PNPLA6
-
Official Full Name
patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 6 -
Overview
This gene encodes a phospholipase that deacetylates intracellular phosphatidylcholine to produce glycerophosphocholine. It is thought to function in neurite outgrowth and process elongation during neuronal differentiation. The protein is anchored to the cytoplasmic face of the endoplasmic reticulum in both neurons and non-neuronal cells. Mutations in this gene result in autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia, and the protein is the target for neurodegeneration induced by organophosphorus compounds and chemical warfare agents. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
PNPLA6;patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 6;neuropathy target esterase;NTE;sws;EC 3.1.1.5;NTEMND;Patatin like phospholipase domain containing 6;Patatin like phospholipase domain containing protein 6;Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 6;PLPL6_HUMAN;SPG39
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- Mammalian cells
- His
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
- Flag
Background
What is PNPLA6 protein?
PNPLA6 gene (patatin like phospholipase domain containing 6) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19p13. This gene encodes a phospholipase that deacetylates intracellular phosphatidylcholine to produce glycerophosphocholine. It is thought to function in neurite outgrowth and process elongation during neuronal differentiation. The protein is anchored to the cytoplasmic face of the endoplasmic reticulum in both neurons and non-neuronal cells. Mutations in this gene result in autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia, and the protein is the target for neurodegeneration induced by organophosphorus compounds and chemical warfare agents. The PNPLA6 protein is consisted of 1375 amino acids and PNPLA6 molecular weight is approximately 151.0 kDa.
What is the function of PNPLA6 protein?
The function of the PNPLA6 protein is primarily related to its role as a phospholipase enzyme. It is involved in the hydrolysis of intracellular phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho), generating glycerophosphocholine (GroPtdCho). This enzyme acts on both the sn-2 and sn-1 positions of PtdCho and is also capable of hydrolyzing lysophospholipids and monoacylglycerols. The PNPLA6 protein is associated with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane and is implicated in lipid metabolic processes and lipid catabolic processes. It is also known as neuropathy target esterase (NTE) and is highly expressed in the developing human brain, where it is thought to function in neurite outgrowth and process elongation during neuronal differentiation.
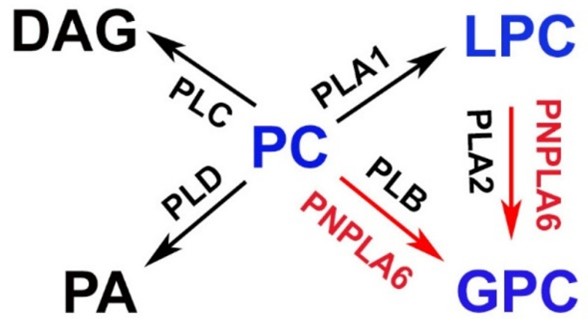
Fig1. Proposed functions of PNPLA6/NTE in lipid metabolism. (Doris Kretzschmar, 2022)
PNPLA6 Related Signaling Pathway
PNPLA6 functions as a phospholipase B that deacylates intracellular phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho) to generate glycerophosphocholine (GroPtdCho). This process is part of the lipid metabolic process and lipid catabolic process. PNPLA6 is the primary target of toxic organophosphorous compounds found in agricultural pesticides and chemical warfare agents. These compounds cause axonal degeneration in large neurons by phosphorylating and inhibiting the catalytic domain of PNPLA6. Recent research has linked biallelic PNPLA6 mutations to photoreceptor degeneration and various forms of childhood blindness, suggesting a role for PNPLA6 in photoreceptor survival. PNPLA6 may also be involved in the synthesis of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter, by producing glycerophosphocholine, which is a precursor in the synthesis of acetylcholine.
PNPLA6 Related Diseases
PNPLA6 protein-related diseases include a range of neurodegenerative diseases and developmental disorders that are typically manifested by cerebellar ataxia, upper motor neuron involvement, visual impairment, anterior pituitary hypofunction, and peripheral neuropathy. Specific disorders include Boucher-Neuhauser syndrome, Gordon Holmes syndrome, Oliver-McFarlane syndrome, Laurent-Moon syndrome, and spastic paraplegia type 39 (SPG39). These diseases are usually caused by biallelic mutations in the PNPLA6 gene, resulting in reduced neural-target esterase activity, affecting the normal function and survival of nerve cells.
Bioapplications of PNPLA6
The PNPLA6 protein has become the focus of research and potential therapeutic interventions due to its key role in a variety of neurological disorders. Its applications are mainly focused on the following aspects: as biomarkers for disease diagnosis and classification, especially in neurodegenerative diseases and developmental disorders; As a target for drug development to develop drugs to treat related diseases by modulating the activity or function of PNPLA6; In neuroscience research, it is used to explore the mechanisms of development, function, and degeneration of nerve cells; And in toxicological studies, as a model for evaluating the effects of certain organophosphorus compounds on the nervous system.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Rudy J Richardson, 2020
Systemic inhibition of neuropathy target esterase (NTE) with certain organophosphorus (OP) compounds produces OP compound-induced delayed neurotoxicity (OPIDN), a distal degeneration of axons in the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS), thereby providing a powerful model for studying a spectrum of neurodegenerative diseases. This chapter defines NTE and OPIDN, presents an overview of OP compounds, provides a rationale for NTE research, and traces the history of discovery of NTE and its relationship to OPIDN. It then briefly describes subsequent studies of NTE, including practical applications of the assay; aspects of its domain structure, subcellular localization, and tissue expression; abnormalities associated with NTE mutations, knockdown, and conventional or conditional knockout; and hypothetical models to help guide future research on elucidating the role of NTE in OPIDN.
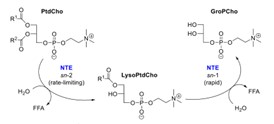
Fig1. Catalytic activity of NTE as a phospholipase B.

