NR2E1
-
Official Full Name
NR2E1 nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group E, member 1 -
Synonyms
NR2E1;nuclear receptor subfamily 2, group E, member 1;TLX;nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group E member 1;TLL;XTLL;hTll;tailless homolog;nuclear receptor TLX;tailes-related receptor;protein tailless homolog
Recombinant Proteins
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Mammalian Cell
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- His&T7
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- GST
Background
What is NR2E1 protein?
NR2E1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group E member 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 6 at locus 6q21. NR2E1, also known as TLX or TLL, is a protein that belongs to the nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group E member 1. It is an orphan nuclear receptor, which means it does not have a known natural ligand but still plays a crucial role in various biological processes. NR2E1 is classified as a nuclear receptor and a transcription factor, which means it can bind to DNA and regulate gene expression. NR2E1 is specifically localized to neurogenic regions of the forebrain and retina throughout development and adulthood, indicating its importance in neural development and function. The NR2E1 protein is consisted of 385 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 42.6 kDa.
What is the function of NR2E1 protein?
NR2E1 is a critical regulator of neurogenesis, the process by which neurons are generated from neural stem cells. It helps maintain the pool of neural stem cells and promotes their differentiation into neurons. NR2E1 is essential for the development of the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. As a transcription factor, NR2E1 binds to specific DNA sequences and can either activate or repress the transcription of target genes. NR2E1 helps maintain the balance between self-renewal and differentiation of neural stem cells, ensuring a continuous supply of new neurons throughout life.
NR2E1 Related Signaling Pathway
As a transcription factor, NR2E1 is expected to be part of signaling pathways that involve the regulation of gene expression in response to various stimuli. NR2E1 plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of the nervous system, which implicates it in signaling pathways that regulate cell differentiation and proliferation. These pathways may include those involving growth factors and morphogens that pattern the developing brain. As indicated in the search results, NR2E1 may interact with the p21 pathway, which is a part of the cell cycle regulation and plays a role in controlling cell proliferation. Given its potential role in maintaining neural stem cells, NR2E1 could also be associated with signaling pathways that regulate apoptosis or programmed cell death.

Fig1. The interaction between TLX and TGF-β may play an important role in the regulation of proliferation and tumor-initiating properties of glioblastoma cells. (Erik Johansson, 2016)
NR2E1 Related Diseases
Given its role in neural development, NR2E1 may be implicated in neurodevelopmental disorders, although specific disorders are not listed in the search results. Recent studies suggest that dysregulation of TLX pathways plays a role in the pathogenesis of brain tumors. According to one source, NR2E1 is known to be a factor in metabolic diseases. A study suggests that Nr2e1 deficiency aggravates insulin resistance and chronic inflammation of visceral adipose tissues in a diet-induced obese mice model, potentially linking NR2E1 to diabetes.
Bioapplications of NR2E1
NR2E1 could be a target for the development of small molecule drugs or other therapeutics that modulate its activity, with potential applications in treating diseases where its function is impaired. With the advent of gene therapy and genetic editing technologies, NR2E1 offers a potential target for the correction of genetic mutations associated with neurological disorders. NR2E1's interaction with various proteins could be studied in a proteomics context to understand its network within the cell and its influence on cellular pathways.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Hyo-Jung Park, 2010
A growing body of evidence indicates that deregulation of stem cell fate determinants is a hallmark of many types of malignancies. The neural stem cell fate determinant TLX plays a pivotal role in neurogenesis in the adult brain by maintaining neural stem cells. Here, the researchers report a tumorigenic role of TLX in brain tumor initiation and progression. Increased TLX expression was observed in a number of glioma cells and glioma stem cells, and correlated with poor survival of patients with gliomas. Ectopic expression of TLX in the U87MG glioma cell line and Ink4a/Arf-deficient mouse astrocytes (Ink4a/Arf(-/-) astrocytes) induced cell proliferation with a concomitant increase in cyclin D expression, and accelerated foci formation in soft agar and tumor formation in in vivo transplantation assays. Furthermore, overexpression of TLX in Ink4a/Arf(-/-) astrocytes inhibited cell migration and invasion and promoted neurosphere formation and Nestin expression, which are hallmark characteristics of glioma stem cells, under stem cell culture conditions.

Fig1. Increased cell proliferation in TLX- overexpressing U87MG glioma cells.

