Fri, 2024/07/19
The Dual Role of IRF1 in Cancer Therapy
Fri, 2024/07/19
A Novel Gene Therapy Is Expected To Treat Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy

Fri, 2024/07/19
Not Everyone Is Suitable For Vegetarianism! Genetic Factors Play an Important Role in It
Fri, 2024/07/19
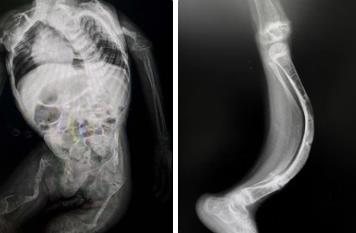
ZAK Kinase Activates UV Mediated Programmed Cell Death
Mon, 2024/07/01
Mon, 2024/07/01
MYCT1 Plays a Crucial Role in Self-Renewal of Human Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Mon, 2024/07/01
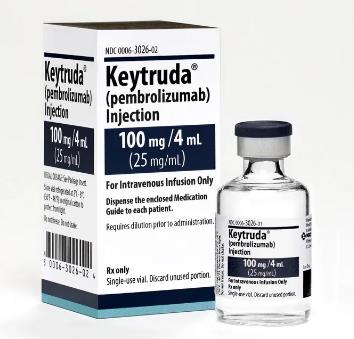
Mon, 2024/07/01
MSD PD-1 Inhibitor Approved By FDA for First-Line Treatment of Advanced Cancer
