Uncategorized Sunday, 2025/04/13
Nivolumab and pembrolizumab, known as the "OK duo" of immune checkpoint inhibitors, have both failed in clinical trials for small cell lung cancer (SCLC), leading to the withdrawal of their FDA accelerated approvals for this indication. Subsequent PD-L1 inhibitors, such as atezolizumab and durvalumab, achieved breakthroughs in overall survival (OS) and were approved by the FDA.
In the face of robust evidence from clinical trials, a widespread, albeit informal, consensus has emerged in the medical community: PD-1 inhibitors may improve progression-free survival (PFS) in SCLC but fail to translate this into OS benefits. Therefore, PD-L1 inhibitors are preferred over PD-1 inhibitors for SCLC treatment.
However, the ASTRUM-005 trial, led by Professor Cheng Ying from Jilin Provincial Tumor Hospital, demonstrated a significant breakthrough with the PD-1 inhibitor serplulimab. Combined with chemotherapy as first-line treatment for extensive-stage SCLC (ES-SCLC), serplulimab achieved the longest median OS in first-line immunotherapy for ES-SCLC. This success was confirmed in a Phase III clinical trial.
The results of the ASTRUM-005 study were presented at the 2022 ASCO and ESMO conferences and published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) in September 2022, garnering international attention and recognition. On January 17, 2023, China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) approved serplulimab in combination with carboplatin and etoposide for the first-line treatment of ES-SCLC. In November 2022, serplulimab also initiated its journey toward U.S. approval, with a head-to-head bridging study comparing serplulimab to the standard first-line treatment atezolizumab already enrolling its first patient in the U.S.
Serplulimab has injected new confidence into immunotherapy and PD-1 research for SCLC. Thanks to the success of the ASTRUM-005 study, serplulimab has become the new king of SCLC treatment. Below is a summary of Phase III clinical trials of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in ES-SCLC.
Our Related Proteins
Serplulimab: ASTRUM-005 Study
The ASTRUM-005 study enrolled 585 treatment-naïve patients with ES-SCLC from six countries, randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive serplulimab plus carboplatin and etoposide (EC regimen) or placebo plus EC regimen. After four cycles, patients entered the maintenance phase with serplulimab or placebo until disease progression or intolerable toxicity. The primary endpoint was OS, with secondary endpoints including PFS, ORR, DoR, and safety.
The OS analysis showed significant and durable efficacy of serplulimab. The OS curves began to diverge at month 4 and continued to separate, with a wider gap starting at month 18. As of October 22, 2021, the median OS in the serplulimab group was 15.4 months, the longest result in first-line immunotherapy for ES-SCLC, compared to 10.9 months in the control group, representing a 4.5-month extension and a 37% reduction in the risk of death (HR: 0.63 [0.49, 0.82]).
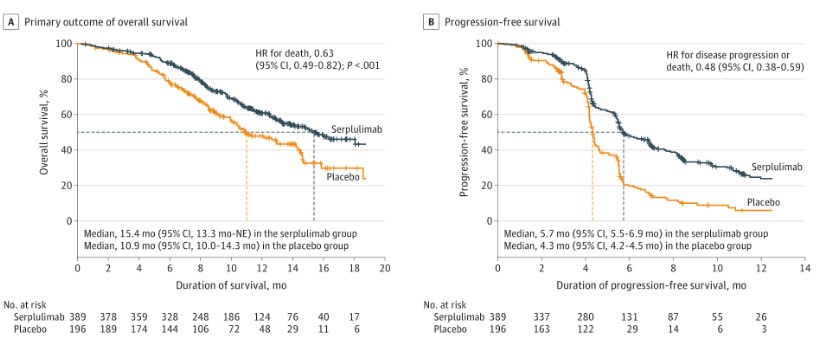
The 12-month OS rates were 60.7% in the serplulimab group and 47.8% in the control group, while the 24-month OS rates showed a fivefold difference (43.1% vs. 7.9%), meaning serplulimab plus chemotherapy enabled nearly half of the patients to survive over two years. For secondary endpoints, the PFS curves also diverged early (after one month of treatment) and continued to separate, with 6-month PFS rates of 48.1% and 19.7%, and 12-month PFS rates of 23.8% and 6.0% in the serplulimab and control groups, respectively. Serplulimab reduced the risk of disease progression by 52%, with median PFS of 5.7 months vs. 4.3 months.
