
Fri, 2024/04/26
A New Mechanism Linking Poor Diet with Increased Cancer Risk
Tue, 2024/03/19
Activating GCN2 Can Metabolize Reprogrammed T Cells and Enhance Their Anti-Tumor Immunity
Tue, 2024/03/19
RHBDL4 - A Novel Regulatory Mechanism for Controlling the Body's Immune System
Tue, 2024/03/19
Tue, 2024/03/19
Regulatory Mechanism of RAS Palmitoyltransferase
Tue, 2024/03/19
Revealing Prognostic Markers for Small Cell Lung Cancer
Tue, 2024/03/19
The Molecular Mechanism of Fusion Protein Intercepting Gene Regulators and Inducing Childhood Cancer
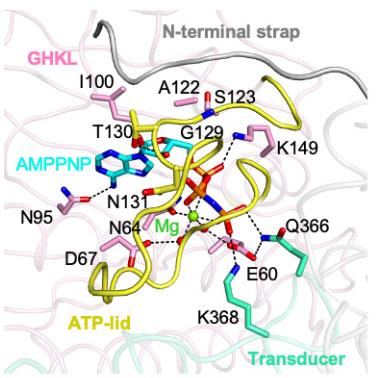
Tue, 2024/03/19
