CLDN2
-
Official Full Name
claudin 2 -
Overview
This gene product belongs to the claudin protein family whose members have been identified as major integral membrane proteins localized exclusively at tight junctions. Claudins are expressed in an organ-specific manner and regulate tissue-specific physiologic properties of tight junctions. This protein is expressed in the intestine. Alternatively spliced transcript variants with different 5' untranslated region have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
CLDN2;claudin 2;SP82;claudin-2;OTTHUMP00000023793;PSEC0059;UNQ705/PRO1356
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Bovine
- Dog
- Mus musculus
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- Baculovirus-Insect cells
- HEK293T
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- E.coli expression system
- GST
- Non
- His
- Flag
- Myc&DDK
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLDN2-11292H | Recombinant Human CLDN2 protein(184-230 aa), GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 184-230 aa | |
| CLDN2-2948H |
Active Recombinant Human CLDN2 Full Length Transmembrane protein(Nanodisc)
|
HEK293 | Human | Non | Full L. |
|
| CLDN2-1282Z | Recombinant Zebrafish CLDN2 | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| CLDN2-1438H | Recombinant Human CLDN2 Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| CLDN2-26706TH | Recombinant Human CLDN2 | Wheat Germ | Human | Non | 52 amino acids |
|
| CLDN2-5001C | Recombinant Chicken CLDN2 | Mammalian Cell | Chicken | His |
|
|
| CLDN2-7466HCL | Recombinant Human CLDN2 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| CLDN2-0405H | Recombinant Human CLDN2 Protein (Met1-Val230), C-His-tagged | Baculovirus-Insect cells | Human | His | Met1-Val230 |
|
| CLDN2-06HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human claudin 2 Protein, Flag tagged | HEK293T | Human | Flag | Full L. 1-230aa |
|
| CLDN2-1091H | Recombinant Human CLDN2 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | HEK293T | Human | Myc&DDK |
|
|
| CLDN2-2052HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CLDN2 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 230 amino acids |
|
| Cldn2-900M | Recombinant Mouse Cldn2 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293T | Mouse | Myc&DDK |
|
|
| RFL21893BF | Recombinant Full Length Bovine Claudin-2(Cldn2) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli expression system | Bovine | His | Full L. Full Length (1-230) |
|
| RFL23223CF | Recombinant Full Length Dog Claudin-2(Cldn2) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli expression system | Dog | His | Full L. Full Length (1-230) |
|
| RFL29997MF | Recombinant Full Length Mouse Claudin-2(Cldn2) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli expression system | Mus musculus | His | Full L. Full Length (1-230) |
|
| RFL8713HF | Recombinant Full Length Human Claudin-2(Cldn2) Protein, His-Tagged | E.coli expression system | Human | His | Full L. Full Length (1-230) |
|
Background
What is CLDN2 protein?
CLDN2 gene (claudin 2) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome X at locus Xq22. This gene product belongs to the claudin protein family whose members have been identified as major integral membrane proteins localized exclusively at tight junctions. Claudins are expressed in an organ-specific manner and regulate tissue-specific physiologic properties of tight junctions. This protein is expressed in the intestine. The CLDN2 protein is consisted of 230 amino acids and CLDN2 molecular weight is approximately 24.5 kDa.
What is the function of CLDN2 protein?
The CLDN2 protein is a critical component of the tight junctions in epithelial and endothelial cells. It forms paracellular channels that are selective for cations and water, contributing to the permeability of the epithelial barrier. Claudin-2 plays a significant role in the intestines, particularly in the proximal tubules of the kidneys and the gut, where it aids in the energy-efficient transport of ions and water. It is also implicated in various diseases, including cancer, inflammation, and fibrosis, and its expression levels can be correlated with disease progression. Furthermore, Claudin-2 has been identified as a potential biomarker for conditions like colorectal cancer and is targeted by vitamin D receptor signaling, which suggests its involvement in cellular processes beyond its known effects on tight junction function.

