FMR1
-
Official Full Name
fragile X mental retardation 1 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene binds RNA and is associated with polysomes. The encoded protein may be involved in mRNA trafficking from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. A trinucleotide repeat (CGG) in the 5 UTR is normally found at 6-53 copies, but an expansion to 55-230 repeats is the cause of fragile X syndrome. Expansion of the trinucleotide repeat may also cause one form of premature ovarian failure (POF1). Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms and which are located in different cellular locations have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010] -
Synonyms
FMR1;fragile X mental retardation 1;POF;FMRP;POF1;FRAXA;fragile X mental retardation protein 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Mamanlian cells
- GST
- His
- Non
- Myc&DDK
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
Background
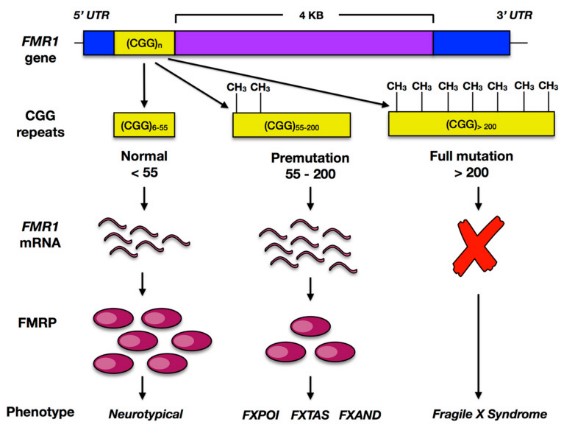
Fig1. The FMR1 gene and Fragile X pathology. (William Fyke, 2021)
What is FMR1 protein?
FMR1 (fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome X at locus Xq27. The protein encoded by this gene binds RNA and is associated with polysomes. The encoded protein may be involved in mRNA trafficking from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. A trinucleotide repeat (CGG) in the 5' UTR is normally found at 6-53 copies, but an expansion to 55-230 repeats is the cause of fragile X syndrome. Expansion of the trinucleotide repeat may also cause one form of premature ovarian failure (POF1). The FMR1 protein is consisted of 632 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 71.2 kDa.
What is the function of FMR1 protein?
The main biological functions of FMR1 protein include that it is involved in regulating mRNA stability and translation efficiency as an mRNA binding protein, thereby affecting gene expression. It regulates cell development and function by binding to specific mRNA molecules and affecting the localization, stability, and translation of these molecules. The FMR1 protein is also involved in synaptic plasticity and neurodevelopment, and plays an important role in brain function and cognitive ability.
FMR1 Related Signaling Pathway
The FMR1 protein plays a role in the nervous system by binding to specific mRNA molecules, affecting their stability and translation, thereby regulating the expression of proteins related to synaptic formation and neurodevelopment; FMR1 is associated with the rapamycin target protein (mTOR) signaling pathway, which plays a key role in cell growth, proliferation, and metabolism. As an RNA-binding protein, FMR1 can affect gene transcription and translation, involving RNA polymerase-related signaling pathways, and plays an important role in the regulation of intracellular gene expression. FMR1 protein is also involved in signaling pathways for cell cycle regulation and apoptosis, and its abnormality may be associated with tumorigenesis.
FMR1 Related Diseases
Diseases Associated with FMR1 protein include Fragile X Syndrome (FXS) and Fragile X-associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome. FXTAS and FMR1-associated Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI). Fragile X syndrome is an inherited intellectual disorder and a monogenic cause of the most common autism spectrum disorder, usually caused by gene silencing due to overexpansion of the CGG repeat of the FMR1 gene. FXTAS is a late-onset disease affecting adult men and women characterized by movement and cognitive problems associated with a premutation of the FMR1 gene. In addition, abnormalities in the FMR1 gene are associated with primary ovarian dysfunction, which can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, early menopause, and fertility problems.
Bioapplications of FMR1
Based on the role of FMR1 protein in Fragile X syndrome and tumor immune escape, small molecule inhibitors targeting FMR1 protein may be potential drugs for the treatment of Fragile X syndrome and certain cancers. The cloning, expression and purification of FMR1 protein provide experimental materials for studying its RNA-binding properties and functions. Testing for the FMR1 gene can help families understand genetic risk and guide family members' reproductive planning.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Meng Li, 2020
RNA-binding proteins (RNA-BPs) play critical roles in development and disease to regulate gene expression. However, genome-wide identification of their targets in primary human cells has been challenging. Here, the researchers applied a modified CLIP-seq strategy to identify genome-wide targets of the FMRP translational regulator 1 (FMR1), a brain-enriched RNA-BP, whose deficiency leads to Fragile X Syndrome (FXS), the most prevalent inherited intellectual disability. They identified FMR1 targets in human dorsal and ventral forebrain neural progenitors and excitatory and inhibitory neurons differentiated from human pluripotent stem cells. In parallel, they measured the transcriptomes of the same four cell types upon FMR1 gene deletion. They discovered that FMR1 preferentially binds long transcripts in human neural cells. FMR1 targets include genes unique to human neural cells and associated with clinical phenotypes of FXS and autism. Integrative network analysis using graph diffusion and multitask clustering of FMR1 CLIP-seq and transcriptional targets reveals critical pathways regulated by FMR1 in human neural development.

