CFL2
-
Official Full Name
cofilin 2 (muscle) -
Overview
This gene encodes an intracellular protein that is involved in the regulation of actin-filament dynamics. This protein is a major component of intranuclear and cytoplasmic actin rods. It can bind G- and F-actin in a 1:1 ratio of cofilin to actin, and it reversibly controls actin polymerization and depolymerization in a pH-dependent manner. Mutations in this gene cause nemaline myopathy type 7, a form of congenital myopathy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. -
Synonyms
CFL2;cofilin 2 (muscle);cofilin-2;cofilin, muscle isoform;NEM7
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HEK293T
- GST
- His
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
Background

Fig1. Transcripts of human CFL2 gene. (C Thirion, 2001)
What is CFL2 protein?
CFL2 (cofilin 2) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 14 at locus 14q13. CFL2 is a protein that belongs to the actin-depolymerizing factor/cofilin family. It plays a crucial role in the regulation of actin filament dynamics, which is a critical process for various cellular functions, including cell motility, intracellular transport, and muscle contraction. CFL2 controls the reversible polymerization and depolymerization of actin filaments in a pH-sensitive manner. CFL2 is a predicted intracellular protein that is also classified as a plasma protein. The N-terminal α-amino SUMOylation of cofilin-1 (CFL1), a close homologue of CFL2, is critical for its depolymerizing activity. The CFL2 protein is consisted of 166 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 18.7 kDa.
What is the function of CFL2 protein?
CFL2 is an actin-depolymerizing factor that helps control the balance between monomeric (G-actin) and filamentous (F-actin) actin, which is essential for cellular motility and the restructuring of the cytoskeleton. CFL2 is particularly important in muscle cells, where it is required for the maintenance of muscle tissue and may play a role in the exchange of alpha-actin forms during early postnatal development of muscle fibers. CFL2 is found in the cytoplasm and is a component of intranuclear and cytoplasmic actin rods, which are filamentous structures composed of actin and associated proteins. CFL2 may be involved in the early postnatal remodeling of the sarcomere, which is a key structural unit of muscle fibers responsible for muscle contraction. Although primarily intracellular, CFL2 is also classified as a plasma protein, suggesting it may have functions outside of cells as well.
CFL2 Related Signaling Pathway
CFL2 controls the reversible polymerization and depolymerization of actin filaments in a pH-sensitive manner, which is fundamental to cellular processes such as cell motility and muscle contraction. CFL2 activity is regulated by the Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) which phosphorylates LIMK (LIM domain kinase), leading to the phosphorylation and inactivation of CFL2. This pathway is critical for the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Mutations in the CFL2 gene are associated with NEM7, a form of nemaline myopathy. The molecular mechanisms underlying this disease may involve disruptions in actin filament dynamics within muscle cells. CFL2 is suggested to be involved in various signaling pathways within muscle cells, including those that regulate muscle maintenance and adaptation to stress.
CFL2 Related Diseases
CFL2 (Cofilin 2) is a protein that is integral to the regulation of actin dynamics within cells, and its dysfunction has been associated with several diseases. Nemaline Myopathy 7 (NEM7) is a form of nemaline myopathy, a congenital myopathy characterized by the presence of rod-shaped bodies in muscle cells. CFL2 mutations are known to cause NEM7, highlighting the importance of CFL2 in maintaining normal muscle structure and function. Congenital Fiber-Type Disproportion (CFTD) is a rare myopathy where there is an abnormal proportion of different muscle fiber types. CFL2 is among the genes associated with this condition. The actin cytoskeleton, which CFL2 helps regulate, is involved in cell migration and invasion processes that are critical in cancer metastasis. While CFL2's direct link to cancer is not specified in the resources, its role in actin dynamics could theoretically have implications for cancer biology. CFL2, through its regulation of actin dynamics, may also play a role in the host response to infectious agents, as actin rearrangements are a common strategy used by pathogens to facilitate infection.