Fig1. Claudin-2 structure and interactions with cytosolic multidomain adapters. (Shruthi Venugopal, 2019)
CLDN2 related signaling pathway
The CLDN2 protein, a component of tight junctions, forms paracellular channels that are selectively permeable to cations and water, influencing the epithelial barrier's permeability. It plays a crucial role in ion and water transport in the kidneys and gut. Beyond its structural function, CLDN2 is implicated in cellular processes such as proliferation, migration, and cell fate determination, which are relevant to diseases like cancer, inflammation, and fibrosis. Dysregulation of CLDN2 is associated with various pathologies, and signaling pathways that are overactivated in diseases can alter CLDN2 expression. For instance, in colorectal cancer, CLDN2 has been shown to promote tumor growth and metastasis by suppressing the transcription of NDRG1, a metastasis suppressor gene, and is being explored as a potential biomarker for cancer detection and prognosis.
CLDN2 related diseases
CLDN2 is associated with several diseases, particularly inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), where its expression is elevated in inflamed gut tissue. This dysregulation contributes to increased intestinal permeability and may play a role in the pathogenesis of IBD. Additionally, CLDN2 has been implicated in cancer, particularly colorectal cancer, where it promotes tumor growth and metastasis. Recent studies suggest that CLDN2 may also serve as a biomarker for pre-diabetes, with elevated levels observed in patients with impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes. Its expression is influenced by various inflammatory cytokines, indicating its potential role in metabolic disorders and inflammation-related diseases.
Bioapplications of CLDN2
CLDN2 has bioapplications in various medical fields, primarily serving as a tight junction protein crucial for paracellular transport of ions and water in leaky epithelia. It is notably implicated in the progression of inflammatory bowel disease due to its role in intestinal barrier function. Furthermore, CLDN2's expression is elevated in several cancers, including colorectal, where it promotes tumor growth and metastasis, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target. Additionally, CLDN2 has emerged as a promising biomarker for early diagnosis of pre-diabetes, with its expression significantly upregulated in both diabetic mice models and human patients with impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes. These applications underscore CLDN2's significance in disease diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment strategies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Mingtian Wei, 2021
In colorectal cancer (CRC), Claudin-2 (CLDN2) is linked to tumor progression and poor survival rates. This research shows that reducing CLDN2 expression enhances NDRG1 transcription, thereby inhibiting CRC growth and spread. This effect is due to the disruption of the CLDN2/ZO1/ZONAB complex, allowing ZONAB to enter the nucleus and activate NDRG1. This finding points to a new CLDN2/ZO1/ZONAB-NDRG1 pathway in CRC and positions CLDN2 as a potential therapeutic target.
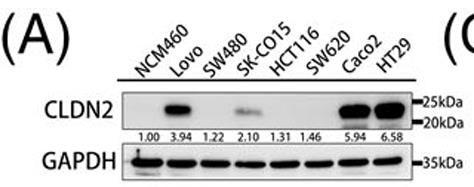
Fig1. Representative band of CLDN2 levels in CRC cell lines by western blot analysis.

Fig2. The interaction and correlation between ZONAB and ZO1/NDRG1/CLDN2 in HT29 cells knocking out CLDN2.
Case Study 2: Yang Songtao, 2024
Pre-diabetes, a precursor to diabetes, represents a critical metabolic state that allows for early intervention. Identifying this condition early is vital for preventing diabetes, making the search for accurate biomarkers essential. Researchers analyzed gene expression in clinical samples across non-diabetic, impaired glucose tolerance, and type 2 diabetes groups using the GSE164416 dataset and confirmed our findings in mice models with high-fat diets and STZ-induced diabetes. The analysis revealed shared differentially expressed genes (Co-DEGs) in impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes, with CLDN2 being a standout.
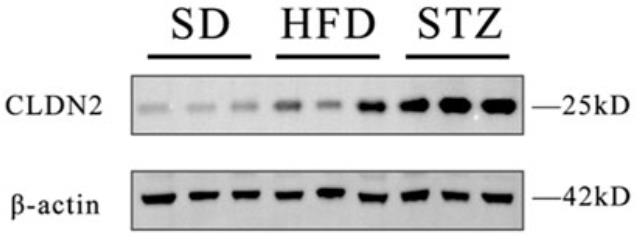
Fig3. Western blot showing the overexpression of CLDN2 in both HFD and STZ mice.
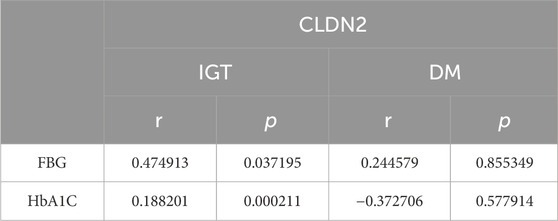
Fig4. Correlation of CLDN2 level with clinical parameters.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
CLDN2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CLDN2 participated on our site, such as Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs),Tight junction,Leukocyte transendothelial migration, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CLDN2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hepatitis C | IKBKB,PIK3R1,CLDN23,PDPK1,TRAF6,LDLR,IFNA8,TYK2,PPP2CA,ARAF |
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | PIK3CB,CTNNA3,MYL7,RASSF5,CLDN3,GNAI3,PECAM1,ITGAL,PIK3R3,RAP1A |
| Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | CLDND,CLDNK,CD2,ITGAL,CLDN18,NRXN2A,PVR,ITGB7,HLA-DRB4,LRRC4B |
| Tight junction | MPP5,PRKCA,PTEN,PARD6A,PPP2R2C,MYHC4,MYHZ1.1,CLDN22,ACTB2,MYH11A |
Protein Function
CLDN2 has several biochemical functions, for example, identical protein binding,protein binding,structural molecule activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CLDN2 itself. We selected most functions CLDN2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CLDN2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | ARL16,ALAS1,ACCS,NOSIP,NF2,FAM40A,ITPR3,PRPF3,GHRL,CNBP |
| structural molecule activity | CLDN10B,CYT1L,PGM5,GNL1,KRT33B,COPE,INAA,KRT77,TUBGCP3,COL18A1 |
| identical protein binding | MCIN,PRPF19,GRB7,RYR2,ST13,ERN1,TLE1,IGF2R,SNCA,C14orf166 |
Interacting Protein
CLDN2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CLDN2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CLDN2.
KRT31;NOTCH2NL;KRTAP4-12;TJP1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References

.jpg)
.jpg)

