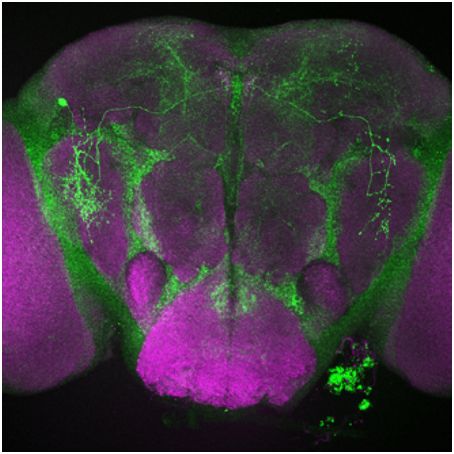
Sun, 2019/03/03
New Study Published on Science Discovered A Gene that Can Promote Sleep While Getting Sick
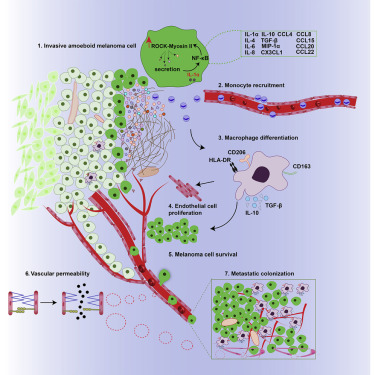
Tue, 2019/02/12
Revealing the Mechanism of Cancer Cells Spreading Through Hijacking of Immune Cells in vivo
Tue, 2019/02/12
The Rhomboid Protease Breaks the "Cell Speed Limit" When Through the Cell Membrane
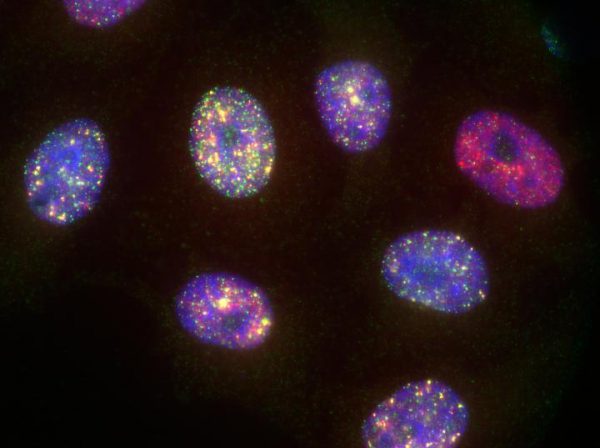
Fri, 2019/02/01
Thu, 2019/01/31

Fri, 2019/01/18
The Essence of Science Journal in December 2018
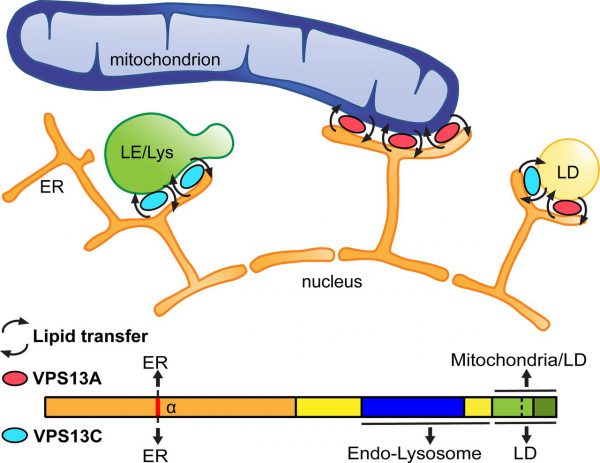
Mon, 2019/01/14
J Cell Biol: How Does a Genetic Mutation Induce a Neurological Disease Such as Parkinson's?

Sat, 2019/01/12
Embo Mol Med: Identification of a Novel Therapeutic Target for the Chronic Inflammatory Colon Cancer
