Uncategorized Tuesday, 2023/04/25
Recently, the Li Zigang/Yin Feng research group at the Shenzhen Graduate School of Peking University published a research paper titled “Targeted biomolecule regulation platform: a Split and Mix PROTAC approach” in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, reporting peptide self-assembly formed Split and Mix PROTAC (SM PROTAC), which achieved significant degradation effects on multiple targets, such as ERα, EGFR, MEK1/2, BRD2/4, CDK4/6, AR, BCR-ABL, etc.
Targeted protein degradation technology (PROTAC), as an emerging protein degradation technology, has potential advantages over small molecule inhibitors such as targeting unreachable drug targets and overcoming drug resistance. It is currently in a period of rapid development.
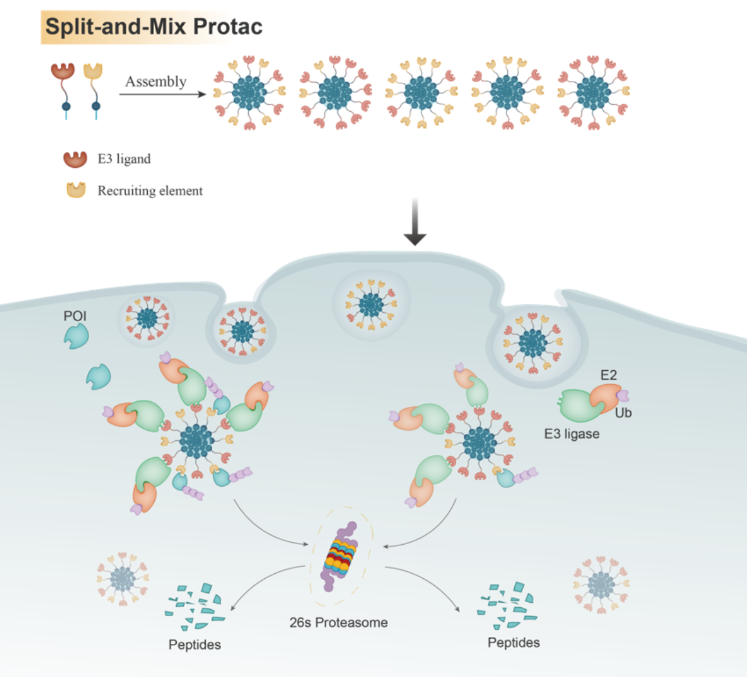
Starting from the phenomenon that different biomolecules can exert their biological functions after mutual recognition, the author of this article assumes that the Split and Mix nano platform can serve as a self-regulation platform, making it easy to screen ligand molecules for assembly and regulate the ligand ratio during the assembly process. The author used PROTAC technology as an example to validate the concept of a Split-and-Mix nano platform and proposed the design concept of Split-and-Mix PROTAC (SM PROTAC) nanospheres formed by peptide self-assembly.
SM PROTAC is different from traditional small molecule PROTAC, in that it separates the small molecule ligand targeting E3 ubiquitin ligase and the small molecule ligand targeting target protein into two modules, and then combines and dissolves the two before assembly. Finally assembled into nanospheres with a diameter range of 50-300 nm (SM-PROTAC). The surface of such nanospheres contains multiple small molecules targeting E3 ligands and multiple small molecules targeting target proteins, thereby recruiting E3 ubiquitin ligases and target proteins. Due to proximity effects, the target protein will be labeled with ubiquitin by E3 ubiquitin ligase, thereby being recognized and degraded by proteasomes. SM-PROTAC can eliminate the time-consuming and laborious process of selecting linkers for traditional small molecule PROTAC, thus shortening the time required for developing PROTAC.
The degradation activity, degradation mechanism, and adjustable proportion ability were verified in ERα and CDK4/6 targets, and the universality of the SM-PROTAC platform was verified on multiple targets such as AR, EGFR, MEK1/2, BRD2/4, and BCR-ABL. SM-PROTAC aims to serve as a PROTAC platform to provide new solutions to some of the challenges encountered in PROTAC drug development, such as rapid and effective screening of target protein ligands, rapid screening of E3 ubiquitin ligase ligands, expanding the usable range of E3 ubiquitin ligases in PROTAC, and helping to rationalize the design of traditional small molecule PROTACs.
In summary, this study successfully developed a new drug development platform, SM-PROTAC, by applying the separation and recombination nanoplatforms and peptide self-assembly technology to PROTAC technology. It has the advantages of high efficiency, reliability, and time-saving, and has broad application prospects in the field of drug development. The concept of split and mix nanoplatforms can be applied to other degradation agents systems, such as LYTAC, AUTAC, and RIBOTAC, to form SM-LYTAC, SM-AUTAC, SM-RIBOAC, etc. The successful development of SM-PROTAC is of great significance for drug research and development, providing a new approach to drug research and development.
Related Products
PROTAC Targets
