Cdc25b
-
Official Full Name
cell division cycle 25 homolog B -
Overview
cdc25 is a protein phosphatase responsible for dephosphorylating and activating cdc2, a crucial step in regulating the entry of all eukaryotic cells into mitosis. cdc25C is constitutively phosphorylated at Ser216 throughout interphase by c-TAK1, while pho -
Synonyms
CDC25B;cell division cycle 25 homolog B (S. pombe);cell division cycle 25 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) , cell division cycle 25B;M-phase inducer phosphatase 2;cell division cycle 25B;dual specificity phosphatase Cdc25B
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDC25B-11000H | Recombinant Human CDC25B, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 1-300a.a. | |
| CDC25B-1512H |
Active Recombinant Human CDC25B, GST-tagged
|
Sf9 Cells | Human | GST | Full length |
|
| CDC25B-547H |
Active Recombinant Human CDC25B Protein, Met & His-tagged
|
E.coli | Human | His | Glu377-Gln566 |
|
| CDC25B-0916H | Recombinant Human CDC25B Protein, GST-Tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| CDC25B-1272R | Recombinant Rat CDC25B Protein | Mammalian Cells | Rat | His |
|
|
| CDC25B-6535Z | Recombinant Zebrafish CDC25B | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| CDC25B-7665HCL | Recombinant Human CDC25B 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| CDC25B-7666HCL | Recombinant Human CDC25B 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| CDC25B-3053HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CDC25B Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 580 amino acids |
|
| CDC25B-930R | Recombinant Rat CDC25B Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| CDC25B-930R-B | Recombinant Rat CDC25B Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
Background
What is CDC25B Protein?
CDC25B gene (cell division cycle 25B) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 20 at locus 20p13. CDC25B is a member of the CDC25 family of phosphatases. CDC25B activates the cyclin dependent kinase CDC2 by removing two phosphate groups and it is required for entry into mitosis. CDC25B shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm due to nuclear localization and nuclear export signals. The protein is nuclear in the M and G1 phases of the cell cycle and moves to the cytoplasm during S and G2. The CDC25B protein is consisted of 580 amino acids and CDC25B molecular weight is approximately 65.0 kDa.
What is the Function of CDC25B Protein?
CDC25B protein is an important cell cycle regulator. It belongs to the bispecial phosphatase family, and its main function is to remove inhibitory phosphate groups on cell cycle dependent kinases (CDKs), so as to activate CDKs and promote the process of cell cycle. CDC25B activity and localization are regulated by a variety of factors, including phosphorylation, interaction with 14-3-3 proteins, and influence of nuclear input and output signals. It shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm, changing its location according to different stages of the cell cycle. During mitosis and G1 phase, CDC25B is located in the nucleus, while during S phase and G2 phase, it is transferred to the cytoplasm.
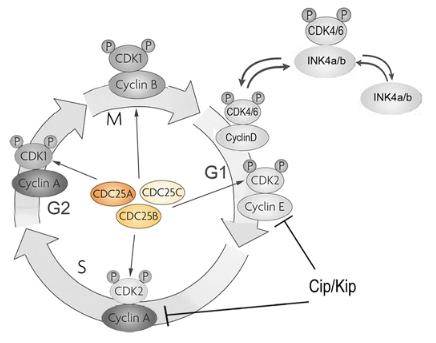
Fig1. A simplified schematic representation of the cell cycle. (Eric Agius, 2015)
CDC25B Related Signaling Pathway
CDC25B is an important cell cycle regulatory protein, belonging to the bispecic phosphatase family, which is essential for G2/M conversion of the cell cycle. The activity and localization of CDC25B are finely regulated during G2/M conversion. For example, the ArorA-A kinase specifically phosphorylates CDC25B during mitosis, promoting its localization in the centrosome. PLK1 (Polo-like kinase 1) activates CDC25B through phosphorylation of multiple sites and promotes its transfer from cytoplasm to nucleus during G2-M conversion. In addition, CDC25B activity is regulated by 14-3-3 proteins, whose binding to CDC25B prevents its interaction with CDK1-cyclin B, thereby inhibiting its activity.
CDC25B Related Diseases
Abnormal expression of CDC25B protein has been associated with a variety of diseases, especially in the field of cancer. Its overexpression is often associated with tumor growth, invasiveness, metastasis, and poor prognosis. Specifically, CDC25B has been found to be overexpressed in a variety of cancers, including breast, ovarian, lung, and colorectal cancers, and may work by promoting tumor cell proliferation and helping tumor cells bypass checkpoint control of the cell cycle. In addition, high expression of CDC25B is associated with p53-dependent tumor suppression, which may be achieved by inducing cell senescence. In some cases, phosphatase activity of CDC25B is necessary to induce cellular senescence, which provides potential targets for the development of new anti-cancer strategies.
Bioapplications of CDC25B
Because CDC25B is expressed at elevated levels in a variety of cancers and is associated with tumor proliferation, invasion, and metastasis, it becomes an attractive target for cancer therapy. By developing small molecule inhibitors or antibodies targeting CDC25B, it is possible to inhibit the cell cycle progression of tumor cells, thereby slowing tumor growth. Based on the key role of CDC25B in cell cycle regulation, drugs are being developed that can specifically inhibit CDC25B activity, which may be selectively toxic to cancer cells and have less effect on normal cells. Changes in CDC25B expression levels in some cancers can be used as biomarkers of disease progression and prognosis, contributing to early diagnosis of cancer, treatment response monitoring and prognosis assessment.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jie Xu, 2021
Previous studies showed high β-amyloid (Aβ) expression levels in the nuclei of the lens epithelial cells (LECs) of healthy subjects and revealed that Aβ monomers could protect LECs from oxidative damage. Here, researchers further explored the mechanism by which Aβ monomers act as transcription factors to regulate the oxidative stress of LECs through high-throughput studies. Combining the literature review with KEGG analysis results, in the current study, they chose four target genes related to oxidative stress, namely, CDC25B, SOS2, CTNNA1 and Cox6a1. Then, ChIP-PCR assays, dual-luciferase reporter assays, real-time PCR and Western blotting were performed to validate the regulatory effects of Aβ on these targets. The data suggested that Aβ monomers could upregulate the mRNA and protein expression levels of CDC25B in LECs. They also confirmed that Aβ monomers could activate the Akt/Nrf2 pathway in a CDC25B-dependent manner by knockdown experiments in cultured LECs. Furthermore, Aβ monomers significantly improved the antioxidant capacity (the GSH level, SOD activity and total antioxidant capacity) and decreased the oxidative stress (the ROS and MDA levels) of LECs, while CDC25B knockdown decreased the antioxidant effects of Aβ, disrupting redox homeostasis.

