Wed, 2021/04/21
Foxp3 Mediates Immune Tolerance of Thymic Treg Cells through IL-2

Wed, 2021/04/21
Wed, 2021/04/21
Mon, 2021/03/15
Scientists May Be Able To Turn Off the Key Proteins in Cancer Cells That Depend On for Survival
Mon, 2021/03/15
“New Partner” of PD-1 Antibody: Fusion of IL-21 Improves Anti-tumor Efficacy

Wed, 2021/02/03
New Co-stimulatory Signal Enables CAR-T to Show Its Potential in the Treatment of Solid Tumors

Wed, 2021/02/03
AIM2 Can Regulate the Normal Function of T Cells and Play a Key Role in Reducing Autoimmune Diseases
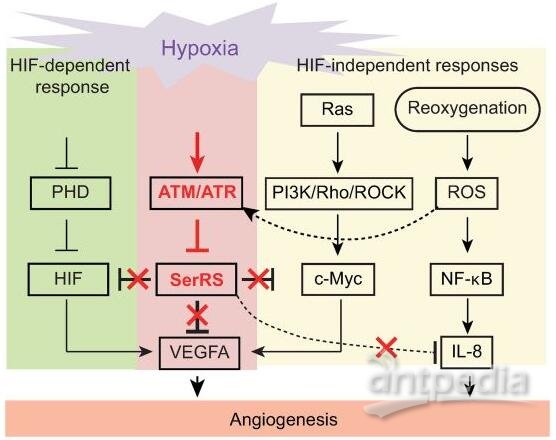
Mon, 2021/01/04
Blocking the Effect of ATM / ATR on Serine tRNA Synthetase can Reduce Tumor Growth
