Tissue Lysates
SubCategories
Background
Overview
Tissue lysate is a type of sample commonly used in biomedical research. It is a mixture of cells in a tissue sample that are split apart by physical or chemical methods to release proteins and other biomolecules inside the cells. This lysate can be used for a variety of biological and biochemical analyses, including protein expression analysis, signal transduction studies, metabolite analysis, gene expression studies, etc. Tissue lysates are prepared to study protein expression, purification, and interactions between proteins and other molecules within tissues or cells. This is the first step in performing immunoblotting (WB), immunoprecipitation (IP), immunoprecipitation (Co-IP), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP).
Preparation Process
Sample collection: First, collect the required tissue samples, including various plant or animal tissues.
Lysis: Tissue samples are treated with lysis buffers (which may contain non-ionic surfactants, ionic surfactants, protease inhibitors, etc.) to lyse cell membranes and release cell contents.
Homogenization and centrifugation: The homogenization and centrifugation steps remove insoluble components such as unlysed cell fragments and nuclei, resulting in a relatively clear lysate.
Lysis Methods
When choosing a tissue lysis method, the following factors need to be considered:
Stability and activity requirements of target molecules; composition of the lysate, including the type and concentration of the detergent; downstream applications such as protein analysis, RNA extraction or metabolite analysis; the type and characteristics of the tissue, such as hardness, fat content, etc.
The following are some commonly used tissue lysis methods:
Mechanical cracking: The use of physical methods such as grinding, homogenizing, or ultrasonic treatment to destroy tissue structure and release cellular contents.
Chemical cracking: Specific cracking buffers containing detergents (e.g. Triton X-100, NP-40, etc.) and other ingredients (e.g. Protease inhibitors) are used to crack the cell membrane.
Freeze-thaw lysis: Destruction of cell membranes by rapidly freezing and thawing tissue samples, releasing cell contents.
Enzymatic cleavage: Tissue is treated with specific enzymes, such as trypsin, to digest the extracellular matrix and cell membranes, releasing cell contents.
Advantages
Comprehensiveness: Tissue lysates contain all cell types and cell components in the tissue, providing a comprehensive biological sample.
Applicability: Suitable for a variety of analytical techniques, it is an important bridge connecting tissue level research and molecular level research.
Notes
Sample handling: Protein degradation and RNA degradation need to be avoided during preparation, so protease inhibitors and RNase inhibitors are usually added.
Standardization: In order to ensure the comparability of experimental results, appropriate standardization of lysates, such as protein concentration or total RNA amount, is required.
Sample preservation: The lysate should be stored under appropriate conditions to prevent sample degradation.

Applications
- Protein analysis: Tissue lysates are often used in Western Blot, ELISA and other techniques to detect the expression level or modification status of a specific protein.
- Signaling studies: By analyzing specific signaling molecules in lysates, signaling pathways within cells can be studied.
- Metabolite analysis: Metabolites in lysates can be used in metabolomics studies to help understand the metabolic state of tissues.
- Gene expression studies: By extracting the total RNA in the lysate, gene expression analysis can be performed, real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR).
Case Study
Case Study 1: Beans Lysate, Total Protein
Increased oxidative stress contributes to the functional impairment of endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs), the pivotal players in the servicing of the endothelial cell lining. This study investigated the effects of Lisosan G (LG), a Triticum Sativum grain powder, and Lady Joy (LJ), a bean lysate, on function of EPCs exposed to oxidative stress. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated and plated on fibronectin-coated culture dishes; adherent cells, identified as early EPCs, were pre-treated with different concentrations of LG and LJ and incubated with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Viability, senescence, adhesion, ROS production and antioxidant enzymes gene expression were evaluated. Lysate-mediated Nrf-2 (nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2)/ARE (antioxidant response element) activation, a modulator of oxidative stress, was assessed by immunocytochemistry. Both lysates increase glutathione peroxidase-1 and superoxide dismutase-2 (SOD-2) expression; upon H2O2 exposure, pre-treatment with LJ allows higher SOD-2 expression. Heme oxigenase-1 increases in EPCs pre-treated with LG even upon H2O2 exposure. Finally, incubation with LG 0.7 mg/ml results in Nrf-2 translocation into the nucleus both at baseline and after the oxidative challenge.
