BAZ1B
-
Official Full Name
bromodomain adjacent to zinc finger domain, 1B -
Overview
The human WSTF gene is located within the common Williams Syndrome (WS) deletion area at chromosome 7q11.23. Several WSTF gene products have been detected with little difference in length of polypeptides. Functional motifs identified by sequence-homology -
Synonyms
BAZ1B;bromodomain adjacent to zinc finger domain, 1B;WBSCR9, WBSCR10;tyrosine-protein kinase BAZ1B;transcription factor WSTF;Williams Beuren syndrome chromosome region 9;Williams Beuren syndrome chromosome region 10;WSTF;hWALp2;williams syndrome
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- His
- GST
- His&Flag
- His&Strep&GST
- His&Strep
- His&Fc&Avi
Background
What is BAZ1B Protein?
BAZ1B, also known as the Williams syndrome transcription factor (WSTF), is a versatile protein found in the cell nucleus. It's heavily involved in reshaping chromatin, the complex of DNA and proteins in the cell. BAZ1B acts as a helper subunit in two major chromatin-remodeling complexes, crucial during processes like DNA replication, repair, and transcription. By adjusting the activity of RNA polymerases I, II, and III, BAZ1B helps create open chromatin, making DNA more accessible. It also plays a role in repairing DNA damage, aiding cells in deciding between survival and death by tagging H2AX nucleosomes for specific protein modifications. When BAZ1B isn't working right, it can be linked to several diseases, including cancer and neurodevelopmental disorders such as Williams syndrome.What is the Function of BAZ1B Protein?
BAZ1B, a part of the bromodomain protein family, plays a key role in managing how genes are expressed by working with chromatin. This protein is deleted in Williams-Beuren syndrome, affecting multiple genes. BAZ1B influences many other genes and is crucial for developing facial features and the neural crest. Some studies suggest that changes in BAZ1B might even be linked to how humans have evolved characteristics over time.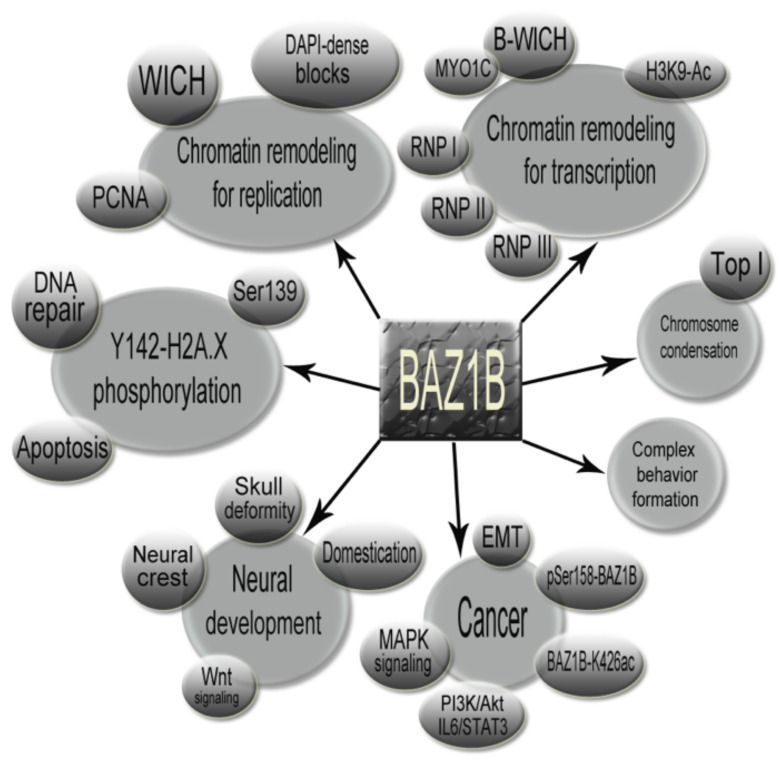
Fig1. Concept map illustrating the major functional events mediated by BAZ1B as well as other related events and factors that are important to be considered. (Shahin Behrouz Sharif, 2021)
BAZ1B Related Signaling Pathway
BAZ1B plays a role in several signaling pathways, especially around chromatin structure and gene regulation. It's part of the chromatin remodeling complexes that adjust how tightly DNA is packed, which in turn affects how genes get turned on or off. BAZ1B works alongside other proteins to influence DNA replication and repair, ensuring the genetic material is accurately copied and fixed when needed. It also has ties to pathways involved in cell growth and response to DNA damage, acting as a helper in resolving stress or damage by guiding proteins to necessary sites on the DNA. Alterations in how BAZ1B functions can lead to a ripple effect in these pathways, impacting everything from development to stress responses.BAZ1B Related Diseases
BAZ1B is linked to several health conditions, primarily because of its role in chromatin remodeling and gene regulation. One of the most recognized connections is with Williams-Beuren syndrome, which happens when a part of the chromosome that includes BAZ1B goes missing. This can cause unique facial traits, delays in development, and heart-related issues. Moreover, changes in BAZ1B expression have been observed in some cancers, where it may affect cell growth and survival. There are also links between BAZ1B and certain neurodevelopmental disorders, as its normal function is crucial for brain development and function. Alterations in BAZ1B's activity might contribute to various disease processes by affecting the regulation of a wide array of genes.Bioapplications of BAZ1B