Fig1. Validation of the CDC25B gene using a luciferase reporter assay.
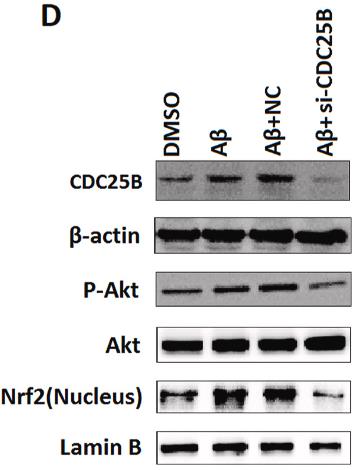
Fig2. Western blot analysis to verify the CDC25B-dependent activity of the Akt/Nrf2 pathway.
Case Study 2: Liang Cui, 2018
Cell division cycle 25 B (CDC25B) is a member of the CDC25 phosphatase family. It can dephosphorylate cyclin-dependent kinases and regulate the cell division cycle. Moreover, siRNA knockdown of CDC25B impairs influenza A virus (IAV) replication. Here, to further understand the regulatory mechanism of CDC25B for IAV replication, a CDC25B-knockout (KO) 293T cell line was constructed using CRISPR/Cas9. The present data indicated that the replication of IAV was decreased in CDC25B-KO cells. Additionally, CDC25B deficiency damaged viral polymerase activity, nucleoprotein (NP) self-oligomerization, and NP nuclear export. Most importantly, the NP phosphorylation levels were significantly increased in CDC25B-KO cells.

Fig3. Effects of CDC25B on cRNA, mRNA and vRNA levels of viral M1 protein.

Fig4. CDC25B deficiency reduces the activity of viral polymerase and NP self-oligomerization.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CDC25B-0916H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CDC25B-1099H)
Involved Pathway
Cdc25b involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Cdc25b participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Cell cycle,Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Cdc25b were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | HSP90AA1.2,HSP90AA1.1,PIK3R1,MAPK8B,CPEB4,RPS6KAL,RPS6KA1,PPP1R2P9,PRKACAA,HSP90AB1 |
| Cell cycle | YWHABA,CENPL,SMC3,EP300,RBX1,OIP5,CDC25C,B9D2,SMC1A,HIST3H2BB |
| MicroRNAs in cancer | RAF1,PRKCB,RPTOR,TRP63,PRKCA,FZD3,PDGFB,ST14,NOTCH2,SOS1 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | MKNK2A,NGF,PPM1BB,MAP3K7,MKNK2,ARRB2A,TGFB2,PRKACAB,MEF2CB,GNG12A |
Protein Function
Cdc25b has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,protein kinase binding,protein tyrosine phosphatase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Cdc25b itself. We selected most functions Cdc25b had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Cdc25b. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein tyrosine phosphatase activity | LRP8,MTM1,PTPRU,CDC14AA,EPM2A,DUSP14,PTPN9,DUSP11,CDC25C,PTPN3 |
| protein binding | CD1d1,RAB34,CD8B1,CTSH,OGT,PIH1D3,RPS28,FAM127B,MAP3K3,RNF182 |
| protein kinase binding | KIF14,CCND2,CENPJ,FGFR1OP,FAM83D,CD36,CDKN2A,CCNY,FOXO3,CDKN2B |
Interacting Protein
Cdc25b has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Cdc25b here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Cdc25b.
YWHAZ;YWHAB;YWHAH
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Lee, KH; Tsutsui, T; et al. Overexpression of mutant cell division cycle 25 homolog B (CDC25B) enhances the efficiency of selection in Chinese hamster ovary cells. CYTOTECHNOLOGY 65:1017-1026(2013).
- Kang, H; Hwang, SC; et al. Cdc25B phosphatase participates in maintaining metaphase II arrest in mouse oocytes. MOLECULES AND CELLS 35:514-518(2013).