Pembrolizumab: KEYNOTE-604 Study
The KEYNOTE-604 study was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase III trial. Patients with untreated ES-SCLC were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive pembrolizumab 200 mg or placebo, along with four cycles of standard-dose EP regimen. The primary endpoints were OS and PFS, while secondary endpoints included ORR, DOR, and safety.
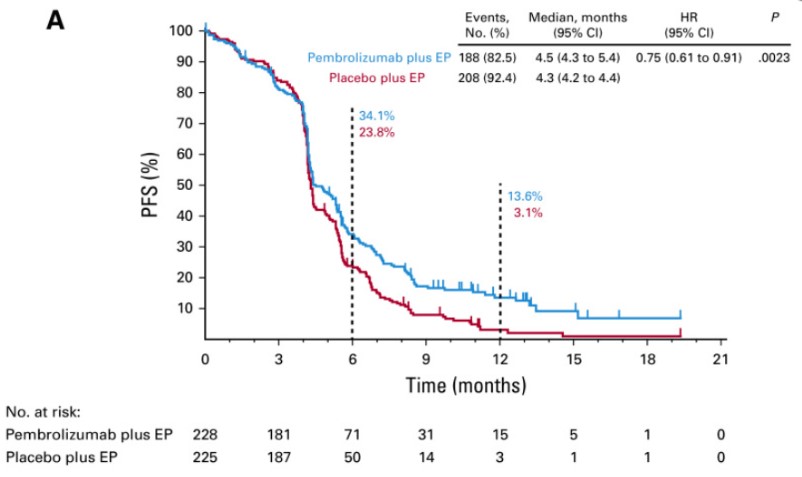 The study met one of its dual primary endpoints, PFS (HR = 0.75 [95% CI, 0.61-0.91, p = 0.0023]), but the other primary endpoint, OS, did not achieve statistical significance (p ≤ 0.0128). The median OS was 10.8 months in the pembrolizumab group vs. 9.7 months in the control group (HR = 0.80; 95% CI: 0.64-0.98; p = 0.0164). However, due to the failure of the confirmatory Phase III KEYNOTE-604 trial, Merck voluntarily withdrew the accelerated approval of pembrolizumab for SCLC.
The study met one of its dual primary endpoints, PFS (HR = 0.75 [95% CI, 0.61-0.91, p = 0.0023]), but the other primary endpoint, OS, did not achieve statistical significance (p ≤ 0.0128). The median OS was 10.8 months in the pembrolizumab group vs. 9.7 months in the control group (HR = 0.80; 95% CI: 0.64-0.98; p = 0.0164). However, due to the failure of the confirmatory Phase III KEYNOTE-604 trial, Merck voluntarily withdrew the accelerated approval of pembrolizumab for SCLC.Nivolumab: CheckMate 451 Study