Fig2. Neurosphere formation of TLX-overexpressing Ink4a/Arf-/- astrocytes in low-density seeding and neural stem cell culture conditions.
Case Study 2: Jiayi Zhou, 2021
High-grade gliomas are rapidly progressing tumors of the central nervous system, and are associated with poor prognosis and highly immunosuppressive microenvironments. In the present study, the researchers elucidate the functional significance of the orphan nuclear receptor TLX in human glioma, and its functional role in immune suppression through regulation of PD-L1/PD-1 axis. Protein expression and cellular localization of TLX, PD-L1, and PD-1, as well as the prevalence of cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), in the glioma immune microenvironment were analyzed via tissue microarray by immunohistochemistry and multiplex immunofluorescence. Glioma allografts and xenografts with TLX manipulation (knockdown/knockout or reverse agonist) were inoculated subcutaneously, or orthotopically into the brains of immunodeficient and immunocompetent mice to assess tumor growth by imaging, and the immune microenvironment by flow cytometry. PD-L1 transcriptional regulation by TLX was analyzed by chromatin immunoprecipitation and luciferase reporter assays. TLX and PD-L1 expression was positively associated with macrophage-mediated immunosuppressive phenotypes in gliomas. TLX showed significant upregulation and positive correlation with PD-L1. Meanwhile, suppression of TLX significantly inhibited in vivo growth of glioma allografts and xenografts. Mechanistically, TLX binds directly to CD274 (PD-L1) gene promoter and activates CD274 transcription.
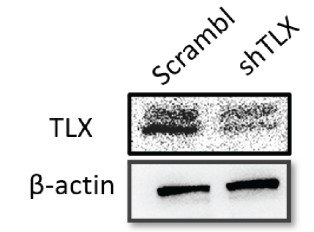
Fig3. Protein expression of TLX in A1235-scramble and shTLX by Western blot.

Fig4. Luciferase reporter assay of PD-L1 gene promoter-driven reporters performed in HEK293 cells transfected with different dose of TLX or its truncated mutants.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (NR2E1-6081H)
Involved Pathway
NR2E1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways NR2E1 participated on our site, such as Gene Expression,Generic Transcription Pathway,Nuclear Receptor transcription pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with NR2E1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Gene Expression | EEF1A1,BAZ2A,NR1I2,ZNF221,CCAR1,ZFP37,SUGP1,ASZ1,MED25,NFIA |
| Generic Transcription Pathway | ZNF658,ZNF26,ZIK1,ZNF596,NR2F6,NR2C1,ZNF79,ZNF434,ZNF839,GLS2B |
| Nuclear Receptor transcription pathway | NR1H3,NRBF2B,RARAB,ESRRG,NR1D2B,NR4A2B,NR5A1B,NR2F6A,NRBP1,ESRRGA |
| Nuclear Receptors | RARGB,NR1H3,NR2F2,NR2F1A,NR1D2,NR2F1,RARGA,NR2C2,ROR1,NR4A2A |
Protein Function
NR2E1 has several biochemical functions, for example, histone deacetylase binding,sequence-specific DNA binding,steroid hormone receptor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by NR2E1 itself. We selected most functions NR2E1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with NR2E1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| transcriptional repressor activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding | NFATC2,BCL11A,BACH1,ATF7,SALL1,TCF21,NKX6-2,ATF3,POU4F2,PROX1 |
| steroid hormone receptor activity | NR2F5,RARB,THRAA,GPR30,NR1D2,NR2F6,PAQR7A,NR2F1B,VDR,NR1H4 |
| histone deacetylase binding | PKN1,PHB,USF1,HIF1A,NR2C1,MEF2A,DDX20,RAD9,SP1,YY1 |
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding | RAX,PPARA,ZIC1,CEBPB,NKX2-8,FOS,EBF4,POU4F1,FOXJ2,TFE3 |
| sequence-specific DNA binding | NR2F6A,TCF7L2,MEIS3,HOXB1B,RAD21A,BPTF,ISX,ESR2B,TFAP2B,ERF |
| zinc ion binding | MTA3,ADAMTS12,PXN,ZMIZ1,FTR50,KDM5BA,PIAS2,RNF222,CECR1,Npepo |
Interacting Protein
NR2E1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with NR2E1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of NR2E1.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Olausson, KH; Maire, CL; et al. Prominin-1 (CD133) Defines Both Stem and Non-Stem Cell Populations in CNS Development and Gliomas. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).
- Gopisetty, G; Xu, J; et al. Epigenetic regulation of CD133/PROM1 expression in glioma stem cells by Sp1/myc and promoter methylation. ONCOGENE 32:3119-3129(2013).