BAZ1B is involved in various bioapplications, particularly because of its role in gene regulation and chromatin remodeling. In research, BAZ1B is used to understand how chromatin structures are maintained and regulated, impacting gene expression. This is particularly important in studying developmental syndromes like Williams-Beuren syndrome, where BAZ1B deletions can lead to characteristic features. Additionally, BAZ1B's function in the neural crest and face development makes it a focal point in evolutionary biology studies, as it might have been involved in traits that distinguish modern humans. BAZ1B is also explored for its potential in cancer research, given its influence on cell growth and division.Case Study
Case Study 1: Ohta S. et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019
In mitosis, chromosomes condense to ensure proper cell division. Non-histone proteins like TOP2A and SMC2 are thought to form a scaffold structure, though its existence is debated. This study, using DT40 cells, identified BAZ1B as a new scaffold component. Loss of BAZ1B causes delays in prophase due to issues in chromosome condensation and mitosis, especially if BAZ1A is also absent. Despite this, prometaphase chromosomes remain unchanged. BAZ1 proteins are key for timely chromosome condensation at mitosis start and need further study.-
 Fig1. GFP-BAZ1B were expressed in human epithelial U2OS cells and analyzed for intracellular localization.
Fig1. GFP-BAZ1B were expressed in human epithelial U2OS cells and analyzed for intracellular localization. -
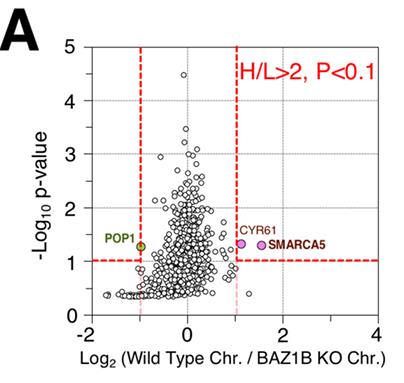 Fig2. The lack of BAZ1B decreased the association of SMARCA5 with mitotic chromosomes in BAZ1B KO cells to ∼30% of that in WT.
Fig2. The lack of BAZ1B decreased the association of SMARCA5 with mitotic chromosomes in BAZ1B KO cells to ∼30% of that in WT.
Case Study 2: Yang L. et al. Eur J Histochem. 2021
Williams syndrome transcription factor (WSTF) is involved in various cell functions, including how cancer cells grow and move around. In glioblastoma (GBM), a type of brain cancer, WSTF levels are higher. Boosting WSTF through genetic methods increases GBM cell growth and invasion, while reducing WSTF levels slows these processes down. When WSTF is increased, GBM cells show less apoptosis, marked by lower Bax and cleaved caspase-3 levels. Conversely, cutting down WSTF raises these levels, leading to more cell death. The PI3K/AKT pathway, which is part of cell growth signaling, is more active when WSTF is abundant. Blocking this pathway can reduce the aggressive growth and spread of GBM cells driven by WSTF. In summary, WSTF promotes GBM cell survival and movement by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway.-
 Fig3. Protein expression of WSTF was enhanced in U251MG and LN-229.
Fig3. Protein expression of WSTF was enhanced in U251MG and LN-229. -
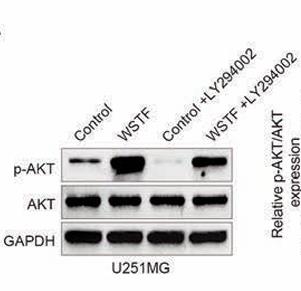 Fig4. LY294002 treatment attenuated WSTF overexpression- induced increase of AKT phosphorylation in U251MG.