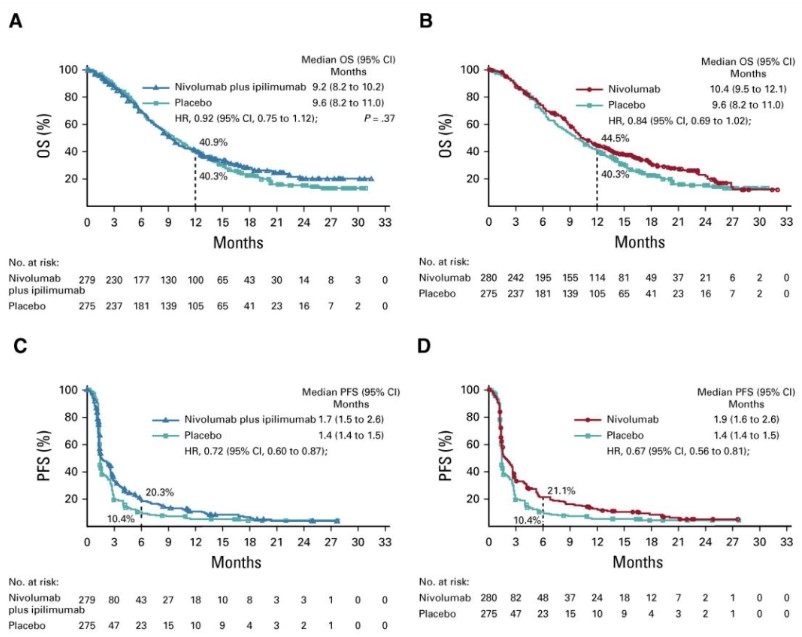
The CheckMate 451 study compared nivolumab plus ipilimumab or nivolumab monotherapy as maintenance therapy after first-line chemotherapy in ES-SCLC. The primary endpoint was OS. The results showed no significant improvement in OS for either the combination or monotherapy group compared to placebo. The median OS was 9.2 months for the combination group, 10.4 months for the monotherapy group, and 9.6 months for the placebo group. Similarly, PFS showed modest improvements but no statistical significance. In December 2020, BMS withdrew the approval of nivolumab for SCLC in the U.S.
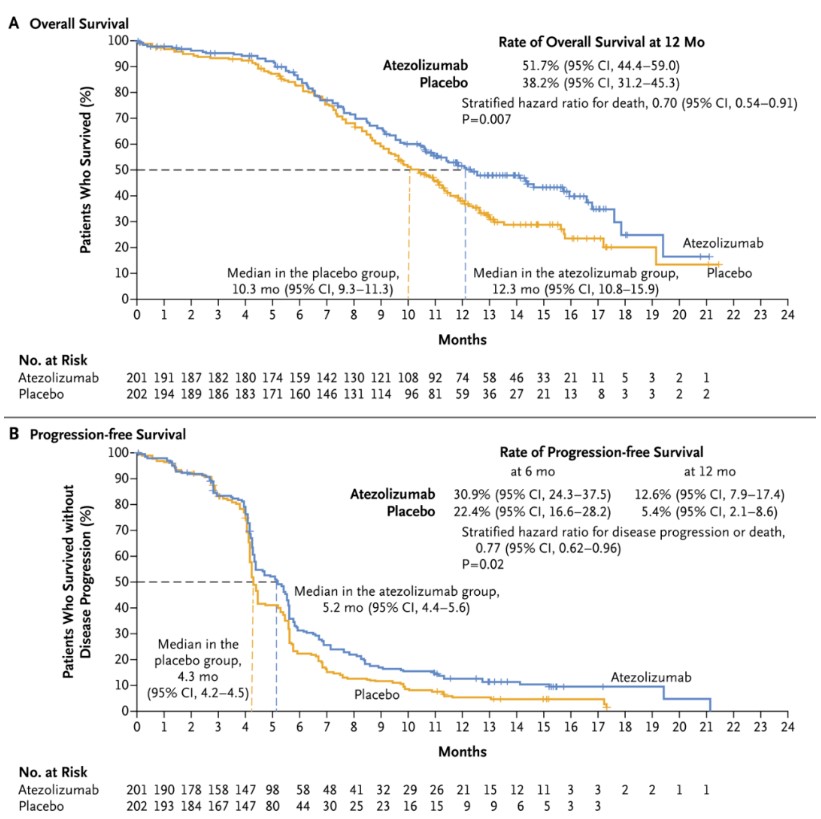
Atezolizumab: IMpower133 Study
The IMpower133 study demonstrated that atezolizumab plus chemotherapy improved both OS and PFS in first-line ES-SCLC. The median OS was 12.3 months in the atezolizumab group vs. 10.3 months in the placebo group (HR = 0.70, 95% CI: 0.54-0.91; p = 0.007), and the median PFS was 5.2 months vs. 4.3 months (HR = 0.77; 95% CI: 0.62-0.96; p = 0.02). In February 2020, atezolizumab was approved by the NMPA for ES-SCLC.