Fig2. Toxicological consequences of NTE inhibition and aging.
Case Study 2: Alyson Sujkowski, 2015
Mutations in the Drosophila NTE homolog swiss cheese (sws) cause early-onset, progressive behavioral defects and neurodegeneration characterized by vacuole formation. Researchers investigated sws5 flies and show for the first time that this allele causes progressive vacuolar formation in the brain and progressive deterioration of negative geotaxis speed and endurance. They demonstrate that inducible, neuron-specific expression of full-length human wildtype NTE reduces vacuole formation and substantially rescues mobility. Indeed, neuron-specific expression of wildtype human NTE is capable of rescuing mobility defects after 10 days of adult life at 29°C, when significant degeneration has already occurred, and significantly extends longevity of mutants at 25°C.

Fig3. hNTE protein is present in heads of adult hNTE rescue flies.

Fig4. Time to fatigue is increased in hNTE rescue flies.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PNPLA6-920HFL)
Involved Pathway
PNPLA6 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PNPLA6 participated on our site, such as Glycerophospholipid metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PNPLA6 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Glycerophospholipid metabolism | AGPAT9L,LYPLA2,GPD1C,PPAP2B,CEPT1,AGPAT6,PPAP2C,PLA2G10,PNPLA7,PLA2G2E |
Protein Function
PNPLA6 has several biochemical functions, for example, lysophospholipase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PNPLA6 itself. We selected most functions PNPLA6 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PNPLA6. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| lysophospholipase activity | PNPLA8,PLA2G4F,ASPG,MGLL,PLA2G4AA,PLA2G15,LYPLAL1,PNPLA7A,LYPLA1,PLA2G4B |
Interacting Protein
PNPLA6 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PNPLA6 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PNPLA6.
ssrna_ug
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wei, N; Wang, Y; et al. PU.1 antisense lncRNA against its mRNA translation promotes adipogenesis in porcine preadipocytes. ANIMAL GENETICS 46:133-140(2015).
- Zhou, Y; Llaurado, G; et al. Circulating triacylglycerol signatures and insulin sensitivity in NAFLD associated with the E167K variant in TM6SF2. JOURNAL OF HEPATOLOGY 62:657-663(2015).