Fig1. Western blot detecting FMR1 or FLAG in FMR1-FLAG and WT hPSCs, GAPDH as a loading control.

Fig2. Analysis of length distribution of FMR1 targets in various cell types.
Case Study 2: Rustam Esanov, 2016
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) results from a repeat expansion mutation near the FMR1 gene promoter and is the most common form of heritable intellectual disability and autism. While the role of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) in FMR1 gene silencing has been studied extensively, the role of 5-hydroxymethylation (5hmC), a newly discovered epigenetic mark produced through active DNA demethylation, has not been previously investigated in FXS neurons. Here, the researchers used two complementary epigenetic assays, 5hmC sensitive restriction digest and ten-eleven translocation-assisted bisulfite pyrosequencing, to quantify FMR1 5mC and 5hmC levels. They observed increased levels of 5hmC at the FMR1 promoter in FXS patient brains with full-mutations relative to pre-mutation carriers and unaffected controls. In addition, they found that 5hmC enrichment at the FMR1 locus in FXS cells is specific to neurons by utilizing a nuclei sorting technique to separate neuronal and glial DNA fractions from post-mortem brain tissues.

Fig3. Expression of FMR1 in clinical samples.

Fig4. Site-specific FMR1 DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation assessment in cellular models of FXS.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FMR1-1624H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FMR1-058H)
Involved Pathway
FMR1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FMR1 participated on our site, such as RNA transport, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FMR1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| RNA transport | SUMO3,EIF4G3,KPNB1,NXT2,EIF4E2RS1,SRRM1,EEF1A1B,EIF2B1,EIF1B,EIF4EBP3 |
Protein Function
FMR1 has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA binding,mRNA binding,microtubule binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FMR1 itself. We selected most functions FMR1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FMR1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | RFWD2,SSTR3,NFATC4,USP54,LIPT2,CHPF,TRAF3IP1,PCDH18,CECR2,UNC13A |
| microtubule binding | KIF5AA,DPYSL5B,CLASP1,MAPRE3,NEFH,CDK5RAP2,KIF5B,ARHGEF2,CKAP5,KIF25 |
| RNA binding | SNRPF,KHDC3,HNRNPAB,NPM1,RBM4.1,HNRNPD,IFIT8,RNASEH2A,HNRNPH3,RNASEN |
| mRNA binding | LUC7L3,AGO2,RBM8A,RBMY1A1,ZFP36,CSTF3,RPS26,RBM38,QKI,CPSF5 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | TBCA,CPNE3,GTL3,TNRC6B,RPS8,ESF1,XPO5,ZFP579,MRPS14,APEH |
Interacting Protein
FMR1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FMR1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FMR1.
CYFIP2;CYFIP1;ESR2;STAU1;PRKAA1;HABP4;Rcan1;LIMS1;fhaC2;Cyfip1;TBKBP1;7-methyl-gtp
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Groh, M; Lufino, MMP; et al. R-loops Associated with Triplet Repeat Expansions Promote Gene Silencing in Friedreich Ataxia and Fragile X Syndrome. PLOS GENETICS 10:-(2014).
- Lisik, MZ; Gutmajster, E; et al. Anti-Neuronal Antibodies in Patients with Fragile X Syndrome: Is there a Role of Autoimmunity in Its Pathogenesis?. NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASES 15:45-49(2015).