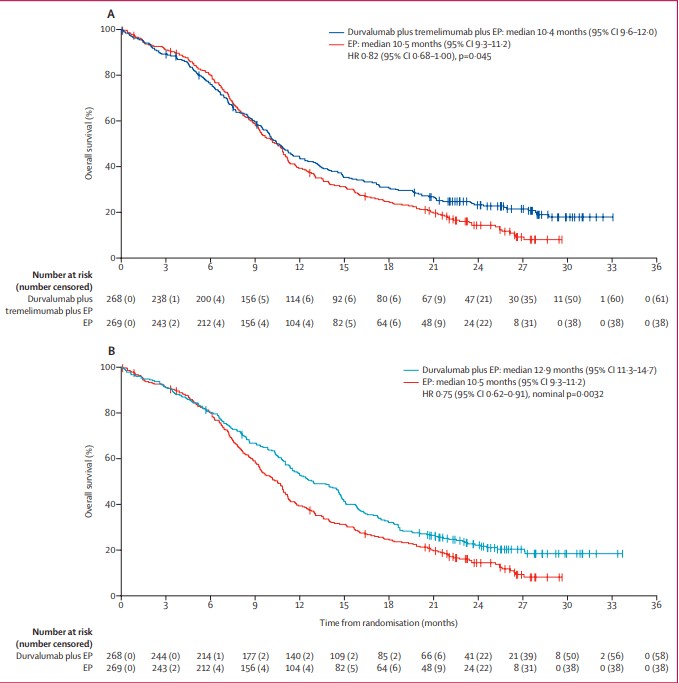
Durvalumab: CASPIAN Study
The CASPIAN study evaluated durvalumab with or without tremelimumab plus chemotherapy in ES-SCLC. The results showed that durvalumab plus chemotherapy significantly improved OS (median OS 12.9 months vs. 10.5 months; HR 0.75; p = 0.0032). In July 2021, the NMPA approved durvalumab for first-line treatment of ES-SCLC.
Adebrelimab: CAPSTONE-1 Study
The CAPSTONE-1 study demonstrated that a Adebrelimab plus chemotherapy significantly improved OS in first-line ES-SCLC, with a median OS of 15.3 months vs. 12.8 months in the placebo group (HR = 0.72; p = 0.0017). The study also explored the optimal duration of immunotherapy in SCLC, with a Adebrelimab consolidation therapy lasting up to two years.
Summary
Both domestic PD-1 (serplulimab) and PD-L1 (Adebrelimab) inhibitors have achieved remarkable results in ES-SCLC, with their findings published in top international journals like JAMA and Lancet Oncology. Serplulimab, in particular, has shown impressive results in PFS, OS, and HR, and its OS in the ASTRUM-005 study is still not reached (NR), suggesting it may continue to set new records in ES-SCLC survival. Serplulimab has been designated an orphan drug for SCLC by the FDA and the European Commission (EC), and its future looks promising as it expands its clinical research globally.
Related Products & Services
- PROTAC Targets
- Cell and Gene Therapy
- Targets of CAR-T Cell Therapy
- Cancer Drug Targets
- Immune Checkpoint Proteins
- Protein Engineering Services
- Protein Interaction Service
- Protein Expression and Purification Services
- Drug Discovery Screening
- Protein Pathway Profiling
Reference
- Cheng Y, et al. JAMA. 2022 Sep 27;328(12):1223-1232.
- Spigel DR,et al. Second-line nivolumab in relapsed small-cell lung cancer: CheckMate 331. Ann Oncol. 2021 May;32(5):631-641.
- Paz-Ares L, et al. Lancet. 2019;394(10212):1929-1939.
- Goldman JW, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2021 Jan;22(1):51-65
- Wang J, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2022 Jun;23(6):739-747
