximately 469.1 kDa.
What is the function of PRKDC protein?
PRKDC proteins, catalytic subunits of DNA-dependent protein kinases (DNA-PKcs), play a variety of important roles in cells. It is essential for the repair of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) during non-homologous end joins (NHEJ), a process that plays an important role in maintaining chromosome stability and preventing the development of tumors. The change of PRKDC expression level is closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors, and the enhancement of PRKDC activity may affect the regulation of some tumor suppressor genes, leading to the malignant progression of tumors. In terms of tumor therapy, the high expression level of PRKDC may enhance the ability of cancer cells to repair DNA damage, thereby reducing the effect of radiotherapy and chemotherapy and affecting the prognosis of patients.
PRKDC related signaling pathway
The signaling pathways associated with PRKDC are mainly involved in DNA damage response and repair. When double-strand DNA breaks, PRKDC is activated and recruited to the damage site to initiate cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, or apoptosis by phosphorylating a series of downstream proteins, such as histone H2AX, tumor suppressor protein p53, and BRCA1. Activation of PRKDC also leads to activation of ATM and ATR kinases, further amplifying DNA damage signals and ensuring that cells have enough time to repair or make other coping decisions.
PRKDC related diseases
PRKDC related diseases mainly involve defects in DNA damage repair, which can lead to a variety of genetic diseases and cancers. Mutations or loss of function in the PRKDC gene are associated with genetic disorders such as radiation sensitivity syndrome and Bloom syndrome, which are characterized by abnormal sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents such as radiation and chemicals, and are prone to chromosome breakage and recombination, increasing the risk of cancer. In addition, PRKDC has also been found to have abnormal expression or functional changes in a variety of tumors, which may be related to tumor occurrence, development and treatment resistance. Therefore, the study of PRKDC and its related pathways is of great significance for understanding the mechanism of DNA damage repair, cancer occurrence, and the development of new therapeutic strategies.

Fig1. Relationship between PRKDC/DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) and cancer development. (Yuting Yin, 2020)
Bioapplications of PRKDC
Recombinant human PRKDC (rhPRKDC) has not yet been developed for clinical use. However, its potential bioapplications are being explored in the field of cancer research. PRKDC is involved in DNA damage repair, and its dysregulation has been linked to various types of cancer. Therefore, understanding the function of PRKDC and its regulation may lead to the development of new targeted therapies for cancer. Additionally, rhPRKDC could potentially be used as a research tool to study DNA damage repair mechanisms and the role of PRKDC in cancer development.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Sung-Jen Wei, 2023
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive neuroendocrine tumor characterized by rapid metastasis and chemoresistance, due to genomic instability from high mutation rates, frequent TP53 and RB1 loss, and MYC family gene amplifications. Researchers identified a novel OCT4-driven MYC activation pathway in neuroblastoma, another neuroendocrine cancer, and found similar expression correlations in SCLC. Some SCLC cell lines show high c-MYC expression without genomic amplification, suggesting alternative activation mechanisms. The studies confirmed interactions between OCT4, DNA-PKcs, and the MYC promoter, revealing a DNA-PKcs/OCT4/c-MYC pathway in SCLC. Targeting this pathway with inhibitors of DNA-PKcs and a DNA-PKcs-OCT4 protein-protein interaction inhibitor showed anticancer effects in SCLC cells and xenografts.
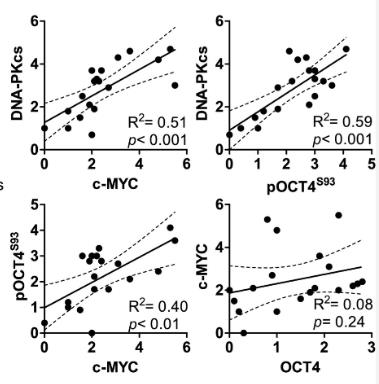
Fig1. Correlations between c-MYC and pOCT4S93 or DNA-PKcs protein levels.
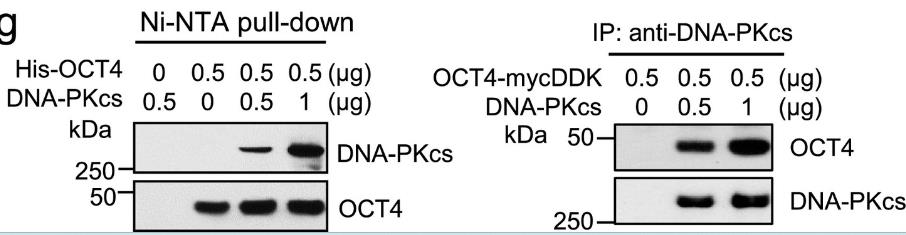
Fig2. OCT4 binds to DNA-PKcs in a cell-free system.
Case Study 2: Wenchao Zhang, 2024
Osteosarcoma's poor prognosis is often due to chemoresistance, particularly to doxorubicin (DOX). This kinome-wide CRISPR screen pinpointed PRKDC as a key factor in DOX sensitivity. Clinical samples revealed hyperactivated PRKDC in osteosarcoma, and experiments showed that PRKDC loss heightened DOX sensitivity. PRKDC's mechanism involves binding GDE2 to stabilize GNAS, leading to AKT phosphorylation and DOX resistance. The PRKDC inhibitor AZD7648, combined with DOX, significantly inhibited osteosarcoma growth in preclinical models, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy.

