LASS2
-
Official Full Name
LAG1 homolog, ceramide synthase 2 -
Overview
This gene encodes a protein that has sequence similarity to yeast longevity assurance gene 1. Mutation or overexpression of the related gene in yeast has been shown to alter yeast lifespan. The human protein may play a role in the regulation of cell growth. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been described. -
Synonyms
LAG1 homolog, ceramide synthase 2;LAG1 longevity assurance homolog 2 (S. cerevisiae);SP260;MGC987;CerS2;OTTHUMP00000033029;FLJ10243;OTTHUMP00000033030;L3;OTTHUMP00000033031;longevity assurance (LAG1, S. cerevisiae) homolog 2;ceramide synthase 2;Tumor metastasis-suppressor gene 1 protein;LAG1 longevity assurance 2;TMSG1;LAG1 longevity assurance homolog 2;LASS2;OTTHUMP00000033028
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LASS2-512H | Recombinant Human LASS2, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | C-66aa | |
| LASS2-2467R | Recombinant Rhesus monkey LASS2 Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian Cells | Rhesus macaque | His |
|
|
| LASS2-8965M | Recombinant Mouse LASS2 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| LASS2-2288R | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque LASS2 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| LASS2-2288R-B | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque LASS2 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rhesus macaque |
|
||
| LASS2-4999M | Recombinant Mouse LASS2 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| LASS2-4999M-B | Recombinant Mouse LASS2 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is LASS2 protein?
LASS2 (CERS2, ceramide synthase 2) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q21. LASS2 is a protein that has important biological functions in the human body. It is a ceramide synthase, also known as longevity Assurance Protein 2 (LASS2), which is an important component of cell membrane structure and plays a key role in signal transduction and membrane transport. LASS2 is a member of the ceramide synthase (CerS) family of six subtypes, each capable of synthesizing ceramides with different acyl chain lengths and tissue-specific distributions. LASS2 is particularly good at synthesizing ceramides with long acyl chains, such as C22:0, C24:0, and C24:1. LASS2 protein is consisted of 380 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 44.9 kDa.
What is the function of LASS2 protein?
LASS2 has been identified as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of primary liver cancer. It can inhibit proliferation, migration, invasion of hepatoma cells and induce apoptosis. LASS2 is involved in the regulation of mitochondrial dynamics, the cell cycle, and the nuclear factor-κB pathways. It has been shown to enhance the chemosensitivity of breast cancer by inhibiting the activity of the V-ATPase proton pump, which counteracts the acidic tumor microenvironment. LASS2 interacts with proteins involved in the ferroptosis signaling pathway, a form of regulated cell death associated with iron metabolism. Studies suggest that LASS2 may play a role in maintaining chromosome stability and preventing abnormal chromosome ploidy.
LASS2 Related Signaling Pathway
LASS2 catalyzes the synthesis of ceramides by transferring a fatty acid to a sphingoid base. This is a key step in the de novo synthesis of sphingolipids, which are critical for the formation and function of cell membranes. The study suggests that LASS2 inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by preventing the nuclear translocation of β-catenin. Ceramides are known to be involved in the induction of apoptosis. LASS2, by regulating ceramide levels, can potentially influence the initiation of programmed cell death.
LASS2 Related Diseases
LASS2 (longevity protein 2) is associated with a variety of diseases, especially tumors and metabolic diseases. In terms of cancer, LASS2, as a tumor suppressor, is associated with the development of liver cancer, prostate cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer and other cancers. Studies have shown that LASS2 can inhibit the proliferation and invasion of tumor cells by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, affecting cell stemness and chemotherapy sensitivity. In addition, the expression level of LASS2 is closely related to the chemotherapy response and prognosis of some cancer patients. In terms of metabolic diseases, LASS2 is associated with fatty liver disease, insulin resistance, etc., and may play a role by affecting cell metabolism and lipid metabolism. In neurological diseases, LASS2 may be associated with myelin defects and cerebellar degeneration.
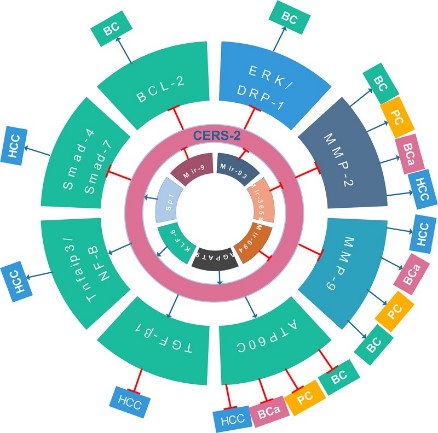
Fig1. Summary of current research on CerS-2 in bladder cancer (BC), hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), breast cancer (BCa) and prostatic cancer (PC). (Qian Zhang, 2019)
Bioapplications of LASS2
Fig1. Summary of current research on CerS-2 in bladder cancer (BC), hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), breast cancer (BCa) and prostatic cancer (PC). (Qian Zhang, 2019)
Case Study
Case Study 1: Hongjin Shi, 2024
Cisplatin is a commonly used chemotherapy agent, but its efficacy in myoinvasive bladder cancer (MIBC) is limited by intrinsic or acquired resistance. Evidence points to cancer stem cells being involved in the development of chemotherapy resistance, but the underlying molecular mechanisms have yet to be elucidated. This study investigated the role of LASS2 in regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in bladder cancer cells, and sought strategies to improve the sensitivity of bladder cancer to cisplatin therapy. Tumor ball formation assay, soft AGAR colony formation assay, EdU assay, apoptosis assay, cell activity and cisplatin sensitivity assay were used to study the function of LASS2. The underlying molecular mechanisms were investigated by immunofluorescence, western blotting, co-immunoprecipitation, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), PCR array, luciferase reporter gene assay, pathway reporter gene array, chromatin immunoprecipitation, functional gain and loss of function. The results showed that overexpression of LASS2 inhibited the self-renewal ability of BCSCs and increased their sensitivity to cisplatin. Mechanistically, LASS2 inhibits the activity of PP2A and dissociates PP2A from β-catenin, preventing the dephosphorylation of β-catenin, leading to the accumulation of cytoplasmic phosphorylated β-catenin, and reducing the transcription of ABCC2 and CD44 downstream genes in BCSCs.

