GAA
-
Official Full Name
glucosidase, alpha; acid -
Overview
This gene encodes acid alpha-glucosidase, which is essential for the degradation of glycogen to glucose in lysosomes. Different forms of acid alpha-glucosidase are obtained by proteolytic processing. Defects in this gene are the cause of glycogen storage disease II, also known as Pompes disease, which is an autosomal recessive disorder with a broad clinical spectrum. Three transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
GAA;glucosidase, alpha;acid;lysosomal alpha-glucosidase;glycogen storage disease type II;Pompe disease;70 kDa lysosomal alpha-glucosidase;Acid alpha glucosidase;Acid maltase;Aglucosidase alfa;Alpha glucosidase;Glucosidase alpha acid (Pompe disease glycogen storage disease type II);Glucosidase alpha acid;Glucosidase alpha;LYAG;LYAG_HUMAN;Lysosomal alpha glucosidase
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- CHO
- HEK293T
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Mamanlian cells
- Non
- His
- Myc&DDK
- GST
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
Background
What is GAA protein?
GAA gene (alpha glucosidase) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q25. This gene encodes lysosomal alpha-glucosidase, which is essential for the degradation of glycogen to glucose in lysosomes. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate multiple intermediate forms and the mature form of the enzyme. Defects in this gene are the cause of glycogen storage disease II, also known as Pompe's disease, which is an autosomal recessive disorder with a broad clinical spectrum. The GAA protein is consisted of 952 amino acids and GAA molecular weight is approximately 105.3 kDa.
What is the function of GAA protein?
GAA protein is a key enzyme that plays a role in lysosomes. It is mainly involved in the breakdown process of glycogen, ensuring that glycogen can be properly degraded into glucose molecules to maintain the normal progress of cellular energy metabolism and other biological processes. The function of the GAA protein is to hydrolyze the alpha-1, 4-glucoside bond and the alpha-1, 6-glucoside bond, which are key steps in the glycogenolysis process. The activity of GAA protein is related to the genotype, and different gene mutations will lead to different degrees of reduced enzyme activity, which will affect the severity of the disease.
GAA related signaling pathway
Gaa-related signaling pathways are mainly involved in glycogen metabolism and energy regulation. When the cell needs energy, glycogen phosphorylase is activated to break down glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate, which is then converted into glucose-6-phosphate through a series of enzymes to enter the glycolysis pathway to produce energy. At the same time, glycogen synthase converts excess glucose into glycogen for storage. This process is regulated by a variety of hormones and signaling molecules, such as insulin and adrenaline.
GAA related diseases
Gaa-related diseases mainly include glycogen storage disease type I (GSD I), which is an autosomal recessive genetic disease. Due to the mutation of GAA gene, the activity of glycogenolytic enzyme is insufficient, resulting in excessive accumulation of glycogen in liver, muscle and other tissues, affecting normal energy metabolism and organ function. The main symptoms of the disease include hypoglycemia, liver enlargement, muscle weakness, etc., which can lead to complications such as cardiomyopathy and respiratory failure in severe cases. At present, there is no cure, and treatment mainly relies on diet control, glucose supplementation and enzyme replacement therapy.
Bioapplications of GAA
Recombinant GAA supplements exogenous GAA to help patients with Pompeii disease decompose glycogen accumulated in the body, thereby improving patients' muscle tone, heart function, respiratory function and other clinical symptoms. Studies have shown that treatment with rhGAA significantly reduces the risk of death in children, improves survival, and reduces reliance on invasive ventilation. Long-term use of rhGAA can stabilize or improve cardiac hypertrophy and heart function in patients, helping to delay disease progression.
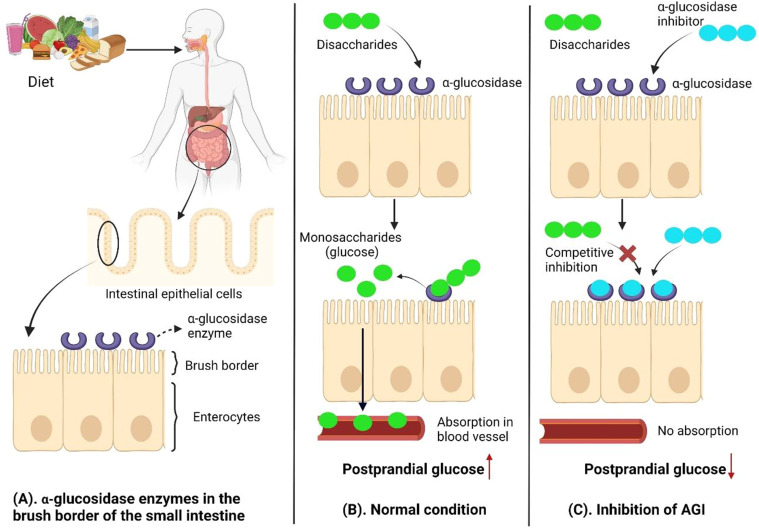
Fig1. Mechanism of α-glucosidase inhibition. (Tiara Ramadaini, 2024)
Case Study
Case Study 1: Nhan H Nguyen, 2021
The protection of critical therapeutic proteins from immune system recognition is a significant challenge, as their immunogenicity can diminish their effectiveness and safety. If the body mounts a persistent immune reaction to these proteins, it can drastically reduce the viable treatment options that are both secure and economically viable. It is essential to mitigate the potential immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins before their initial administration, as reversing an already triggered immune response is typically challenging. In this discussion, we explore a strategic design and evaluation of a nanoparticle system that includes phosphatidylserine, aimed at developing an innovative oral preventive vaccination strategy. This method involves the pre-treatment of therapeutic proteins with nanoparticles to preemptively guard against the immunogenicity associated with protein-based treatments.