Fig3. The whole cell lysate of HOS cells was harvested for immunoprecipitation assay.

Fig4. The 143B and HOS cells were transfected with the indicated siNC or siGNAS #2.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
PRKDC involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PRKDC participated on our site, such as Non-homologous end-joining,Cell cycle, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PRKDC were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell cycle | YWHABB,NDEL1A,SMC1B,KAT5,ODF2B,YWHAQA,PLK1,SET,CDK2,CDKN1BA |
| Non-homologous end-joining | MRE11A,LIG4,FEN1,DNTT,POLM,NHEJ1,DCLRE1C,XRCC6,POLL,XRCC4 |
Protein Function
PRKDC has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,DNA-dependent protein kinase activity,double-stranded DNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PRKDC itself. We selected most functions PRKDC had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PRKDC. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | CHKA,LATS1,PFAS,HIPK2,AK5L,MAGI1,UBE2NB,ATP11C,MYLK3,IRAK1 |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | DMPK,CDK5,NUAK1,MYO3B,CAMK2B1,PKMYT1,MKNK1,FAM20C,EIF2AK2,STK17B |
| enzyme binding | HSPA1B,Alb,PEX5,TSPAN17,KDM4C,PIAS3,UBE2L3,STUB1,MST1R,YES1 |
| transcription factor binding | NKX3,POU5F1,NCOA2,PIM1,JUNBA,BCL10,HDAC2,TFDP1,HES4,PAX2 |
| protein binding | SPRY2,CD1d1,CROP,CAND2,SIAH2,NAT8,CREBZF,KLF3,NEURL1B,CDK16 |
| protein kinase activity | CSNK1G2A,RIPK1L,WEE2,CLK4B,SGK2B,RPS6KA3A,MAP4K1,NAT1,SBK1,SRPK1 |
| double-stranded DNA binding | TEF,IFI16,RAD51C,APTX,KIN,SP1,MEN1,DDX58,AFF3,SP8B |
| poly(A) RNA binding | APEX1,EIF3G,HNRNPH1,MECP2,EIF3D,PTBP2,RPS14,MKI67IP,NOP16,CRNKL1 |
| DNA-dependent protein kinase activity | ATM,ALPK2,XRCC6BP1,HMGA2 |
Interacting Protein
PRKDC has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PRKDC here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PRKDC.
XRCC6;XRCC5;PIDD1;CASP2
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wang, XL; Cho, SY; et al. C-X-C motif chemokine 12 influences the development of extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleens of myelofibrosis patients. EXPERIMENTAL HEMATOLOGY 43:100-109(2015).
- Klanova, M; Soukup, T; et al. Mouse models of mantle cell lymphoma, complex changes in gene expression and phenotype of engrafted MCL cells: implications for preclinical research. LABORATORY INVESTIGATION 94:806-817(2014).

.jpg)
.jpg)