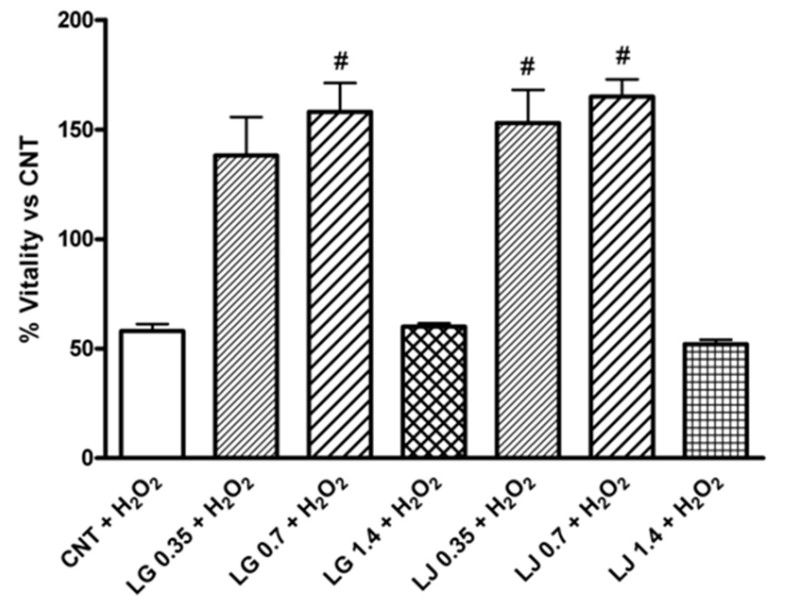
(Daniela Lucchesi, 2014)
Fig1. Effects of Lisosan G (LG) and LJ lysate (LJ) on viability of EPCs in presence of oxidative stress induced by H2O2.
Case Study 2: Rat Corneal Lysate
Increasing evidence suggests that glaucoma affects the ocular surface. This study aimed to investigate the cellular mechanisms underlying the glaucoma-associated corneal alterations in an animal model. Wistar rats underwent the cauterization of two episcleral veins of the left eye to elevate the intraocular pressure (ipsilateral, G-IL). Control animals received a sham procedure (C-IL). Contralateral eyes did not receive any procedure (G-CL or C-CL). Enzymes related to the redox status, oxidative damage to macromolecules, and inflammatory markers were assessed in corneal lysates. Compared to C-IL, NOX4, NOX2, and iNOS expression was increased in G-IL (68%, p < 0.01; 247%, p < 0.01; and 200%, p < 0.001, respectively). The GSH/GSSG ratio decreased in G-IL (80%, p < 0.05), with a decrease in GR activity (40%, p < 0.05). G-IL displayed oxidative (90%, p < 0.01) and nitrosative (40%, p < 0.05) protein damage, and enhanced lipid peroxidation (100%, p < 0.01). G-CL displayed a higher expression of Nrf2 (60%, p < 0.001) and increased activity of SOD, CAT, and GPx (60%, p < 0.05; 90%, p < 0.01; and 50%, p < 0.05, respectively).
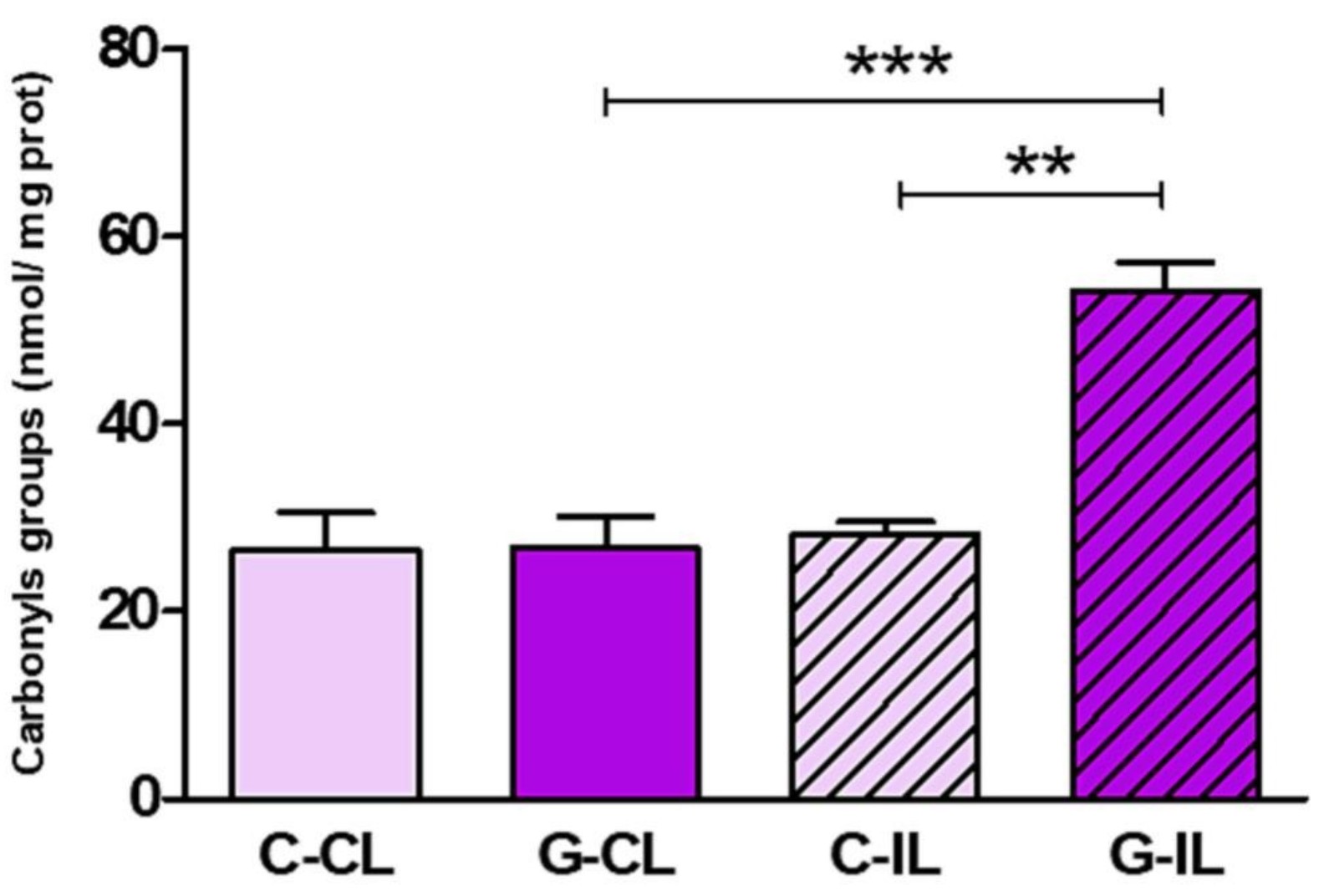
(Ailen G Hvozda Arana, 2023)
Fig2. Glaucoma induces oxidative damage to macromolecules in the cornea. The carbonyl content was evaluated to assess protein oxidative damage.
Case Study 3: Mouse Heart Lysate