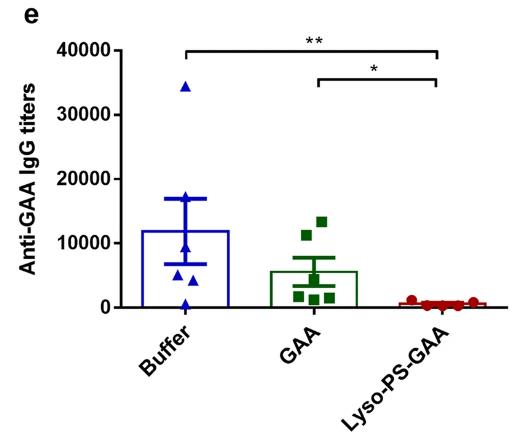
Fig1. Total anti-GAA antibodies after four weekly re-challenges with 1 μg free GAA.
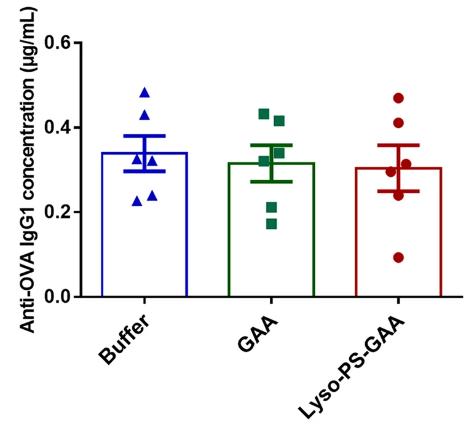
Fig2. Total anti-OVA IgG1 concentration after four weekly re-challenges with 1 μg free OVA.
Case Study 2: Jennifer L Schneider, 2016
Unwanted immune reactions to therapeutic proteins pose a significant clinical issue. The recent findings indicate that presenting Factor VIII with phosphatidylserine (PS) can lead to a reduced immune response upon re-exposure, suggesting PS's role in immune regulation rather than suppression. Given that PS is exposed during apoptosis, we believe it could turn an immunogen into a tolerogen, naturally inducing tolerance. PS's immune-modulating effects on recombinant human acid alpha-glucosidase (rhGAA) was tested, discovering that PS liposomes complex with rhGAA and promote dendritic cells to secrete more transforming growth factor-β. Mice immunized with PS-rhGAA showed decreased antibody responses to rhGAA, even after re-exposure, with many remaining nonresponders.
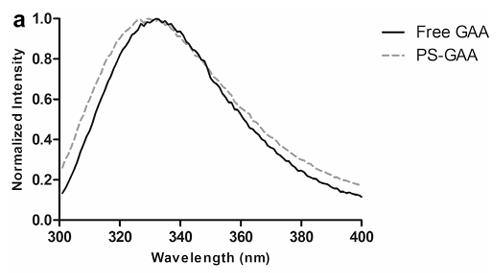
Fig3. Fluorescent spectra to examine the tertiary structure of rhGAA in the presence and absence of PS liposomes.
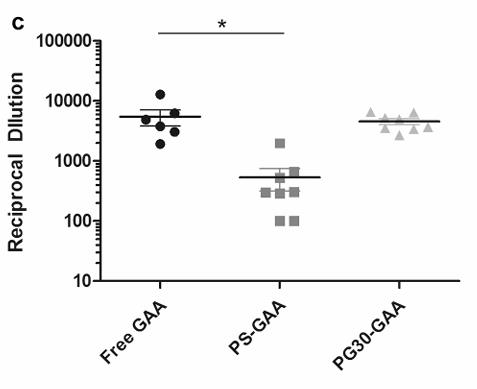
Fig4. Anti-rhGAA antibody titer response after rechallenge with free rhGAA.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GAA-160H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GAA-159H)
Involved Pathway
GAA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GAA participated on our site, such as Galactose metabolism,Starch and sucrose metabolism,Metabolic pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GAA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Galactose metabolism | B4GALT1,AKR1B1,aLA,GLA,PFKP,UGP2B,UGP2,G6PC,SI,G6PCA.2 |
| Lysosome | GLB1,AP3S1,HYAL1,ACP5B,CLN3,GGA1,ABCB9,AGA,SUMF1,CTPS1B |
| Starch and sucrose metabolism | UGDH,UGT1AB,PYGL,GPIA,G6PC3,SI,UGT1A1,UGT1A2,UXS1,GANC |
| Metabolic pathways | AKR1B1L,ADH1B,UGT1A1,SLC27A5,ADA,PPOX,PIGP,Atp5k,CMPK2,TDO2 |
Protein Function
GAA has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GAA itself. We selected most functions GAA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GAA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
GAA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GAA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GAA.
HIVEP1;STAT2;EP300;ypiP;q9wmx2-pro_0000037548;NUMBL;pi3p;cona_canen
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Guo, MH; Hundseth, K; et al. A Distinct Triplex DNA Unwinding Activity of ChlR1 Helicase. JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 290:5174-5189(2015).
- Lukas, J; Pockrandt, AM; et al. Enzyme Enhancers for the Treatment of Fabry and Pompe Disease. MOLECULAR THERAPY 23:456-464(2015).