Fig4. LY294002 treatment attenuated WSTF overexpression- induced increase of AKT phosphorylation in U251MG.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (BAZ1B-097H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (BAZ1B-097H)
Involved Pathway
BAZ1B involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways BAZ1B participated on our site, such as DNA Double Strand Break Response,DNA Double-Strand Break Repair,DNA Repair, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with BAZ1B were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| DNA Double Strand Break Response | RNF168,HTATIP,KDM4B,UIMC1,EYA2,EYA3,BRCC3,UBE2V2,KDM4A,CHEK2 |
| DNA Repair | MGMT,RAD9,RAD18,ZNF830,RAD9B,PNKP,BRE,EME2,POLI,PPIE |
| Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks | EYA3,KDM4B,EYA2,KDM4A,EYA4 |
| DNA Double-Strand Break Repair | RBBP8,KDM4B,EME1,PAXIP1,RTEL1,RNF168,TDP2,PPP4CB,PPP4CA,RAD51AP1 |
-
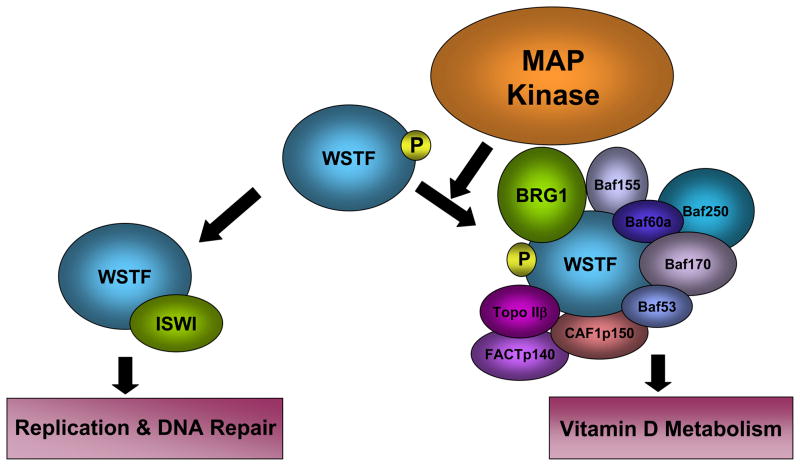 Fig1. A schematic representation of MAP kinase phosphorylation of WSTF. (Chris Barnett, 2011)
Fig1. A schematic representation of MAP kinase phosphorylation of WSTF. (Chris Barnett, 2011)
Protein Function
BAZ1B has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,chromatin binding,histone kinase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by BAZ1B itself. We selected most functions BAZ1B had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with BAZ1B. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| histone kinase activity | CCNB1,CDK1 |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | SYK,RIPK2,PTK2B,ZNF143B,SRMS,JAK2B,JAK1,FRK,EIF2AK2,PTK2 |
| chromatin binding | URI1,EZH2,GATA6,BARX2,MTA1,SFPQ,PATZ1,MSL1A,GATA2A,HMGB3A |
| protein binding | PAK3,NDE1,SNRPE,ZFYVE28,ZFPM1,TATDN1,ACTN3,DNAJC11,SPHK2,CA |
| zinc ion binding | ALKBH8,PDLIM5,ANKIB1A,RGN,USP13,CPD,NR1I3,MYCBP2,ZFP276,AJUBA |
| lysine-acetylated histone binding | PSME4,SMARCA4,CARM1,BRD2,BRDT,ATAD2B,BRD3,PSME4B,BRD7,TAF1 |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | ERBB4,IGF1R,JAK2A,MAP2K5,JAK2,KITA,MATK,EGFR,MAP2K2,BMX |
| ATP binding | SCYL2,PTK7A,LANCL2,CAMKK2,MCM5,ATAD5B,MYH9A,MCM2,MSH5,PAK7 |
Interacting Protein
BAZ1B has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with BAZ1B here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of BAZ1B.
SMARCA5;MYH1;NR4A2;Smarca5;BAZ1A;BAZ2A;PHLDA3;pi3p;IGHM;Eif3a;HNRNPU;VP35;PYHIN1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Pfeiffer, MJ; Taher, L; et al. Differences in embryo quality are associated with differences in oocyte composition: A proteomic study in inbred mice. PROTEOMICS 15:675-687(2015).
- Hennig, EE; Mikula, M; et al. Comparative kinome analysis to identify putative colon tumor biomarkers. JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE-JMM 90:447-456(2012).