Bioapplications of CFL2
CFL2 is essential for myogenic differentiation, which is the process by which muscle cells develop from myogenic progenitor cells. It is crucial for maintaining skeletal muscle mass and integrity, and its dysregulation can lead to muscle-related pathologies such as muscular dystrophy and metabolic myopathy. The study of CFL2's role in cellular processes could aid in the development of small molecule inhibitors or activators that could modulate its function, potentially leading to new drugs for treating diseases where CFL2 function is impaired.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Marcello Pignataro, 2020
Cofilins are small protein of the actin depolymerizing family. Actin polymerization/depolymerization is central to a number of critical cellular physiological tasks making cofilin a key protein for several physiological functions of the cell. Cofilin activity is mainly regulated by phosphorylation on serine residue 3 making this post-translational modification key to the regulation of myofilament integrity. In fact, in this form, the protein segregates in myocardial aggregates in human idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Since myofilament network is an early target of oxidative stress the researchers investigated the molecular changes induced by oxidation on cofilin isoforms and their interplay with the protein phosphorylation state to get insight on whether/how those changes may predispose to early protein aggregation. Using different and complementary approaches the researchers characterized the aggregation properties of cofilin-2 and its phosphomimetic variant (S3D) in response to oxidative stress in silico, in vitro and on isolated cardiomyocytes. The phosphorylated (inactive) form of cofilin-2 is mechanistically linked to the formation of an extended network of fibrillar structures induced by oxidative stress via the formation of a disulfide bond between Cys39 and Cys80.
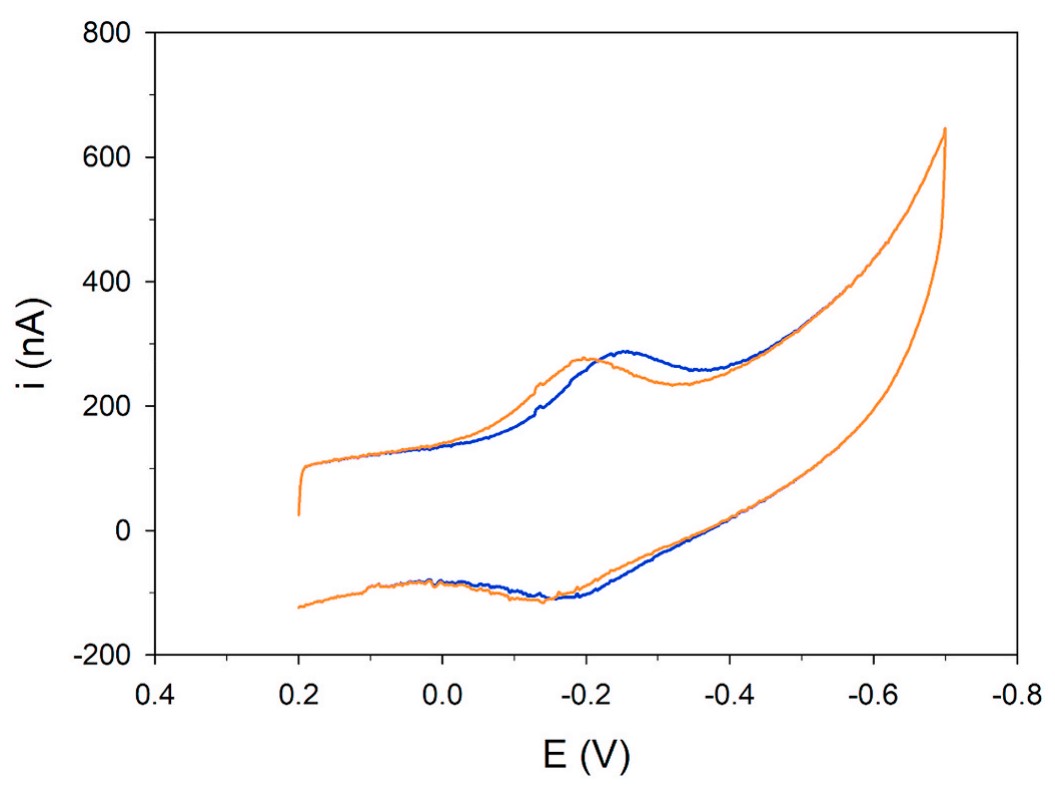
Fig1. Direct oxidation/reduction of cofilin cysteines. Cofilin-2 WT (orange line)
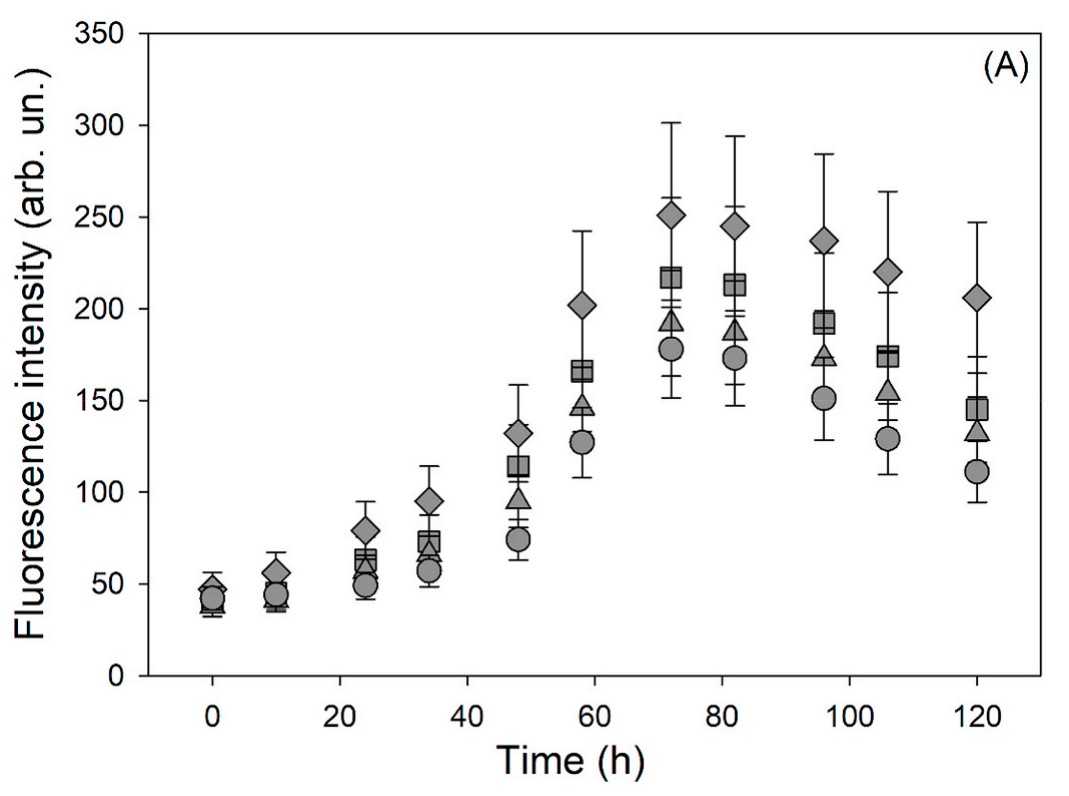
Fig2. Plot of the time course of ThT fluorescence intensity for: ■ cofilin-2 WT, ▲cofilin-2 WT treated with H2O2, ♦ cofilin-2 S3D, ● cofilin-2 S3D treated with H2O2.
