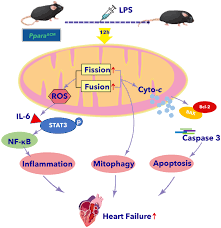
Fri, 2023/07/21
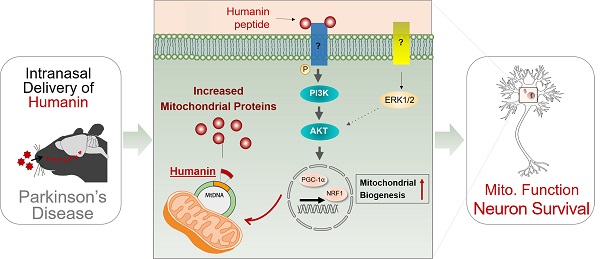
Fri, 2023/07/21
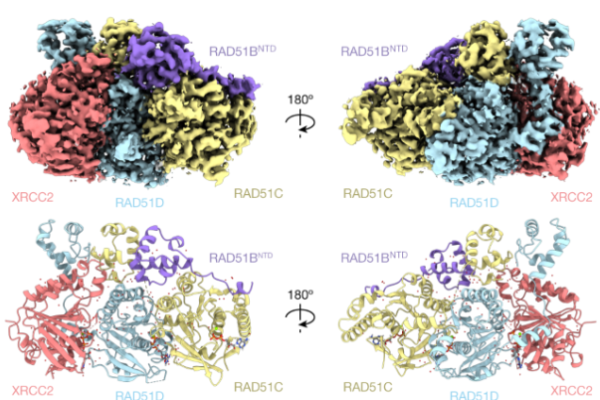
Sat, 2023/07/01
Structure and Function of the RAD51B-RAD51C-RAD51D-XRCC2 Protein Complex
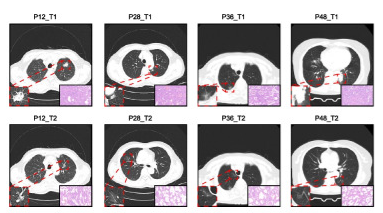
Sat, 2023/07/01
B4GALT1 Promotes Immune Escape in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Sat, 2023/07/01
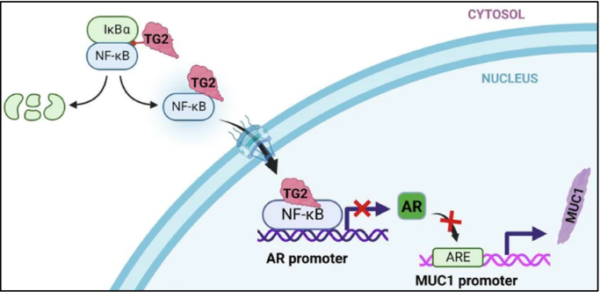
Mutated TG2 Enzyme Promotes the Progression and Diffusion Mechanism of Prostate Cancer
Fri, 2023/06/30
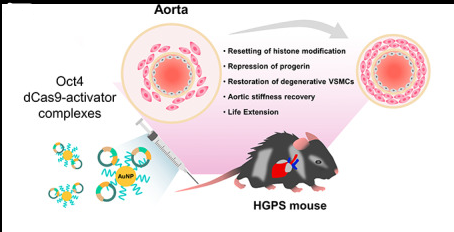
By Activating Oct4, Premature Aging Mouse Cells Can Recover Their Vitality
Mon, 2023/05/15
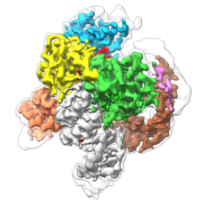
Three Dimensional Structure of the Smallest Programmable Nuclease Tnpb
Mon, 2023/05/15
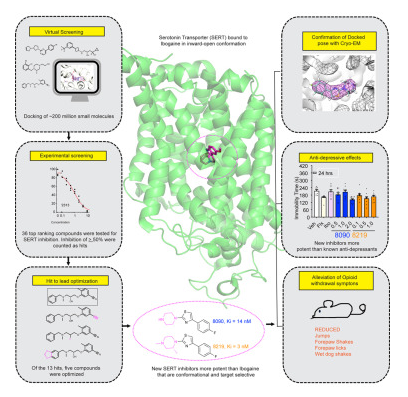
Scientists Have Screened New Serotonin Transporter Inhibitors From Over 20 Billion Molecules