Pathologies including cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and neurological disorders are caused by the accumulation of misfolded/damaged proteins. Intracellular protein degradation mechanisms play a critical role in the clearance of these disease-causing proteins. Chaperone mediated autophagy (CMA) is a protein degradation pathway. To date, steady-state CMA function has been assessed by measuring LAMP2A protein expression. However, this does not provide information regarding CMA degradation activity. To fill this dearth of tools/assays to measure CMA activity, this study generated a CMA-specific fluorogenic substrate assay. A KFERQ-AMC [Lys-Phe-Asp-Arg-Gln-AMC(7-amino-4-methylcou-marin)] fluorogenic CMA substrate was synthesized from Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis. KFERQ-AMC, when cleaved via lysosomal hydrolysis, causes AMC to release and fluoresce. Using an inhibitor of lysosomal proteases, i.e., E64D, responsible for cleaving CMA substrates, the actual CMA activity was determined. Essentially, CMA activity=(substrate) fluorescence-(substrate+E64D) fluorescence. To confirm specificity of the KFERQ sequence for CMA, negative control peptides were used. Heart, liver, and kidney lysates containing intact lysosomes were obtained from 4-month-old adult male mice. Of note, liver exhibited the highest CMA (6-fold; p<0.05) > kidney (2.4-fold) > heart (0.4-fold) at 5-hours.
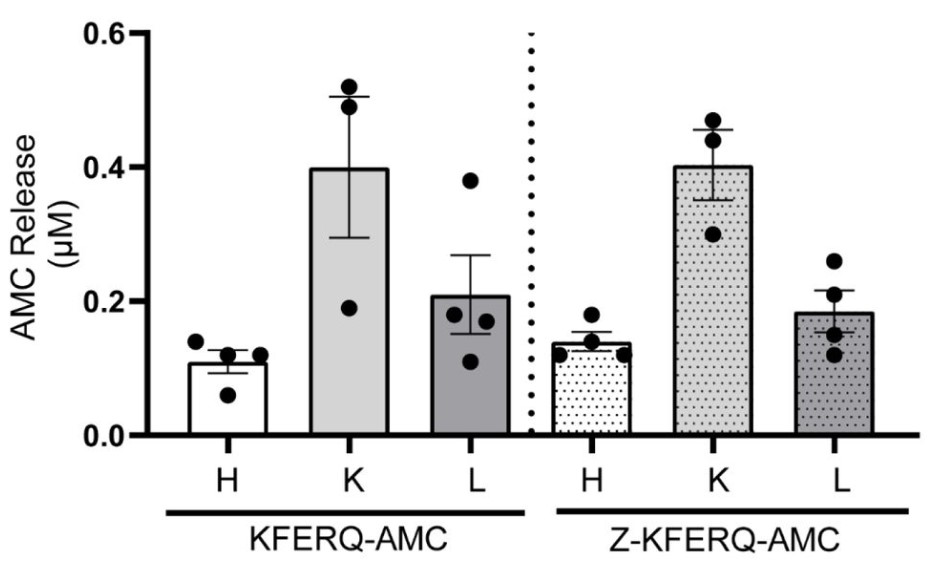
(Anila Jonnavithula, 2023)
Fig3. Heart liver and kidney were incubated with 50 μM of either KFERQ-AMC or Z-KFERQ-AMC for 3 hours. The bar graph represent CMA activity at 3 hours.