Case Study 2: Bin-Bin Yu, 2018
The purpose of this study was to determine whether cofilin-2 could serve as a protein marker for predicting radiotherapy response and as a potential therapeutic target in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Cofilin-2 protein levels in serum and tissue samples from patients with NPC were assessed by sandwich ELISA and IHC. In vitro, cofilin-2 levels in CNE-2R cells were significantly higher than those of CNE-2 cells. Meanwhile, CNE-2R cells were silenced for cofilin-2 to obtain a stable cofilin-2-RNAi-LV3 cell line. Then, cell proliferation, radiosensitivity, invasion and migration abilities, cell cycle, and apoptosis were evaluated by Cell Counting Kit 8 assay (CCK-8), flow cytometry (FCM), clone formation assay, and in vitro. The secreted levels of the cofilin-2 protein in radioresistant NPC patients were significantly higher than those of radiosensitive cases. After cofilin-2 knockdown in nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE-2R cells, proliferation was decreased, while apoptosis and radiosensitivity were enhanced; cell cycle distribution was altered, and the transplanted tumors in nude mice grew significantly less.
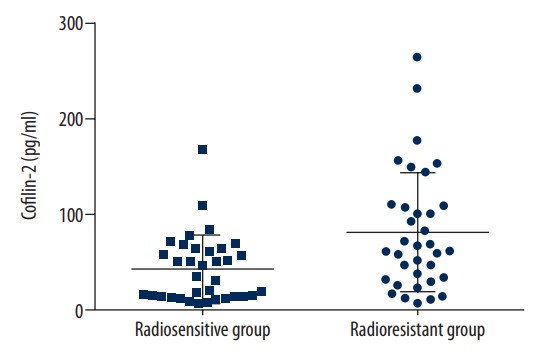
Fig3. Cofilin-2 protein levels in the radioresistance and radiosensitivity groups.
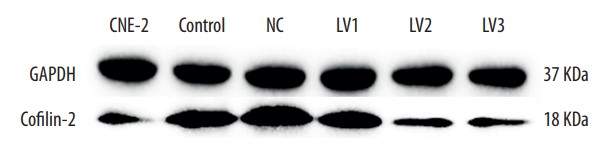
Fig4. Western blot analysis showing cofilin-2 protein expression in different groups.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CFL2-1174H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CFL2-2466HF)
Involved Pathway
CFL2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CFL2 participated on our site, such as Axon guidance,Caspase cascade in apoptosis,Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CFL2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Axon guidance | SEMA7A,MYL12A,PTK2,TRIO,HBEGF,ABL1,ARPC1B,LRRC4C,PLXNA1,SLIT2 |
| Caspase cascade in apoptosis | CASP2,DIABLO,CRADD,SATB1,GAS2,TOP1,LMNB1,TFAP2A,DFFA,ACTA1 |
| Regulation of Microtubule Cytoskeleton | MARK1,TESK2,TPPP,DPYSL2,MARK2,MAP1B |
| Regulation of Actin Cytoskeleton | SSH1,Fgf15,ARHGEF7B,SLC9A1,FGF8,PPP1R12A,VAV2,FGD3,MYLK4,PAK3 |
| Leptin signaling pathway | IL1RN,KHDRBS1 |
| G13 Signaling Pathway | RTKN,MYBPH,SH3RF1,GNA13,ARHGEF1A,MYL1,CIT,DIAPH1,RHPN2,TNK2 |
| Pertussis | FOS,IL-8,C4A,IRAK1,GNAI2,IRF3,CALM2,IL6,IRF1,Hc |
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | PIP5K1B,SPHK1,CFL1,AKT1,FCGR2A,WASF3,GSN,FCGR1,PRKCB,ARPC1A |
Protein Function
CFL2 has several biochemical functions, for example, actin binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CFL2 itself. We selected most functions CFL2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CFL2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | TRIM32,RAB35,CCL18,HIST1H4G,ORAI2,TACSTD2,BRD4,CSNK1G2,CENPP,MARK3 |
| actin binding | ADD1,ACTR2A,FLII,DAAM1,WASF3B,MYH8,MYH15,SYNE1,VILL,TPM2 |
Interacting Protein
CFL2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CFL2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CFL2.
ACTB;ACTG1;CSRP3;MAP3K3;CFL1;STK11;MYO1C;FLNA;MYH9;IQGAP1;CAPZA2;Tpm1;PPP1CB;GRB2;DBN1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