Fig1. Graph showing the LASS2 expression levels and IC50 values of the indicated bladder cancer cell lines from the GDSC database.

Fig2. PP2A was activated in LASS2-overexpressing BCSCs.
Case Study 2: Yamei Wang, 2022
The authors found that the LASS2 gene inhibits the activity of V-ATPase by binding to its C subunit (ATP6L). However, the effect of overexpression and silencing of LASS2 on apoptosis of human lung cancer cells 95D or 95C remains unclear. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effect of LASS2 on apoptosis of 95D and 95C cells and its potential mechanism. Lentiviral vectors with LASS2 overexpression and silencing were transfected into 95D and 95C cells by lentiviral transfection method. The apoptotic capacity of tumor cells was observed by flow cytometry, and the expression levels of LASS2, Bcl-2, Bax, cytochrome C, caspase-9 and caspase-3 were detected by Western blotting. Flow cytometry analysis showed that overexpression of LASS2 could promote the early apoptosis of 95D lung cancer cells. In addition, overexpression of LASS2 decreased the expression of Bcl-2, promoted the release of cytochrome C by mitochondria, and activated caspase-9 and caspase-3. Compared with the normal group and the negative control group, the expression of Bcl-2, cytochrome C, caspase-9 and caspase-3 in the LASS2 overexpression group was significantly different. In contrast, the experiment in lung cancer cells 95C after LASS2 silencing had the opposite effect.

Fig3. The effect of silencing of LASS2 on the apoptosis of 95C cells.

Fig4. The effects of LASS2 overexpression on the protein levels of procaspase-9 and activated caspase-9 in 95D cells.
Involved Pathway
LASS2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways LASS2 participated on our site, such as Sphingolipid metabolism,Metabolic pathways,Sphingolipid signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with LASS2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | SMPD2,SGPL1,ASAH1,PPP2R1B,PIK3CB,ROCK2,RAC2,ROCK1,MS4A2,TNFRSF1A |
| Sphingolipid metabolism | SPHK1,ASAH1B,ARSI,SMPD2A,DEGS1,DEGS2,PPAP2A,CERS4,GALC,SPTLC2 |
| Metabolic pathways | AMACR,AGPAT4,ALDH18A1,GUK1A,MSMO1,DAD1,NME1-NME2,NADKA,EXT1,DCK |
Protein Function
LASS2 has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,sphingosine N-acyltransferase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by LASS2 itself. We selected most functions LASS2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with LASS2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| DNA binding | ZNF146,POU3F3B,LEMD3,HIST1H3H,SUPT3H,ZNF350,VENT,POU5F3,HOXA5,ACD |
| sphingosine N-acyltransferase activity | LASS4,CERS4,CERS4A,CERS5,LASS5,FAM57B,CERS2A,LASS1,CERS2,CERS3B |
Interacting Protein
LASS2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with LASS2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of LASS2.
Ywhae;Hsd3b4;Hsd3b7
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