Case Study 4: Mouse Kidney Lysate
Signaling pathways of regulated necrosis, such as necroptosis and ferroptosis, contribute to acute kidney injury (AKI), but the role of pyroptosis is unclear. Pyroptosis is mediated by the pore-forming protein gasdermin D (GSDMD). Here, this study report a specific pattern of GSDMD-protein expression in the peritubular compartment of mice that underwent bilateral ischemia and reperfusion injury (IRI). Along similar lines, the GSDMD-protein expression in whole kidney lysates increased during the first 84 h following cisplatin-induced AKI. Importantly, unlike whole kidney lysates, no GSDMD-protein expression was detectable in isolated kidney tubules. In IRI and cisplatin-induced AKI, GSDMD-deficient mice exhibited hypersensitivity to injury as assessed by tubular damage, elevated markers of serum urea, and serum creatinine. This hypersensitivity was reversed by a combined deficiency of GSDMD and the necroptosis mediator mixed lineage kinase domain-like (MLKL).
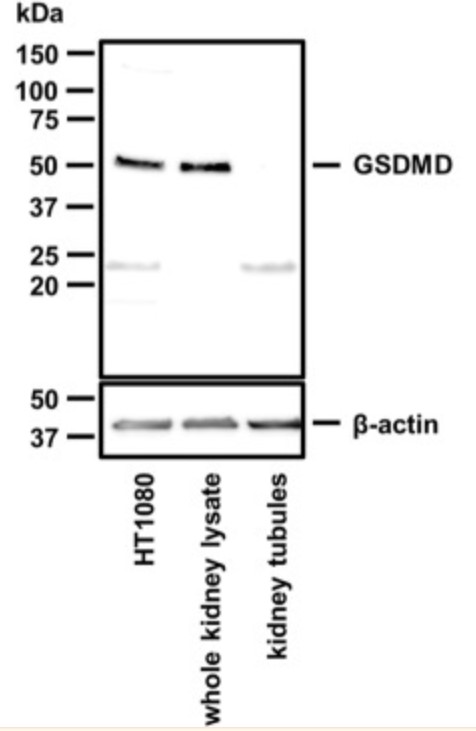
(Wulf Tonnus, 2022)
Fig4. Western blot of murine GSDMD. Note the absence of the GSDMD band in lysates from freshly isolated renal tubules.
Advantages
- Technical support. Purchase our products and you will receive full technical support. Our team of scientists is ready to answer your questions and help you break through your research bottlenecks.
- Reputation Guarantee. We promise that all products are subject to strict quality control, and guarantee fast and safe logistics distribution, so that your research results are not delayed due to supply problems.
- Strong scientific research strength. Our research team has a rich academic background and we are always exploring more popular products.
Creative BioMart can provide various types of Tissue Lysates to meet different research goals. Whether you want to measure enzyme activity, verify function, or explore protein structure, you can find the product you want. You can also let us know if you have any customized requirements. Please contact us for more product details.
References
- Lucchesi D.; et al. Grain and bean lysates improve function of endothelial progenitor cells from human peripheral blood: involvement of the endogenous antioxidant defenses. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e109298.
- Hvozda Arana AG.; et al. Experimental glaucoma triggers a pro-oxidative and pro-inflammatory state in the rat cornea. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2023;1867(9):130426.
- Jonnavithula A.; et al. A Fluorogenic-Based Assay to Measure Chaperone-Mediated Autophagic Activity in Cells and Tissues. Preprint. bioRxiv. 2023;2023.12.14.571785.
- Tonnus W.; et al. Gasdermin D-deficient mice are hypersensitive to acute kidney injury. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(9):792.
